Content for TS 23.586 Word version: 18.2.0
4 Architecture model and concepts
4.1 General concept
4.2 Architectural reference model
4.2.1 Non-roaming reference architecture
4.2.2 Roaming reference architecture
4.2.3 Inter-PLMN reference architecture
4.2.4 Reference points
4.2.5 Service-based interfaces
4.3 Functional entities
4.3.1 UE
4.3.2 PCF
4.3.3 AMF
4.3.4 UDM
4.3.5 UDR
4.3.6 NRF
4.3.7 NEF
4.3.8 LMF
4.3.9 GMLC
4.3.10 AF
4.4 Location Results
4.4.1 General
4.4.2 Range and Direction
4.4.3 Relative Location
4.4.4 Relative Velocity
4 Architecture model and concepts p. 9
4.1 General concept p. 9
Ranging based service provides the distance between two UEs or more UEs and/or the direction of one UE (i.e. Target UE) from another UE (i.e. Reference UE) via PC5 operations.
Sidelink Positioning provides absolute location, relative position, or Ranging information of a UE by using PC5 for the positioning. A Located UE can be used to determine the absolute location of a Target UE using Sidelink Positioning.
The operation of Ranging/Sidelink Positioning can be performed with Network-assisted Operation, Network-based Operation or UE-only Operation:
- In the Network-based Operation, 5GC NF(s) is involved for the service request handling and result calculation.
- In the UE-only Operation, the service request handling and result calculation are performed by UE.
- In the Network-assisted Operation, 5GC NF(s) is involved for the service request handling and assist UE for the result calculation.
4.2 Architectural reference model p. 9
4.2.1 Non-roaming reference architecture p. 9
Figure 4.2.1-1 shows the high-level view of the non-roaming 5G System architecture for Ranging based services and Sidelink Positioning with service-based interfaces within the Control Plane.
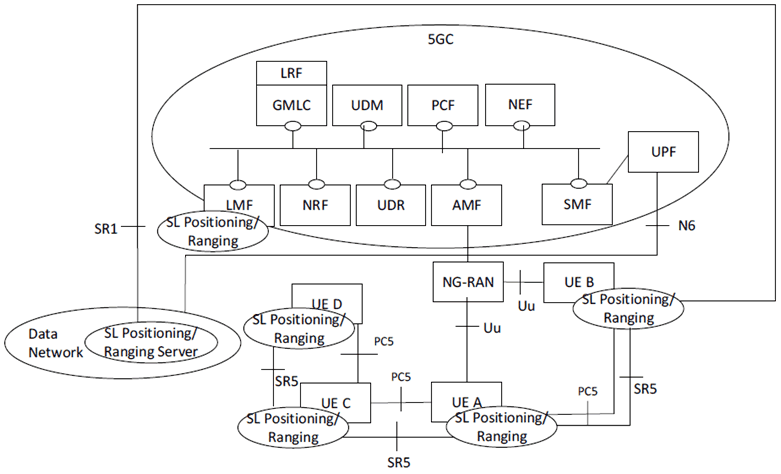
Figure 4.2.1-1: Reference architecture for Ranging based services and Sidelink positioning for non-roaming and same PLMN operation in SBI representation
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
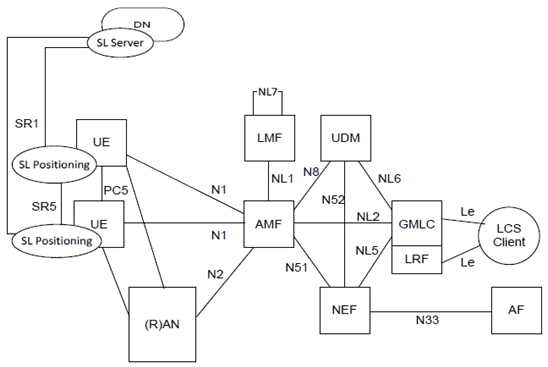
Figure 4.2.1-2: Non-roaming reference architecture for Location Services with ranging and Sidelink positioning in reference point representation
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
4.2.2 Roaming reference architecture p. 11
Figure 4.2.2-1 shows the high-level view of the roaming 5G System architecture for Ranging based services and Sidelink Positioning with service-based interfaces within the Control Plane. In this Figure, UE A use a subscription of the HPLMN.
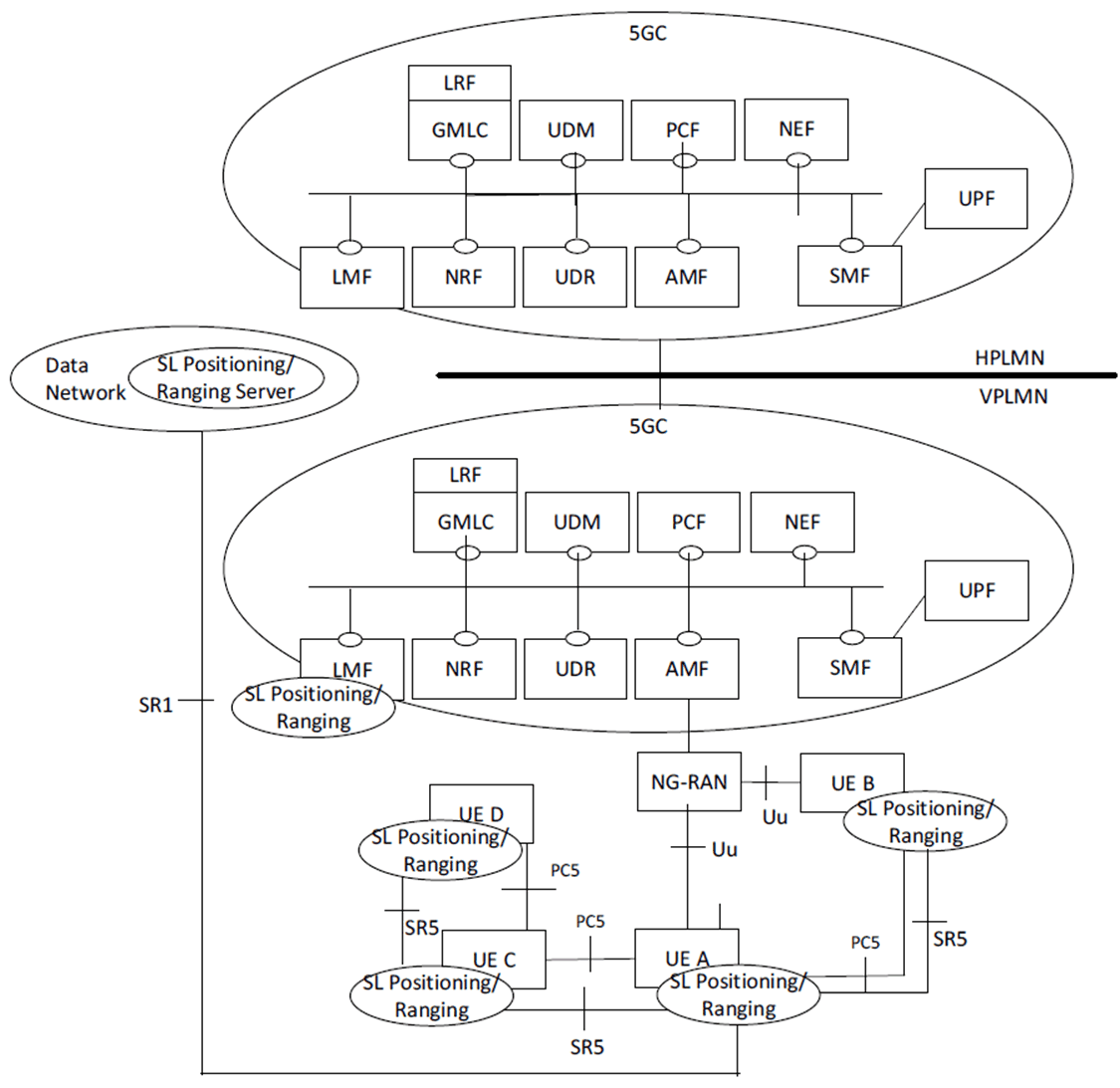
Figure 4.2.2-1: Reference architecture for Ranging based services and Sidelink positioning for roaming and same PLMN operation
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
4.2.3 Inter-PLMN reference architecture p. 11
Figure 4.2.3-1 shows a reference architecture for Ranging based services and Sidelink Positioning for Inter-PLMN non-roaming operation. In this case, the UE A and UE B have subscriptions from different PLMNs, i.e. PLMN-A and PLMN-B respectively.
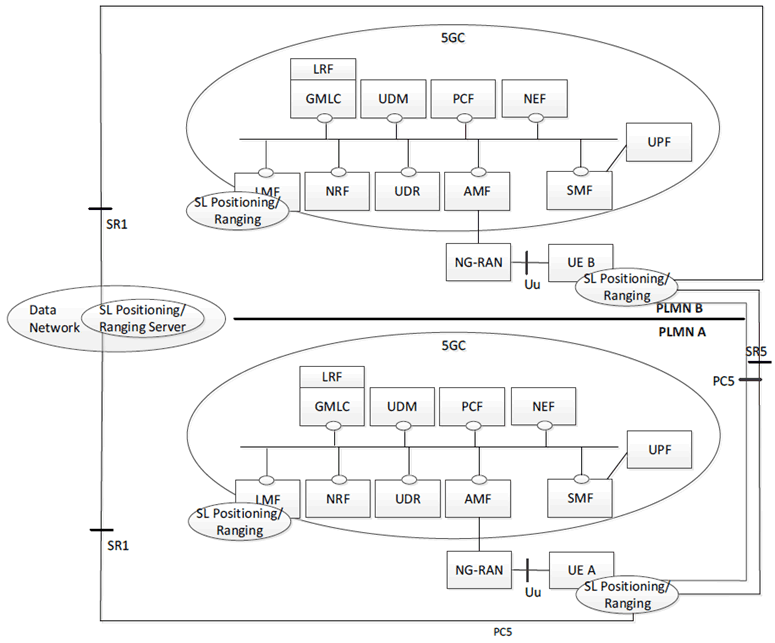
Figure 4.2.3-1: Reference architecture for Ranging based services and Sidelink positioning for inter-PLMN operations
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
Figure 4.2.3-2 shows a reference architecture for Ranging based services and Sidelink Positioning for Inter-PLMN roaming operation. In this case, the UE A and UE B have subscriptions from different PLMNs, i.e. PLMN-A and PLMN-B respectively. UE A is roaming and registered to PLMN-C.
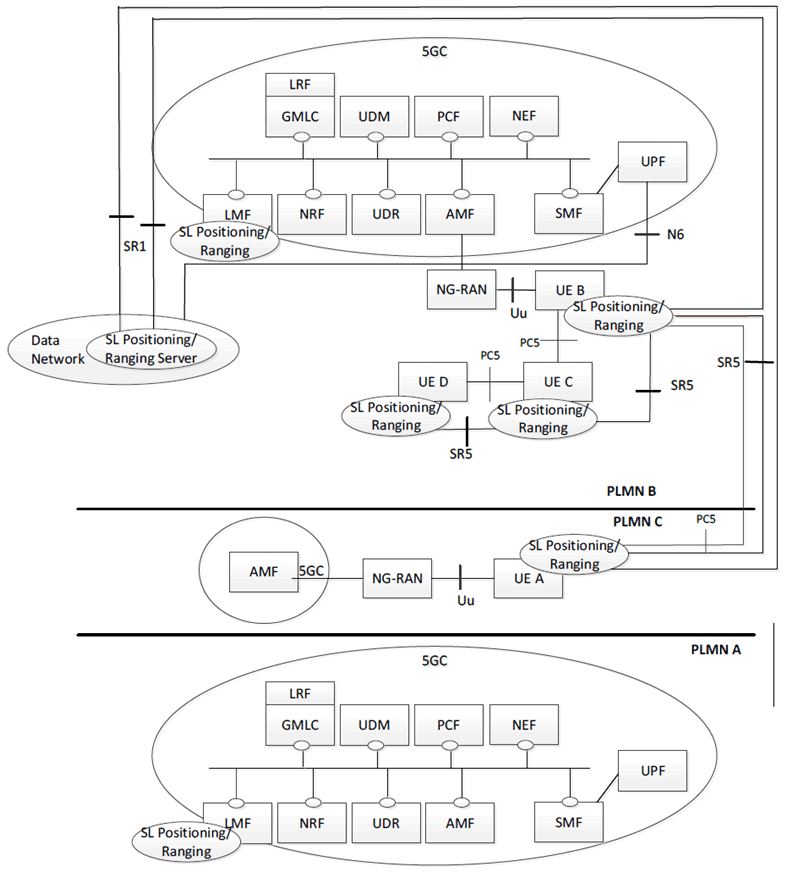
Figure 4.2.3-2: Reference architecture for Sidelink Positioning and Ranging-based services for inter-PLMN operation with roaming
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
4.2.4 Reference points p. 13
SR1:
The reference point between the Sidelink (SL) Positioning and Ranging function in the UE and the SL Positioning/Ranging Server. This reference point is out of scope of this specification. It may be used for the configuration and application layer signalling.
SR5:
The reference point between the Sidelink (SL) Positioning and Ranging function in UEs. It is carried over PC5-U of the PC5 reference point.
PC5:
The reference point between the UEs. It also supports the Sidelink Positioning and Ranging operation defined by RAN WGs.
N1:
In addition to the relevant functions defined in TS 23.501 for N1, in the case of Ranging/SL Positioning Service, it is also used to convey the Ranging/SL Positioning policy and parameters (including service authorization) from AMF to UE, and to convey the UE's Ranging/SL Positioning Capability and PC5 Capability from UE to AMF.
N2:
In addition to the relevant functions defined in TS 23.501 for N2, in the case of Ranging/SL Positioning Service it is also used to convey the Ranging/SL Positioning policy and parameters (including service authorization) from AMF to NG-RAN.
4.2.5 Service-based interfaces p. 14
Nlmf:
In addition to the relevant services defined in TS 23.273, if the LMF support Ranging/SL Positioning service, it may be used to provide service to other NFs related to it.
Nudm:
In addition to the relevant services defined in TS 23.501 for Nudm, in the case of Ranging/SL Positioning service, services provided by UDM are used to get the related subscription information to AMF during Initial registration procedure or UE Configuration Update (UCU) procedure to inform AMF subscription information has changed.
Npcf:
In addition to the relevant services defined in TS 23.501 for Npcf, in the case of Ranging/SL Positioning service, services provided by H-PCF are used to provide SL Positioning and Ranging Service related parameters to V-PCF for UE and NG-RAN in the roaming case.
Nudr:
In addition to the relevant services defined in TS 23.501 for Nudr, in the case of Ranging/SL Positioning service, services provided by UDR are used to notify the PCF and the UDM of the update of the SL Positioning and Ranging-based service related information.
Namf:
In addition to the relevant services defined in TS 23.501 for Namf, in the case of Ranging/SL Positioning service, services provided by AMF are consumed by PCF to provide the Ranging/SL Positioning service related parameters for the UE and the NG-RAN to AMF, and to enable the AMF create or update UE context related to Ranging/SL Positioning service.
Nnef:
In addition to the relevant services defined in TS 23.501 for Nnef, in the case of Ranging/SL Positioning service, services provided by NEF are used by the Application Server to update Ranging/SL Positioning service related information of 5GC.
Nnrf:
In addition to the relevant services defined in TS 23.501 for Nnrf, in the case of Ranging/SL Positioning service, services provided by NRF are used to discover the PCF that supports Ranging/SL Positioning.
4.3 Functional entities p. 14
4.3.1 UE p. 14
In addition to the functions defined in TS 23.287 and TS 23.304, the UE may support the following functions:
-
Reporting the following Ranging/SL Positioning related capabilities to 5GC over the N1 reference point:
- Capability of supporting Ranging/SL Positioning over PC5;
- Capability of supporting SL Positioning Server UE over PC5.
- Procedures for Ranging/SL Positioning over PC5.
- Procedures to Network based SL Positioning, and Network assisted SL Positioning;
- Procedures to Ranging/SL Positioning service exposure.
-
Indicating UE Policy Provisioning Request in UE Policy Container for UE triggered Ranging/SL Positioning Policy provisioning, which requests one or multiple types of policies/parameters as listed below:
- Policy/parameters for Ranging/SL Positioning over PC5;
- Policy/parameters for Located UE;
- Policy/parameters for Target UE in addition to the functions defined in clause 4.3.5 of TS 23.273;
- Policy/parameters for SL Positioning Client UE;
- Policy/parameters for SL Positioning Server UE.
- Receiving the Ranging/SL Positioning Policy from 5GC over N1 reference point.
- Configuration of parameters for Ranging/SL Positioning over PC5. These parameters can be pre-configured in the UE, or, if in coverage, provisioned or updated by signalling over the N1 reference point from the PCF in the HPLMN or over SR1 reference point from the Ranging/SL Positioning Application Server.
4.3.2 PCF p. 15
In addition to the functions defined in TS 23.501 and TS 23.503, the PCF includes functions to provision the UE with necessary policies and parameters to use Ranging/SL Positioning services, as part of the UE Ranging/SL Positioning Policy information as defined in clause 4.2.2 of TS 23.503:
UEPolicyControl_Create Request from the AMF or when receiving the updated subscription data from UDR, the PCF generates the PC5 QoS parameters for RSPP transport over PC5 reference point used by NG-RAN corresponding to a UE as defined in clause 5.4.2 of TS 23.287.
- Authorization policy and parameters for Ranging/SL Positioning over PC5;
- Authorization policy and parameters for Network based SL Positioning, and Network assisted SL Positioning;
- Authorization policy and parameters for Ranging/SL Positioning service exposure.
4.3.3 AMF p. 15
In addition to the functions defined in TS 23.287 and TS 23.304, the AMF performs the following functions:
- Select a PCF supporting Ranging/SL positioning Policy/Parameter provisioning based on indication of Ranging/SL positioning Capability as part of the 5G ProSe Capability/V2X capability in the "5GMM capability" in the Registration Request.
- Store the Ranging/SL positioning Capability.
- Select the LMF supporting Ranging/SL positioning and forward the Ranging/SL positioning Capability of Target UE to LMF.
- Select a GMLC supporting Ranging/SL positioning and request the GMLC for Ranging/SL Positioning result.
- Forward the Ranging/SL positioning Capability to PCF.
- Obtain from UDM the subscription information related to Ranging/SL positioning and store them as part of the UE context data.
- Provision the NG-RAN with indication about the UE authorization status about Ranging/SL Positioning over PC5 (i.e. as Ranging/SL positioning-enabled UE).
- Provision the NG-RAN with PC5 QoS parameters related to RSPP transport over PC5.
4.3.4 UDM p. 16
In addition to the functions defined in TS 23.287 and TS 23.304, the UDM performs the following functions:
- Subscription management for Ranging/SL Positioning over PC5.
- Subscription management for Network based SL Positioning, and Network assisted SL Positioning.
- Subscription management for Ranging/SL Positioning service exposure.
4.3.5 UDR p. 16
In addition to the functions defined in TS 23.287 and TS 23.304, the UDR performs the following functions:
- Stores Ranging/SL Positioning service parameters.
- Stores the mapping between Application Layer ID and GPSI provisioned by AF.
4.3.6 NRF p. 16
In addition to the functions defined in TS 23.287 and TS 23.304, the NRF performs the following functions:
- PCF discovery by considering Ranging/SL Positioning Capability.
- LMF discovery by considering Ranging/SL Positioning Capability.
4.3.7 NEF p. 16
In addition to the functions defined in TS 23.287 and TS 23.304, the NEF supports the following:
- To enable AFs to provide service specific information to the 3GPP network, the NEF supports additional service parameters for Ranging/SL Positioning policy which can use the description of the clause 6.2.5 in TS 23.304.
- Interacting with GMLC for AFs and UEs in Ranging/SL Positioning procedures to perform 5GC-MT-LR.
- Update the UE subscription data stored in the UDR with Onboarding Enrolment Information.
4.3.8 LMF p. 16
In addition to the functions defined in TS 23.273, the LMF supports the following:
-
The Network based SL Positioning and Network assisted SL Positioning;
- Trigger Ranging/Sidelink positioning.
- Exchange the Ranging/Sidelink Positioning capability.
- Exchange the Ranging/Sidelink Positioning assistant data.
- Exchange Ranging/Sidelink positioning signal measurement data/result.
- Support of receiving stored Ranging/Sidelink Positioning capability from AMF and support of providing updated Ranging/Sidelink Positioning capability to AMF.
- Determine Ranging/SL positioning method based on the positioning QoS requirement, UE's Ranging/Sidelink Positioning capability.
- Determine the required QoS for Located UE positioning.
- In case if the scheduled location time is absent, optionally determine the same scheduled location time for the Ranging/SL positioning and the positioning of the Located UE(s).
- Determine the location of the Target UE based on the Ranging/SL positioning measurement data or result reported by Target UE and the location of Located UE(s).
- Interaction with GMLC to get the location of Located UE/Reference UE using the Application Layer ID.
- Delivering the Ranging/Sidelink positioning service request/response for the Ranging service exposure to UE.
4.3.9 GMLC p. 17
In addition to the functions defined in TS 23.273, the GMLC supports the following:
- enable trusted AFs and NFs to perform MT-LR by accessing GMLC directly with additional service parameters for Ranging/SL Positioning.
- enable AFs and NFs to perform MT-LR by accessing GMLC through NEF with additional service parameters for Ranging/SL Positioning.
- determine the serving AMF instances for the UEs involved in the Ranging/SL Positioning request and forward the request to respective serving AMF.
- receive response from AMF and event reports from and return Ranging/SL Positioning result to NFs and AFs.
- perform Application Layer ID to SUPI resolution.
4.3.10 AF p. 17
In addition to the functions defined in TS 23.501, the AF supports the following:
- provision mapping between Application Layer ID and GPSI to UDR in application data.
4.4 Location Results p. 17
4.4.1 General p. 17
Location results that may be obtained for a target UE are summarized here and defined in more detail in TS 23.032.
4.4.2 Range and Direction p. 17
A range refers to a straight line distance between the target UE and another UE, such as another target UE, a Located UE or a Reference UE. A direction refers to a direction to the target UE from another UE, such as another target UE, a Located UE or a Reference UE. A direction may also refer to a direction from the target UE to another UE, such as another target UE, a Located UE or a Reference UE.
4.4.3 Relative Location p. 17
A relative location refers to the location of a target UE relative to a network element or another UE. The relative location can be in 2 dimensions or 3 dimensions.
4.4.4 Relative Velocity p. 18
A relative velocity refers to the velocity of a target UE relative to another UE. A relative velocity of a target UE includes a radial component equal to a rate of change of a range between the target UE and the other UE and a transverse component at right angles to the radial component.