Content for TS 23.246 Word version: 17.0.0
8.8 MBMS Session Update procedure
8.8.1 General
8.8.2 SGSN initiated Session Update for GERAN and UTRAN for MBMS Multicast service
8.8.3 BM-SC initiated Session Update for GERAN and UTRAN for MBMS Broadcast service
8.8.4 BM-SC initiated Session Update for EPS with E-UTRAN and UTRAN
...
...
8.8 MBMS Session Update procedure p. 53
8.8.1 General |R7| p. 53
The MBMS Session Update procedure may be invoked by BM-SC or by SGSN. The BM-SC uses the procedure to update the service area or the QoS(ARP) for an ongoing MBMS Broadcast service session. The SGSN can also use the procedure to update the list of RAs where MBMS multicast users are located for an ongoing MBMS Multicast service session.
For the distributed MCE architectures, i.e. when the MCE is part of the eNB as described in clause 15.1.1 of TS 36.300, an absolute time stamp for when data can be expected, "MBMS data transfer start", should be used at MBSFN operation mode to ensure synchronized session control and to facilitate a graceful reallocation of resources for the MBSFN when needed. When the parameter "MBMS data transfer start" is present, a receiving supporting node shall ignore the parameter "time to MBMS data transfer". For session stop signalling, the parameter "MBMS data transfer stop" is if present used to schedule the release of the radio resources in order to ensure a synchronized session control. The MME also sends an MBMS Session Start Request message to any added MCEs, and an MBMS Session Stop Request message to any removed MCEs. The MME shall set "MBMS Data Transfer Start" to "Time of MBMS Data Transfer" or "Time of MBMS Data Stop" respectively as specified in TS 36.444.
8.8.2 SGSN initiated Session Update for GERAN and UTRAN for MBMS Multicast service |R7| p. 54
If the SGSN has provided a list of RAs in the MBMS Session Start Request message (even if the list was empty) and RAs are added or removed from the list, the SGSN shall use the MBMS Session Update procedure to inform the RNCs that the list has changed. The SGSN sends the Session Update message only to the RNCs that are affected by the list change. The procedure is used only during the MBMS Multicast service session and when SGSN has already sent a MBMS Session Start Request message to the RNC.
If the SGSN has provided a list of RAs in the MBMS Session Start Request message (even if the list was empty) the SGSN shall send the Session Update to a RNC when:
- the first UE which have activated the service enters in a RA that is not in the list;
- the last UE which have activated the service leaves from a RA that was in the list.
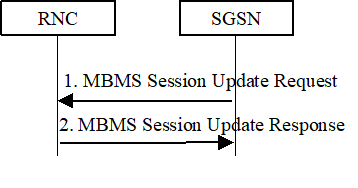
- The SGSN sends MBMS Session Update Request message to a RNC.
- The RNC acknowledges the MBMS Session Update Request with the MBMS Session Update Response message.
8.8.3 BM-SC initiated Session Update for GERAN and UTRAN for MBMS Broadcast service |R7| p. 54
The BM-SC initiates the MBMS Session Update procedure when the service area for an ongoing MBMS Broadcast service session shall be modified.
The attributes that can be modified by the Session Update Request are the MBMS Service Area, and the list of downstream nodes for GGSN (Broadcast only). A node receiving the Session Update Request determines how the attributes have changed by comparing the attributes in the message with corresponding attributes in its stored MBMS Bearer Context.
A Session Update received in one node, results in a Session Update being sent to downstream nodes, to inform of the changed MBMS Service Area. If a Session Update with the List of SGSN parameter included is received in the GGSN, it does also result in a Session Start being sent to new downstream nodes, and in a Session Stop being sent to downstream nodes that have been removed from the list.
The overall Session Update procedure is presented in Figure 13b.
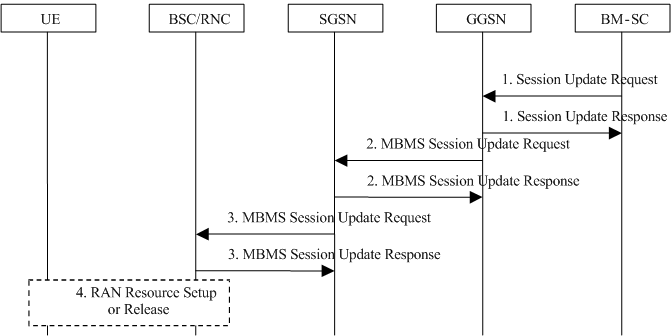
Step 1.
The BM-SC Session and Transmission function sends a Session Update Request (TMGI, Flow Identifier (Broadcast only), QoS, MBMS Service Area, Session identifier, estimated session duration, broadcast/multicast, list of downstream nodes for GGSN, time to MBMS data transfer) to the BM-SC Proxy and Transport function, which then forwards it to the GGSNs listed in the "list of downstream nodes" parameter of the corresponding MBMS Bearer Context. The TMGI and Session identifier identifies the ongoing session. The QoS, broadcast/multicast attributes and the 2G/3G indicator shall be identical as in the preceding Session Start message. The MBMS Service Area and the List of downstream nodes for GGSN define the new service area. The time to MBMS data transfer shall be set to 0 and the estimated session duration shall be set to a value corresponding to the remaining part of the session.
The GGSN stores the new session attributes and the list of downstream nodes in the MBMS Bearer Context and sends a Session Update Response message to the BM-SC Proxy and Transport function which forwards it to the BM-SC Session and Transmission function. The BM-SC Proxy and Transport function copies the Session Update Request to the BM-SC Membership function for charging purposes.
Step 2.
The GGSN compares the new list of downstream nodes with the list of downstream nodes it has stored in the MBMS Bearer Context. It sends an MBMS Session Start Request message to any added SGSN, an MBMS Session Stop Request to any removed SGSN, and an MBMS Session Update Request to the remaining SGSNs in the new list.
Step 3.
The SGSN receiving an MBMS Session Update Request message, sends an MBMS Session Update Request message including the session attributes (TMGI, QoS, MBMS service Area, Session identifier, estimated session duration, broadcast/multicast, time to MBMS data transfer, list of RAs, etc.) to each BSC and/or each RNC that is connected to this SGSN.
Step 4.
The BSCs/RNCs establish or release the necessary radio resources for the transfer of MBMS data to the interested UEs.
8.8.4 BM-SC initiated Session Update for EPS with E-UTRAN and UTRAN |R9| p. 55
The BM-SC initiates the MBMS Session Update procedure when the service attributes (e.g. Service Area, list of cell IDs or ARP) for an ongoing MBMS Broadcast service session shall be modified, e.g. the Session Update procedure for EPS is initiated by BM-SC to notify eNBs to join or leave the service area. Update of the QoS(ARP) is triggered when the priority of a broadcast data flow of a group communication service is changed as specified in TS 23.468.
The attributes that can be modified by the Session Update Request are the MBMS service area, list of cell IDs, Access indicator, MBMS data transfer start, QoS(ARP) and the List of MBMS control plane nodes. A node receiving the Session Update Request determines how the attributes have changed by comparing the attributes in the message with corresponding attributes in its stored MBMS Bearer Context.
A Session Update received in one node, results in a Session Update being sent to downstream nodes, to inform of the changed MBMS service attributes. If a Session Update with the List of MME and SGSN parameter included is received in the MBMS GW, it does also result in a Session Start being sent to new downstream nodes, and in a Session Stop being sent to downstream nodes that have been removed from the list.
The overall Session Update procedure is presented in Figure 13c-1 and Figure 13c-2.
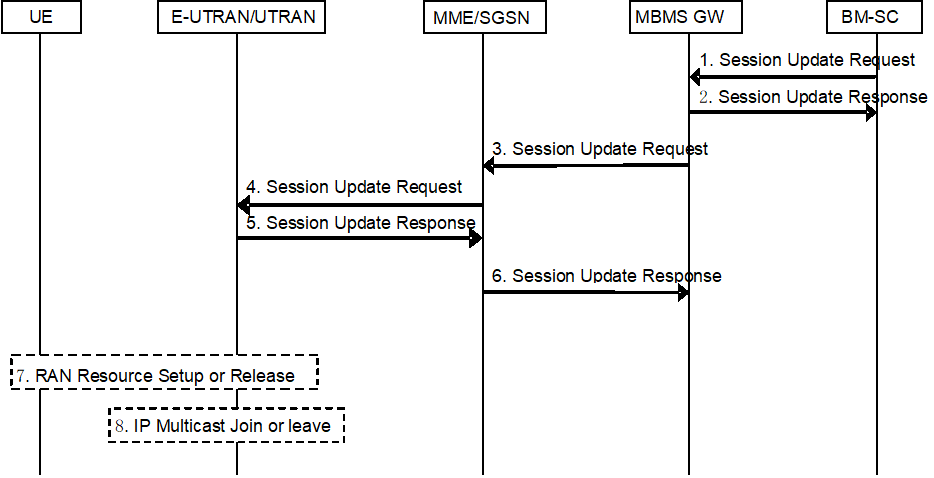
Figure 13c-1: Session Update procedure for EPS with E-UTRAN and UTRAN
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
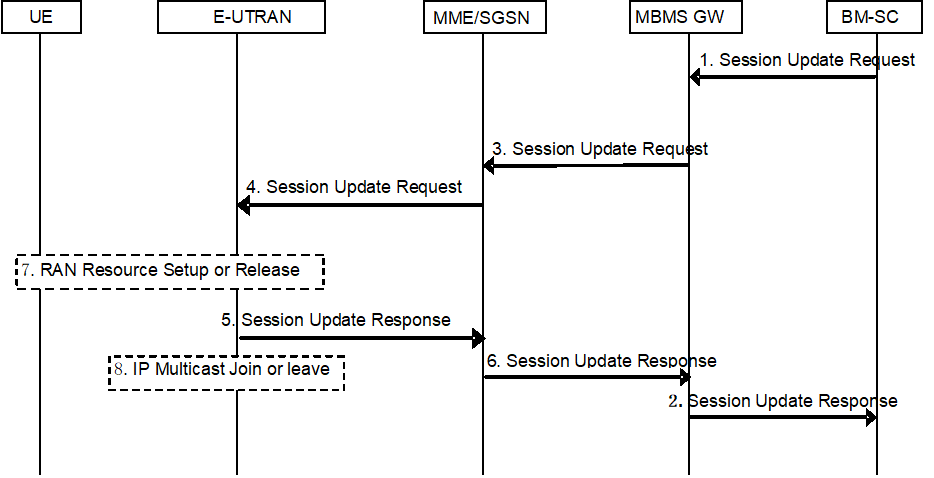
Figure 13c-2: Session Update procedure for EPS with E-UTRAN with delayed response
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
Step 1.
The BM-SC sends a Session Update Request (TMGI, Flow Identifier, QoS, MBMS Service Area, list of cell IDs if available, Session identifier, estimated session duration, the list of MBMS control plane nodes(MMEs, SGSNs) for MBMS GW, time to MBMS data transfer, MBMS data transfer start, Access Indicator, ...) to MBMS GW. The TMGI and Session identifier identifies the ongoing session. Apart from the ARP parameter, all other parameters in the QoS profile shall be identical as in the preceding Session Start message. The ARP parameter may be different if it is to be updated. The MBMS Service Area and the list of MBMS control plane nodes (MMEs, SGSNs) for MBMS GW define the new service area. The estimated session duration shall be set to a value corresponding to the remaining part of the session. If radio access of MBMS service is updated the Access indicator shall be included to indicate in which radio access types the MBMS service should be broadcasted, i.e. UTRAN, or E-UTRAN, or both. The ARP parameter may be updated only if the Access Indicator indicates E-UTRAN. The Access indicator may be included in charging information generated by the MBMS GW.
If MBMS GW is configured to delay response to BMSC when access type is E-UTRAN, then MBMS GW delays response to BMSC (i.e. Step 2) until after step 6 is executed as shown in Figure 13c-2. This configuration should be only performed when E-UTRAN executes step 7 below before responding to the MBMS Session Update message as specified in TS 36.300.
Step 2.
The MBMS GW stores the new session attributes in the MBMS Bearer Context and sends a Session Update Response message to the BM-SC, if Figure 13c-1 is executed. The MBMS GW responds only after first MME response in step 6 is received, if it is configured to do so as shown in Figure 13c-2.
Step 3.
The MBMS GW filters the new list of MBMS control plane nodes using the Access indicator to ignore entries not consistent with the Access indicator, and compares remaining entries in the new list of MBMS control plane nodes with the list of MBMS control plane nodes it has stored in the MBMS Bearer Context. It sends an MBMS Session Start Request message to any added MME/SGSN, an MBMS Session Stop Request to any removed MME/SGSN, and an MBMS Session Update Request (TMGI, Flow Identifier, QoS, MBMS Service Area, list of cell IDs if available, Session identifier, estimated session duration, ...) to the remaining MME/SGSNs in the new list. The handlings of the MBMS Session Start/Stop Request message are described in clauses 8.3.2 and 8.5.2.
Step 4.
The MME/SGSN receiving an MBMS Session Update Request message, sends an MBMS Session Update Request message including the session attributes (TMGI, QoS, MBMS service Area, list of cell IDs if available, Session identifier, estimated session duration, broadcast (for UTRAN only), transport network IP Multicast Address, IP address of the muticast source, C TEID, etc.) to each eNodeB/MCE/RNC that is connected to the MME/SGSN.
For E-UTRAN, when connected to multiple MCEs, the MME should filter the distribution of MBMS Session Update Request messages to the MCEs based on the MBMS service area.
For UTRAN, if one or more of the downstream nodes newly added to the MBMS Service Area accepts the Session Update and the proposed IP Multicast and Source address for backbone distribution and the proposed C TEID, the SGSN includes an indication that IP Multicast distribution is accepted in the MBMS Session Update Response message to MBMS GW. If one or more of the downstream nodes newly added to the MBMS Service Area does not accept the proposed IP Multicast and Source address for backbone distribution or the proposed C TEID, the SGSN falls back to normal point-to-point MBMS bearer establishment for these nodes and responds with an MBMS Session Update Response message providing the TEID for bearer plane that the MBMS GW shall use for forwarding the MBMS data. Otherwise if all nodes accept multicast, the SGSN returns the C TEID and the IP Multicast distribution address in the Session Update Response message.
E-UTRAN may respond to Session Update Request after first successful MBMS resources have been set up or released (i.e. Step 7) which indicates to the BMSC that there are resources already available for MBMS data delivery, as shown in Figure 13c-2.
Step 5.
If the E-UTRAN/UTRAN has no MBMS bearer context with the TMGI indicated in the MBMS Session Update Request message, the E-UTRAN/UTRAN creates an MBMS bearer context and sets its state attribute to 'Active' (in UTRAN only). Otherwise the E-UTRAN/UTRAN compare the new service area with the one it has stored in the MBMS Bearer Context and make the corresponding update. Then the E-UTRAN/UTRAN responds the MME/SGSN to confirm the reception of the Session Update Request message. When a cell ID list is included in the Session Start Request, E-UTRAN uses it to determine a set of radio resources to be used for the broadcast. Based on the cell ID list, the set of radio resources selected may be reduced from the full set of resources defined by the MBMS service area. The E-UTRAN ensures that all of its corresponding nodes make the same decision on the reduced set.
For UTRAN, if an RNC newly added to the MBMS Service Area accepts the Session Update and the proposed IP Multicast and Source address for backbone distribution and the proposed C-TEID the RNC sends an MBMS Session Update Response message to SGSN including an indication that IP Multicast distribution is accepted. If an RNC newly added to the MBMS Service Area does not accept the proposed IP Multicast and Source address for backbone distribution (or the proposed C TEID), the RNC falls back to normal point-to-point MBMS bearer establishment.
Step 6.
The MME/SGSN updates the session attributes in its MBMS Bearer Context and responds to the MBMS GW. The SGSN should wait for a response from all UTRAN nodes (until an acceptable duration) if the Service Area has been changed to be able to report to the MBMS GW whether all, part or none of any newly added RNCs have accepted IP multicast distribution and to provide an SGSN IP address and TEID for user plane over Sn if some RNCs did not accept IP multicast distribution. The MME may return a response to the MBMS-GW as soon as the session update request is accepted by one E-UTRAN node.
If the MBMS GW is configured to delay response to the BMSC, MBMS GW waits until step 6 occurs before responding to the BMSC as shown in Figure 13c-2.
Step 7.
The E-UTRAN/UTRAN establishes/releases the radio resources for the transfer of MBMS data to the interested UEs. If the ARP parameter is updated the MCE shall ensure that any necessary changes to radio resources are synchronized across all eNBs in the corresponding MBSFN area. For E-UTRAN the radio resource set up is scheduled using the MBMS data transfer start parameter if it is present, otherwise using the time to MBMS data transfer parameter if it is present. The MBMS data transfer start parameter is not used by UTRAN.
Step 8.
The eNodeBs/RNCs send IP multicast Join or Leave message to the received user plane IP multicast address allocated by the MBMS GW. If multiple MBMS bearers services shares the same IP multicast address, this shall be considered before a Join or Leave message is sent.