Content for TS 23.379 Word version: 19.2.0
1…
7…
7.4…
10…
10.5…
10.6…
10.6.2.2.13…
10.6.2.2.24…
10.6.2.3…
10.6.2.3.1.2…
10.6.2.3.2…
10.6.2.4…
10.6.2.4.3…
10.6.2.5…
10.6.2.5.2.3…
10.6.2.6…
10.6.2.6.2…
10.6.2.7…
10.6.2.10…
10.6.3…
10.7…
10.7.2.2…
10.7.2.3…
10.7.3…
10.7.4…
10.7.5…
10.7.5.2.3a…
10.7.6…
10.7.6.2.3…
10.9…
10.9.1.3…
10.9.1.3.2…
10.9.1.3.3…
10.9.1.4…
10.9.1.5…
10.9.2…
10.9.2.6…
10.10…
10.12…
10.14…
10.15…
10.19…
10.19.2.11…
10.19.3…
10.19.3.1.4…
10.19.3.2…
10.19.3.2.4…
10.19.3.2.6…
A…
A.4…
B…
10.7.5 MCPTT call forwarding for private calls
10.7.5.1 General
10.7.5.1.2 MCPTT private call forwarding request (MCPTT client to MCPTT server and MCPTT server to MCPTT server)
10.7.5.1.3 MCPTT private call forwarding response (MCPTT server to MCPTT client)
10.7.5.1.4 MCPTT private call forwarding request (MCPTT server to MCPTT client)
10.7.5.1.5 MCPTT private call forwarding response (MCPTT client to MCPTT server and MCPTT server to MCPTT server)
10.7.5.2 Procedures
10.7.5.2.1 Update configuration for MCPTT private call forwarding
10.7.5.2.2 MCPTT immediate private call forwarding in a single MCPTT system
10.7.5.2.3 MCPTT private call forwarding no answer in a single MCPTT system
...
...
10.7.5 MCPTT call forwarding for private calls |R16| p. 135
10.7.5.1 General p. 135
Call forwarding of MCPTT private calls allows users to configure forwarding of incoming private calls (with or without Floor control) to another MCPTT user depending on the following conditions:
- Immediate
- No answer: If the incoming private call is a call with manual commencement mode and the MCPTT User does not answer within a configured period
10.7.5.1.1 Void
10.7.5.1.2 MCPTT private call forwarding request (MCPTT client to MCPTT server and MCPTT server to MCPTT server) p. 136
Table 10.7.5.1.2-1 describes the information flow of the MCPTT private call forwarding request from the MCPTT client to the MCPTT server and MCPTT server to MCPTT server.
| Information Element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| MCPTT ID | M | The MCPTT ID requesting the call forwarding |
| MCPTT ID | M | The MCPTT ID originating the MCPTT private call |
| MCPTT ID (see NOTE) | O | The target MCPTT ID of the call forwarding |
| Functional alias (see NOTE) | O | The target functional alias of the call forwarding |
|
NOTE:
One identity shall be present
|
||
10.7.5.1.3 MCPTT private call forwarding response (MCPTT server to MCPTT client) p. 136
Table 10.7.5.1.3-1 describes the information flow of the MCPTT private call forwarding response from the MCPTT server to the MCPTT client.
| Information Element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| MCPTT ID | M | The MCPTT ID requesting the call call forwarding |
| Result | M | Result of the call forwarding request - success or fail |
10.7.5.1.4 MCPTT private call forwarding request (MCPTT server to MCPTT client) p. 136
Table 10.7.5.1.4-1 describes the information flow of the MCPTT private call forwarding request from the MCPTT server to the MCPTT client.
| Information Element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| MCPTT ID | M | The MCPTT ID of the party to be forwarded |
| MCPTT ID | M | The target MCPTT ID of the call forwarding |
10.7.5.1.5 MCPTT private call forwarding response (MCPTT client to MCPTT server and MCPTT server to MCPTT server) p. 136
Table 10.7.5.1.5-1 describes the information flow of the MCPTT private call forwarding response from the MCPTT client to the MCPTT server and MCPTT server to MCPTT server.
| Information Element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| MCPTT ID | M | The MCPTT ID of the party to be forwarded |
| MCPTT ID | M | The MCPTT ID of the target of the forwarding |
| Result | M | Result of the call forwarding request - success or fail |
10.7.5.2 Procedures p. 137
10.7.5.2.1 Update configuration for MCPTT private call forwarding p. 137
An authorized user can update the call forwarding related parameters stored in the user profile using the procedures as defined in subclause 10.1.4.5 of TS 23.280.
10.7.5.2.2 MCPTT immediate private call forwarding in a single MCPTT system p. 137
Figure 10.7.5.2.2-1 below illustrates the procedure of immediate call forwarding of MCPTT private calls.
Pre-conditions:
- MCPTT client 2 is authorized to use call forwarding and has immediate call forwarding enabled with the destination MCPTT client 3.
- MCPTT client 1 is authorized to make private calls to client 2.
- The redirection counter is below the limit.
- MCPTT client 1 has the necessary security information to initiate a private call with MCPTT client 2 and MCPTT client 3 if end2end encryption is required for the private call.
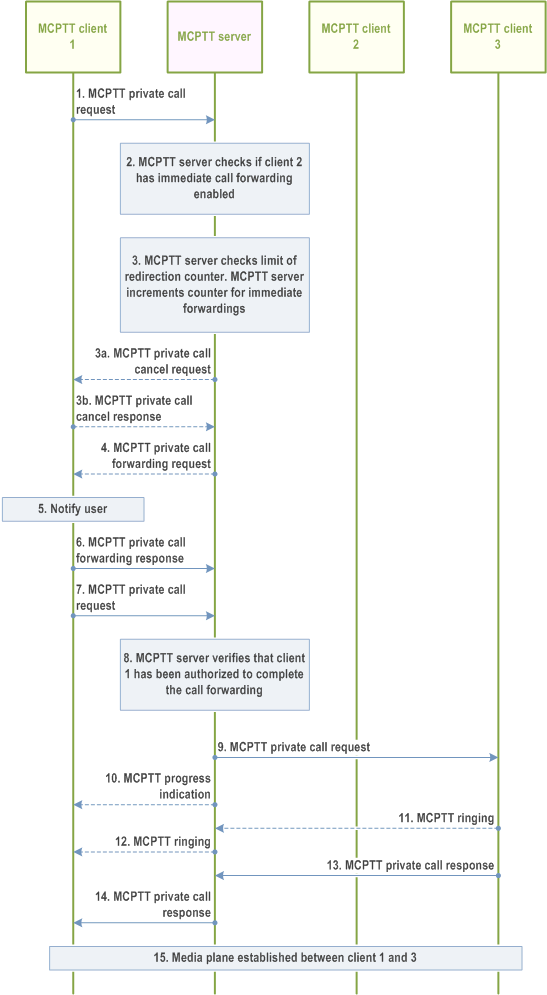
Step 1.
MCPTT client 1 sends an MCPTT private call request towards the MCPTT server.
Step 2.
The MCPTT server detects that MCPTT client 2 has immediate call forwarding enabled.
Step 3.
The MCPTT server checks that the limit of immediate forwardings is not reached. The MCPTT server increments the redirection counter for immediate forwardings. If the target of the MCPTT private call forwarding is a functional alias instead of an MCPTT ID the MCPTT server resolves the functional alias to the corresponding MCPTT ID for which the functional alias is active.
Step 3a.
If the target of the call forwarding is a functional alias that is not active, or if the target functional is simultaneously active by multiple users and the outcome of the selection is a rejection, the MCPTT private call forwarding is cancelled, and the MCPTT server sends an MCPTT private call cancel request towards MCPTT client 1. Otherwise, the procedure continues with step 4.
Step 3b.
MCPTT client 1 sends an MCPTT call private cancel response back to the MCPTT server, and the procedure ends.
Step 4.
The MCPTT server sends an MCPTT private call forwarding request towards MCPTT client 1.
Step 5.
The user at MCPTT client 1 is notified that a call forwarding is in process.
Step 6.
MCPTT client 1 sends an MCPTT call private forwarding response back to the MCPTT server.
Step 7.
MCPTT client 1 sends an MCPTT private call request towards the MCPTT server that includes a call forwarding indication set to true. MCPTT client 1 and MCPTT client 3 set up a security association if end-to-end encryption is used for this call.
Step 8.
The MCPTT server verifies that client 1 is authorized to perform the MCPTT private call as a result of the MCPTT private call forwarding request. The MCPTT server verifies that the MCPTT private call request contains MCPTT client 3 that is the authorized target from step 4, and the forwarding indication is set to true.
Step 9.
The MCPTT server sends an MCPTT private call request towards MCPTT client 3.
Step 10.
Optionally the MCPTT server sends an MCPTT progress indication to MCPTT client 1.
Step 11.
The user at MCPTT client 3 is alerted. MCPTT client 3 sends an MCPTT ringing to the MCPTT server. This step is not required in case of automatic commencement mode.
Step 12.
The MCPTT server sends an MCPTT ringing to MCPTT client 1. This step is not required in case of automatic commencement mode.
Step 13.
MCPTT client 3 sends an MCPTT private call response to the MCPTT server. In manual commencement mode this occurs after the user at MCPTT client 3 has accepted the call.
Step 14.
The MCPTT server sends an MCPTT private call response to MCPTT client 1 indicating that MCPTT client 3 has accepted the call.
Step 15.
The media plane for communication between MCPTT client 1 and MCPTT client 3 is established.
10.7.5.2.3 MCPTT private call forwarding no answer in a single MCPTT system p. 139
Figure 10.7.5.2.3-1 below illustrates the procedure of call forwarding no answer of MCPTT private calls.
Pre-conditions:
- MCPTT client 2 is authorized to use call forwarding and has call forwarding no answer enabled with the destination MCPTT client 3.
- MCPTT client 1 is authorized to make private calls to MCPTT client 2.
- No forwarding with no answer or based on manual user input has so far occurred in this call.
- MCPTT client 1 has the necessary security information to initiate a private call with MCPTT client 2 and MCPTT client 3 if end2end encryption is required for the private call.

Step 1.
MCPTT client 1 sends an MCPTT private call request towards the MCPTT server.
Step 2.
The MCPTT server checks if MCPTT client 2 has call forwarding no answer enabled. If the MCPTT server detects that MCPTT client 2 is not registered, the procedure continues with step 7. Otherwise, the MCPTT server starts a timer with the configured no answer timeout.
Step 3.
The MCPTT server sends an MCPTT private call request in manual commencement mode towards MCPTT client 2. If the MCPTT server detects that MCPTT client 2 is not reachable, the procedure continues with step 7.
Step 4.
The user at MCPTT client 2 is alerted. MCPTT client 2 sends an MCPTT ringing to the MCPTT server.
Step 5.
The MCPTT server sends an MCPTT ringing to the MCPTT client 1. This step is not required in case of automatic commencement mode.
Step 6.
The MCPTT server detects that MCPTT client 2 does not answer within the specified time interval.
Step 7.
The MCPTT server verifies that no other forwarding with the condition no answer or based on manual user input has occurred so far. If the target of the MCPTT private call forwarding is a functional alias instead of an MCPTT ID the MCPTT server resolves the functional alias to the corresponding MCPTT ID for which the functional alias is active.
Step 7a.
If the target of the call forwarding is a functional alias that is not active, or if the target functional is simultaneously active by multiple users and the outcome of the selection is a rejection, the MCPTT private call forwarding is cancelled, and the MCPTT server sends an MCPTT private call cancel request towards MCPTT client 1. Otherwise, the procedure continues with step 8.
Step 7b.
MCPTT client 1 sends an MCPTT call private cancel response back to the MCPTT server, and the procedure ends.
Step 8.
The MCPTT server sends an MCPTT private call forwarding request towards the MCPTT client 1.
Step 9.
The user at MCPTT client 1 is notified that a call forwarding is in process.
Step 10.
MCPTT client 1 sends an MCPTT private call forwarding response back to the MCPTT server.
Step 11.
MCPTT client 1 sends an MCPTT private call request towards the MCPTT server that includes a call forwarding indication set to true. MCPTT client 1 and MCPTT client 3 set up a security association if end-to-end encryption is used for this call.
Step 12.
The MCPTT server verifies that client 1 is authorized to perform the MCPTT private call as a result of the MCPTT private call forwarding request. The MCPTT server verifies that the MCPTT private call request contains MCPTT client 3 that is the authorized target from step 8, and the forwarding indication is set to true.
Step 13.
The MCPTT server sends an MCPTT private call request towards MCPTT client 3.
Step 14.
Optionally the MCPTT server sends an MCPTT progress indication to MCPTT client 1.
Step 15.
The user at MCPTT client 3 is alerted. MCPTT client 3 sends an MCPTT ringing to the MCPTT server. This step is not required in case of automatic commencement mode.
Step 16.
The MCPTT server sends an MCPTT ringing to MCPTT client 1. This step is not required in case of automatic commencement mode.
Step 17.
MCPTT client 3 sends an MCPTT private call response to the MCPTT server. In manual commencement mode this occurs after the user at MCPTT client 3 has accepted the call.
Step 18.
The MCPTT server sends an MCPTT private call response to MCPTT client 1 indicating that MCPTT client 3 has accepted the call.
Step 19.
The media plane for communication between MCPTT client 1 and MCPTT client 3 is established.