Content for TS 23.246 Word version: 18.0.0
9 Security
10 Charging requirement
10.1 General
10.2 Bearer level charging for MBMS
10.3 Application level charging for MBMS
10.4 Generation of charging records in the VPLMN
11 Roaming Support for MBMS user services
11.1 Scenarios description
11.2 Scenario signalling flow
...
...
9 Security |R18| p. 65
Security of MBMS is found in TS 33.246.
10 Charging requirement |R18| p. 65
10.1 General p. 65
The MBMS architecture shall support on-line and off-line charging.
It shall be possible to collect charging information for the multicast mode. It shall also be possible to collect charging information for MBMS services in visited networks.
MBMS shall collect charging information about the transmission of MBMS broadcast or multicast data that are provided by content or service providers (e.g. 3rd parties). This shall enable billing of broadcast and multicast content or service providers.
To enable billing of broadcast and multicast content providers, data shall be collected at the BM-SC.
10.2 Bearer level charging for MBMS p. 65
To provide bearer level charging for MBMS, mechanisms and functional elements described in TS 23.125 are used for MBMS Bearer Contexts.
For EPS, MBMS GW shall collect charging information about the transmission of MBMS broadcast for UTRAN and E-UTRAN. MBMS Bearer context in MBMS GW should include charging related information elements.
Flow Based Charging (FBC) may be used to collect charging data records for MBMS Bearer Contexts e.g. for the purpose to charge the service provider, cf. TS 23.125.
10.3 Application level charging for MBMS p. 65
For GPRS, in order to meet the MBMS charging requirements in TS 22.146 and TS 22.246, the following elements and functionalities are provided by the GPRS MBMS architecture:
- The MSISDN and IMSI are passed to the BM-SC. This provides the operator with the ability to associate GPRS location information (i.e. serving network idenity) with a user.
- In order to permit differential roaming tariffs, the serving network identity is provided to the BM-SC.
-
Charging for MBMS services is based on application layer mechanisms, since it is only at the application layer that security is provided which can restrict content to authorised users or confirm delivery of content to users:
The following general requirements apply to charging information generated by the BM-SC:
- Charging information generated for application layer charging events should include the above information provided by the GPRS network to facilitate differential roaming tariffs.
- Charging information should include an indication of the point at which the user had access to the content (e.g. if and when decryption keys for encrypted content are sent to the UE.).
10.4 Generation of charging records in the VPLMN p. 66
In this Release, charging for roaming scenario of MBMS in EPS will not be considered.
For GPRS, in order to permit the settlement of inter-operator roaming charges , the SGSN needs to raise CDRs. The information that needs to be included on these CDRs is FFS.
11 Roaming Support for MBMS user services |R18| p. 66
11.1 Scenarios description p. 66
There are three specific scenarios to provide MBMS user services to roaming users.
One uses a GGSN in the HPLMN, the other two are enabled by use of the Mz interface and are further described below:
- A visited PLMN may offer to roaming users MBMS user services from their home PLMN. For this case, the PDP connection, which will be used for the JOIN step, may always be from the UE to the V GGSN due to operator policy or routing optimization, then the authorization is done in the BM-SC in visited PLMN with the authorization information retrieved from the BM-SC in home PLMN. Then the MBMS user traffic is provided by the BM-SC in home PLMN and proxied. An APN indicating a GGSN will be included in the authorisation information sent from home BM-SC to visited BM-SC. Whether GGSN of home or visited PLMN would be used is based on the operator policy, or agreement between PLMNs, for example, the visited BM-SC may modify the APN from the home BM-SC according to configuration of operator policy.
- Or, a visited PLMN may offer its own MBMS user services to roaming users when visited and home PLMN support the same classes of MBMS user services. For this case, the authorization is done in the BM-SC in visited PLMN with the authorization information retrieved from the BM-SC in home PLMN. Then the MBMS user traffic is provided by the BM-SC in visited PLMN.
11.2 Scenario signalling flow p. 66
11.2.1 APN selection p. 66
When a UE is authorized through the BM-SC in the visited PLMN (by proxying the authorization signalling), an APN may be selected and decided by the BM-SC in the home PLMN or the BM-SC in the visit PLMN depending on the operator policy or agreement between PLMNs. See step 4 of the Figure 18.
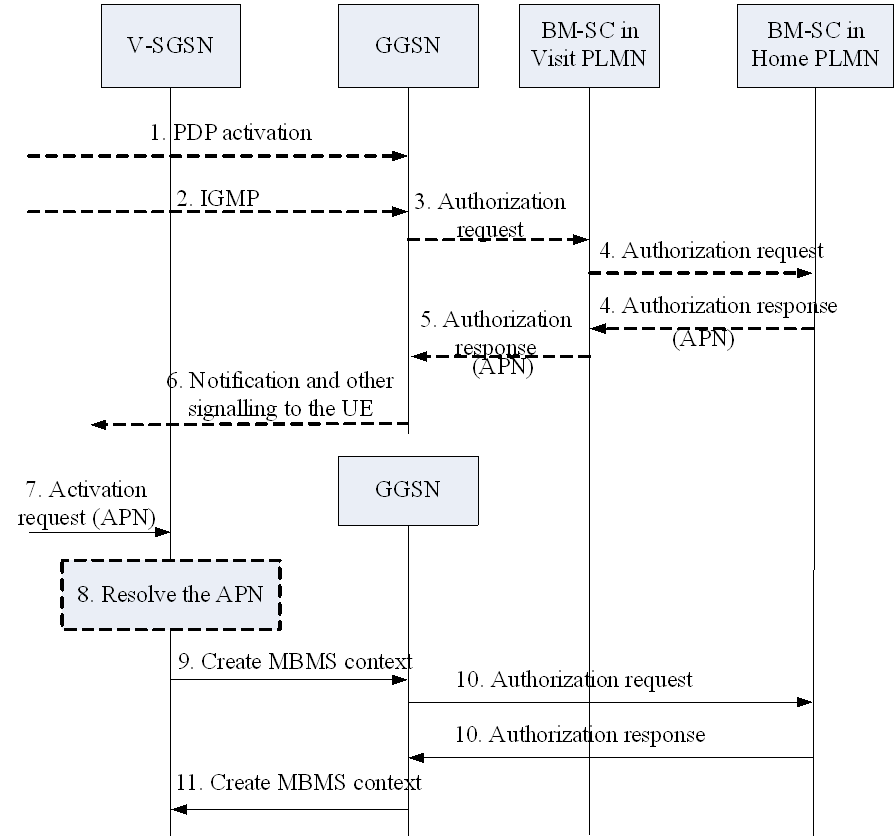
Figure 18 is an extension of MBMS multicast service activation procedure described in clause 8.2, the only revise is that an authorization step (step 4) is added according to clause 11.1.
Step 4.
The BM-SC in visited PLMN finds the BM-SC in home PLMN which will serve the UE based on the multicast IP address, and identity of the user, and sends the authorization request to it. The BM-SC in home PLMN can respond with an APN, which indicates a GGSN in home PLMN which will serve the UE for the specific MBMS service. The BM-SC in the visit network may modify the APN based on the operator policy or agreement between PLMNs.