Content for TS 23.379 Word version: 19.2.0
1…
7…
7.4…
10…
10.5…
10.6…
10.6.2.2.13…
10.6.2.2.24…
10.6.2.3…
10.6.2.3.1.2…
10.6.2.3.2…
10.6.2.4…
10.6.2.4.3…
10.6.2.5…
10.6.2.5.2.3…
10.6.2.6…
10.6.2.6.2…
10.6.2.7…
10.6.2.10…
10.6.3…
10.7…
10.7.2.2…
10.7.2.3…
10.7.3…
10.7.4…
10.7.5…
10.7.5.2.3a…
10.7.6…
10.7.6.2.3…
10.9…
10.9.1.3…
10.9.1.3.2…
10.9.1.3.3…
10.9.1.4…
10.9.1.5…
10.9.2…
10.9.2.6…
10.10…
10.12…
10.14…
10.15…
10.19…
10.19.2.11…
10.19.3…
10.19.3.1.4…
10.19.3.2…
10.19.3.2.4…
10.19.3.2.6…
A…
A.4…
B…
10.7.6.2.3 MCPTT private call announced transfer with target in partner MCPTT system
10.7.6.2.4 MCPTT private call announced transfer with transferring MCPTT user in partner MCPTT system
10.8 Simultaneous session for MCPTT calls (on-network)
...
...
10.7.6.2.3 MCPTT private call announced transfer with target in partner MCPTT system |R18| p. 156
The procedure for MCPTT private call announced transfer covers the case where an MCPTT client requests an ongoing MCPTT private call (with or without floor control) to be transferred to another MCPTT user with prior announcement.
Figure 10.7.6.2.3-1 below illustrates the procedure for MCPTT private call announced transfer with target in partner MCPTT system.
Pre-conditions:
- MCPTT client 2 is authorized to use call transfer.
- MCPTT client 1 is authorized to make private calls to MCPTT client 2.
- MCPTT client 2 is authorized to make private calls to MCPTT client 3.
- MCPTT client 2 is authorized to transfer private calls to MCPTT client 3.
- MCPTT client 2 supports simultaneous sessions for MCPTT private calls (10.8).
- MCPTT client 1 has the necessary security information to initiate a private call with MCPTT client 2 and MCPTT client 3, and MCPTT client 2 has the necessary security information to initiate a private call with MCPTT client 3 if end2end encryption is required for the private call.
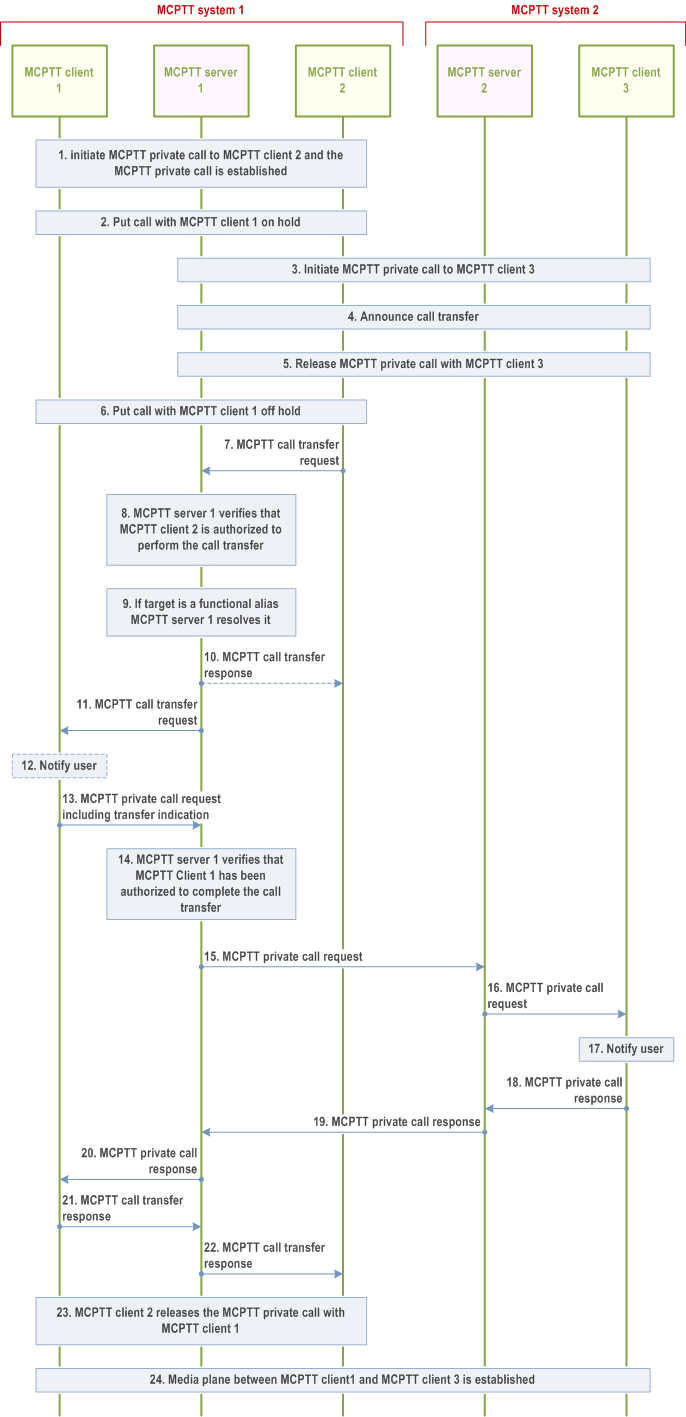
Step 1.
MCPTT client 1 initiates an MCPTT private call to MCPTT client 2 using the normal MCPTT call establishment as described in subclause 10.7.2.2. The MCPTT private call is established, and the user at MCPTT client 1 can talk with the user at MCPTT client 2. The user at MCPTT client 2 decides to transfer the call.
Step 2.
The MCPTT user at MCPTT client 2 puts the call with MCPTT user at MCPTT client 1 on hold.
Step 3.
MCPTT client 2 initiates an MCPTT private call to MCPTT client 3 using the normal MCPTT call establishment procedures as described in subclause 10.7.2.3. The MCPTT private call is established, and the user at MCPTT client 2 can talk with the user at MCPTT client 3.
Step 4.
The user at MCPTT client 2 can talk with the user at MCPTT client 3 and announces the call transfer.
Step 5.
The MCPTT client 2 releases the MCPTT private call with MCPTT client 3 using the normal MCPTT call release procedure as described in subclause 10.7.2.3. This step can occur at any time after step 4.
Step 6.
The MCPTT user at MCPTT client 2 puts the call with MCPTT client 1 off hold and confirms that the call will be transferred.
Step 7.
The MCPTT client 2 sends an MCPTT call transfer request to the MCPTT server 1.
Step 8.
The MCPTT server 1 verifies that MCPTT client 2 is authorized to transfer the MCPTT private call to MCPTT client 3. This check is based on entries in the user profile of the user at MCPTT client 2. First, the MCPTT server 1 checks the value of the "Allow private call transfer" entry. If it is false, the authorization check has failed, and the procedure continues with step 10. Otherwise, the MCPTT server 1 checks if the "Authorised to transfer private calls to any MCPTT user" entry is true. If this is the case the check has passed, and for target type of MCPTT ID the procedure continues with step 10 and for target ID type of functional alias the procedure continues with step 9. The subsequent checking depends on the type of target ID. If the target ID is a MCPTT ID, the MCPTT server 1 checks for a matching entry of the target MCPTT ID in the "List of MCPTT users that the MCPTT user is authorised to use as targets for call transfer" list. If a matching entry is found, the check has passed, if no matching entry is found the check has failed, for any outcome the procedure continues with step 10. If the target ID is a functional alias, the MCPTT server 1 checks for a matching entry of the target functional alias in the "List of functional aliases that the MCPTT user is authorised to use as targets for call transfer" list. If a matching entry is found, the check has passed, and the procedure continues with step 9. If no matching entry is found, the authorization check has failed and the procedure continues with step 10.
Step 9.
If the target of the MCPTT private call transfer is a functional alias instead of an MCPTT ID the MCPTT server 1 resolves the functional alias to the corresponding MCPTT ID for which the functional alias is active.
Step 10.
If the authorization check has failed, or the target of the transfer is a functional alias that is not active, or the target of the transfer is a functional alias that is simultaneously active by multiple users and the outcome of the selection is a rejection, the MCPTT private call transfer is cancelled, and the MCPTT server 1 sends an MCPTT private call transfer response with result "fail" back to MCPTT client 2. The MCPTT private call between MCPTT client 1 and MCPTT client 2 remains up, and the procedure stops. Otherwise the procedure continues.
Step 11.
The MCPTT server 1 sends an MCPTT call transfer request towards the MCPTT client 1.
Step 12.
Optionally the user at MCPTT client 1 is notified that a call transfer is in progress.
Step 13.
MCPTT client 1 sends an MCPTT private call request towards the MCPTT server 1 that includes a call transfer indication set to true.
Step 14.
The MCPTT server 1 verifies that MCPTT client 1 is authorized to perform the MCPTT private call as a result of the MCPTT private call transfer request based on the fact that the transfer indication is present and set to true in the MCPTT private call request.
Step 15.
The MCPTT server 1 sends an MCPTT call request to MCPTT server 2.
Step 16.
The MCPTT server 2 sends an MCPTT call request to MCPTT client 3.
Step 17.
The user at MCPTT client 3 is notified about the incoming call.
Step 18.
MCPTT client 3 sends an MCPTT private call response back to the MCPTT server 2.
Step 19.
MCPTT server 2 sends an MCPTT private call response back to the MCPTT server 1.
Step 20.
The MCPTT server 1 forwards the MCPTT private call response towards MCPTT client 1.
Step 21.
MCPTT client 1 sends an MCPTT call transfer response back to MCPTT server 1.
Step 22.
The MCPTT server 1 forwards the MCPTT private transfer response towards MCPTT client 2.
Step 23.
MCPTT client 2 initiates release of the private call between MCPTT client 1 and MCPTT client 2 as described in subclause 10.7.2.3.
Step 24.
The media plane for communication between MCPTT client 1 and MCPTT client 3 is established.
10.7.6.2.4 MCPTT private call announced transfer with transferring MCPTT user in partner MCPTT system |R18| p. 159
The procedure for MCPTT private call announced transfer covers the case where an MCPTT client requests an ongoing MCPTT private call (with or without floor control) to be transferred to another MCPTT user with prior announcement.
Figure 10.7.6.2.4-1 below illustrates the procedure for MCPTT private call announced transfer with transferring MCPTT user in partner MCPTT system.
Pre-conditions:
- MCPTT client 3 is authorized to use call transfer.
- MCPTT client 1 is authorized to make private calls to MCPTT client 3.
- MCPTT client 3 is authorized to make private calls to MCPTT client 2.
- MCPTT client 3 is authorized to transfer private calls to MCPTT client 2.
- MCPTT client 3 supports simultaneous sessions for MCPTT private calls (10.8).
- MCPTT client 1 has the necessary security information to initiate a private call with MCPTT client 2 and MCPTT client 3, and MCPTT client 3 has the necessary security information to initiate a private call with MCPTT client 2 if end2end encryption is required for the private call.
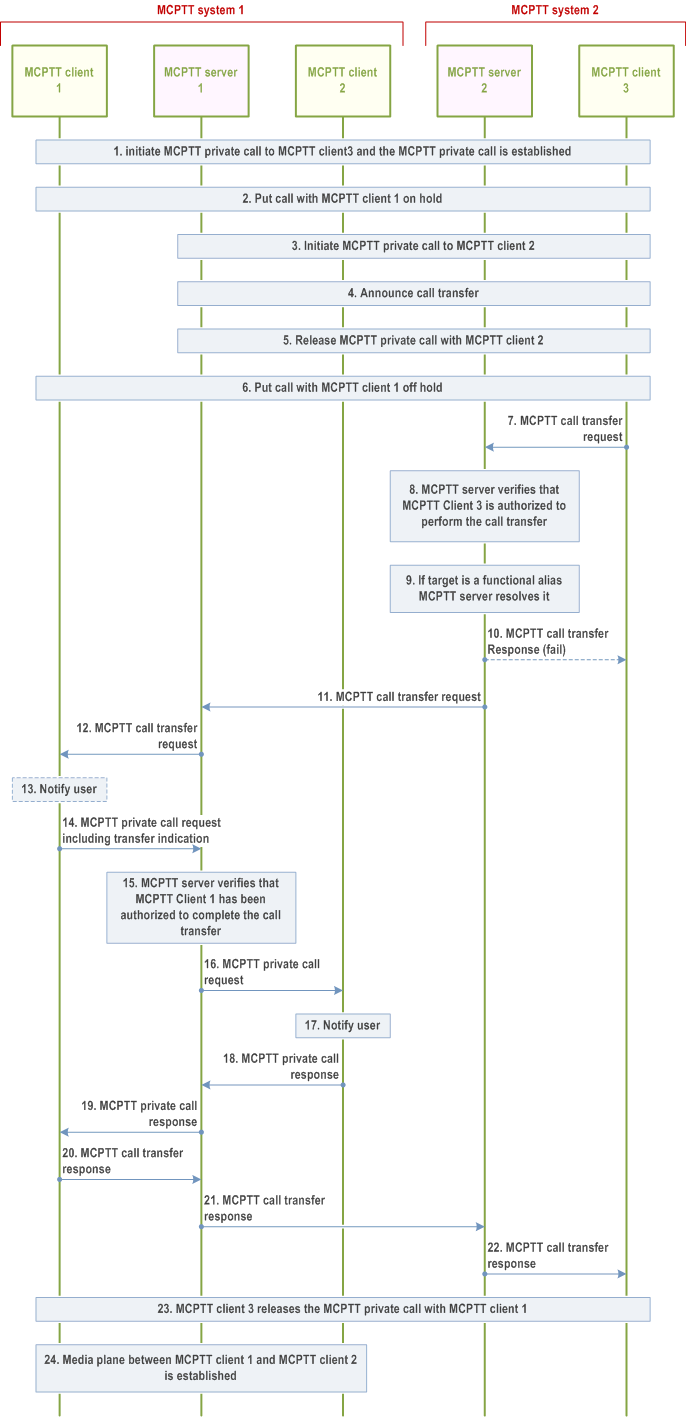
Step 1.
MCPTT client 1 initiates an MCPTT private call to MCPTT client 3 using the normal MCPTT call establishment as described in subclause 10.7.2.3. The MCPTT private call is established, and the user at MCPTT client 1 can talk with the user at MCPTT client 3. The user at MCPTT client 3 decides to transfer the call.
Step 2.
The MCPTT user at MCPTT client 3 puts the call with MCPTT user at MCPTT client 1 on hold.
Step 3.
MCPTT client 3 initiates an MCPTT private call to MCPTT client 2 using the normal MCPTT call establishment procedures as described in subclause 10.7.2.3. The MCPTT private call is established, and the user at MCPTT client 3 can talk with the user at MCPTT client 2.
Step 4.
The user at MCPTT client 3 can talk with the user at MCPTT client 2 and announce the call transfer.
Step 5.
The MCPTT client 3 releases the MCPTT private call with MCPTT client 2 using the normal MCPTT call release procedure as described in subclause 10.7.2.3. This step can occur at any time after step 4.
Step 6.
The MCPTT user at MCPTT client 3 puts the call with MCPTT client 1 off hold and confirms that the call will be transferred.
Step 7.
The MCPTT client 3 sends an MCPTT call transfer request to the MCPTT server 2.
Step 8.
The MCPTT server 2 verifies that MCPTT client 3 is authorized to transfer the MCPTT private call to MCPTT client 2. This check is based on entries in the user profile of the user at MCPTT client 3. First, the MCPTT server 2 checks the value of the "Allow private call transfer" entry. If it is false, the authorization check has failed, and the procedure continues with step 10. Otherwise, the MCPTT server 2 checks if the "Authorised to transfer private calls to any MCPTT user" entry is true. If this is the case the check has passed, and for target type of MCPTT ID the procedure continues with step 10 and for target ID type of functional alias the procedure continues with step 9. The subsequent checking depends on the type of target ID. If the target ID is an MCPTT ID, the MCPTT server 2 checks for a matching entry of the target MCPTT ID in the "List of MCPTT users that the MCPTT user is authorised to use as targets for call transfer" list. If a matching entry is found, the check has passed, if no matching entry is found the check has failed, for any outcome the procedure continues with step 10. If the target ID is a functional alias, the MCPTT server 2 checks for a matching entry of the target functional alias in the "List of functional aliases that the MCPTT user is authorised to use as targets for call transfer" list. If a matching entry is found, the check has passed, and the procedure continues with step 9. If no matching entry is found, the authorization check has failed and the procedure continues with step 10.
Step 9.
If the target of the MCPTT private call transfer is a functional alias instead of an MCPTT ID the MCPTT server 2 resolves the functional alias to the corresponding MCPTT ID for which the functional alias is active.
Step 10.
If the authorization check has failed, or the target of the transfer is a functional alias that is not active, or the target of the transfer is a functional alias that is simultaneously active by multiple users and the outcome of the selection is a rejection, the MCPTT private call transfer is cancelled, and the MCPTT server 2 sends an MCPTT private call transfer response with result "fail" back to MCPTT client 3. The MCPTT private call between MCPTT client 3 and MCPTT client 2 remains up, and the procedure stops. Otherwise the procedure continues.
Step 11.
The MCPTT server 2 sends an MCPTT call transfer request towards the MCPTT server 1.
Step 12.
The MCPTT server 1 sends an MCPTT call transfer request towards the MCPTT client 1.
Step 13.
Optionally the user at MCPTT client 1 is notified that a call transfer is in progress.
Step 14.
MCPTT client 1 sends an MCPTT private call request towards the MCPTT server 1 that includes a call transfer indication set to true.
Step 15.
The MCPTT server 1 verifies that MCPTT client 1 is authorized to perform the MCPTT private call as a result of the MCPTT private call transfer request based on the fact that the transfer indication is present and set to true in the MCPTT private call request.
Step 16.
The MCPTT server 1 sends an MCPTT private call request to MCPTT client 2.
Step 17.
The user at MCPTT client 2 is notified about the incoming call.
Step 18.
MCPTT client 2 sends an MCPTT private call response back to the MCPTT server 1.
Step 19.
The MCPTT server 1 forwards the MCPTT private call response towards MCPTT client 1.
Step 20.
MCPTT client 1 sends an MCPTT call transfer response back to the MCPTT server 1.
Step 21.
The MCPTT server 1 sends an MCPTT call transfer response back to the MCPTT server 2.
Step 22.
The MCPTT server 2 sends an MCPTT call transfer response back to the MCPTT client 3.
Step 23.
MCPTT client 3 initiates release of the private call between MCPTT client 3 and MCPTT client 1 as described in subclause 10.7.2.3.
Step 24.
The media plane for communication between MCPTT client 1 and MCPTT client 2 is established.
10.8 Simultaneous session for MCPTT calls (on-network) p. 162
10.8.1 General p. 162
An MCPTT client and MCPTT server may use a simultaneous session as defined in TS 23.280 for MCPTT calls. The MCPTT client becomes involved in a simultaneous session for MCPTT calls by inviting, joining or accepting more than one MCPTT call, or affiliating to a group.
The MCPTT client can also still handle multiple MCPTT calls in parallel at the same time i.e. using multiple dialogs.
The simultaneous session is established during either an originating on-demand call establishment or during pre-established session establishment or a modification of an already established pre-established session or on-demand call.
It is possible to change the prioritisation while the MCPTT client is engaged in multiple MCPTT calls. The setting of the priority can be made at MCPTT call setup or by performing a modification after the MCPTT call is established. This may result in more than one media bearer.