Content for TS 23.261 Word version: 18.0.0
5 IP Flow Mobility procedures and flows
5.1 General
5.2 PDN connection establishment over first access
5.2.1 General
5.2.2 PDN connection establishment over 3GPP access
5.2.3 PDN connection establishment over WLAN
...
...
5 IP Flow Mobility procedures and flows p. 9
5.1 General p. 9
This clause describes the IP flow mobility procedures for different scenarios. The call flows are described in a common way for I-WLAN and EPS and the procedures which are applicable to EPS only are marked as optional and identified as not applicable to an I-WLAN mobility deployment. Furthermore the call flows do not differentiate between trusted or untrusted accesses as the IP flow mobility procedures are common as soon as the UE configures a Care-of Address.
5.2 PDN connection establishment over first access p. 9
5.2.1 General p. 9
This clause specifies the additional UE procedures when establishing a PDN connection through a 3GPP or through a WLAN access when the UE supports IP flow mobility. In these flows it is assumed that the UE has not established the PDN connection through any access yet.
5.2.2 PDN connection establishment over 3GPP access p. 9
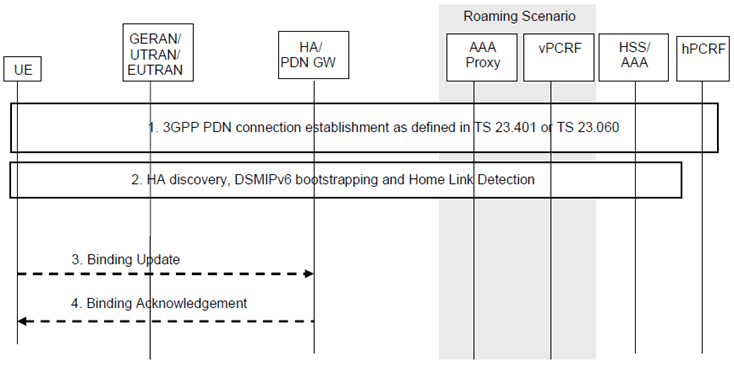
The UE performs the initial PDN connection establishment to a 3GPP access as shown in Figure 5.2.2-1. This procedure applies independently whether the UE attaches to EPS or GPRS.
Step 1.
The initial PDN establishment procedure is performed by the UE according to TS 23.401 or TS 23.060, depending if the PDN connection establishment is to EPS or GPRS. During this step an IPv4 address and/or an IPv6 address/prefix is assigned to the UE.
Step 2.
The UE performs HA discovery, DSMIPv6 bootstrapping and the home link detection procedure as described in TS 23.402 or TS 23.327.
If the UE requests the home network prefix in the Protocol Configuration Option (as in TS 23.402), the UE shall requests in the Protocol Configuration Option an indication of HA support of IP flow mobility.
If the UE obtains the home network prefix using the IKEv2 procedure, the UE shall use IKEv2 signaling to indicate IFOM support. The HA supporting IFOM shall use IKEv2 signaling to confirm the IFOM support.
If the HA does not support IFOM, the UE shall disable IFOM capabilities for that PDN connection.
The presence of ANDSF inter-system routing policies for a given PLMN may be considered by the UE as an implicit indication that the Home Agents of that PLMN support IP flow mobility. If the UE has ANDSF inter-system routing policies, the UE may skip the IKEv2 and PCO procedures to check the IFOM support of the PDN GW for the PDN GWs residing in the PLMN where the ANDSF policies are valid.
Step 3.
If the UE detects it is not on the home link, the UE sends a DSMIPv6 Binding Update (HoA, CoA, Lifetime, BID) message to the HA as specified in RFC 5555 and RFC 5648. The inclusion of the BID mobility option at this stage is an indication that the UE supports IP Flow Mobility extensions. The UE may also include some FID mobility options as described in RFC 6089.
Step 4.
5.2.3 PDN connection establishment over WLAN p. 10
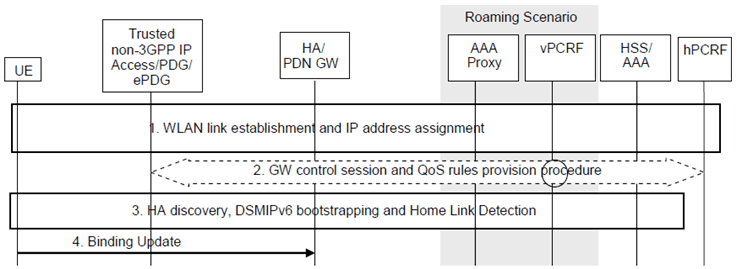
The UE performs the initial PDN connection establishment over a WLAN access as shown in Figure 5.2.3-1.
Step 1.
The UE connects to the WLAN and configures an IPv4 address and/or an IPv6 address/prefix. Depending on the specific scenario considered the UE attaches either to a trusted WLAN, an ePDG via an untrusted WLAN or to a PDG via a I-WLAN access as specified in TS 23.402 or TS 23.327. If the UE connects to PDG or ePDG, an IPv4 address and/or an IPv6 address/prefix is assigned to the UE.
Step 2.
If the UE connects to a Trusted non-3GPP access and dynamic PCC is deployed, a GW control session may be established as specified in TS 23.203.
Step 3.
The UE performs HA discovery, DSMIPv6 bootstrapping and the home link detection procedure as described in TS 23.402 or TS 23.327.
During the home link detection procedure in IKEv2, the UE shall use IKEv2 signalling to indicate IFOM support. The HA supporting IFOM shall use IKEv2 signalling to confirm the IFOM support.
If the HA does not support IFOM, the UE shall disable IFOM capabilities for that PDN connection.
The presence of ANDSF inter-system routing policies for a given PLMN may be considered by the UE as an implicit indication that the Home Agents of that PLMN support IP flow mobility. If the UE has ANDSF inter-system routing policies, the UE may skip the IKEv2 and PCO procedures to check the IFOM support of the PDN GW for the PDN GWs residing in the PLMN where the ANDSF policies are valid.
Step 4.
If the UE detects it is not on the home link, the UE sends a DSMIPv6 Binding Update (HoA, CoA, Lifetime, BID) message to the HA as specified in RFC 5555 and RFC 5648. The inclusion of the BID mobility option at this stage is an indication that the UE supports IP Flow Mobility extensions. The BID mobility option contains the Binding ID of the WLAN access. The UE may also include some FID mobility options as described in RFC 6089.
Step 5.
If the HA function is located in the PDN GW and dynamic PCC is deployed, the PDN GW performs an IP-CAN session establishment procedure with the PCRF as specified in TS 23.203.
Step 6.