TS 22.246
MBMS User Services –
Stage 1
V18.0.1 (PDF)
2024/03 21 p.
V17.0.0
2022/03 20 p.
V16.0.0
2020/06 20 p.
V15.0.0
2018/06 20 p.
V14.0.0
2017/03 20 p.
V13.0.0
2016/01 19 p.
V12.0.0
2014/10 19 p.
V11.0.0
2012/09 19 p.
V10.0.0
2011/04 19 p.
V9.0.0
2009/12 19 p.
V8.5.0
2008/03 19 p.
V7.4.0
2008/12 18 p.
V6.3.0
2006/03 18 p.
- Rapporteur:
- Mr. Bleckert, Peter
Ericsson LM
Content for TS 22.246 Word version: 18.0.1
0 Introduction
1 Scope
2 References
3 Definitions and abbreviations
4 Classification of MBMS User Services
5 High level requirements
6 MBMS User Service requirements
A Use Cases
B Example service scenarios
$ Change history
0 Introduction p. 4
TS 22.146 specifies the multimedia broadcast and multicast service (MBMS) application independent transport service and includes some guidance on application services and bit rates. The present specification defines MBMS User Services that use the capabilities of MBMS. Service related information is defined in this specification to specify requirements in terms of data rates, quality of service requirements, typical volumes of data etc.
MBMS User Services may be delivered to a user at different bit rates and quality of service depending on radio networks and conditions. This technical specification describes service scenarios for MBMS User Services.
In addition scenarios related to security and charging are described providing information for detailed MBMS User Services security and charging mechanisms to be specified. The service scenarios described in this specification are not exhaustive, it is possible that MBMS may be used for services that are not included in this specification. The present specification describes the minimal requirements for interoperability for MBMS based services. This specification establishes a basis which can also be used for future services.
1 Scope p. 5
The present document describes MBMS User Services that use the capabilities of MBMS. Application scenarios including charging, QoS aspects and related service requirements derived from them are described. These scenarios and service requirements can be used as guidance for the design of codecs and bearers.
2 References p. 5
The following documents contain provisions which, through reference in this text, constitute provisions of the present document.
- References are either specific (identified by date of publication, edition number, version number, etc.) or non specific.
- For a specific reference, subsequent revisions do not apply.
- For a non-specific reference, the latest version applies. In the case of a reference to a 3GPP document (including a GSM document), a non-specific reference implicitly refers to the latest version of that document in the same Release as the present document.
[1]
TR 21.905: "Vocabulary for 3GPP specifications".
[2]
TS 22.146: "Multimedia Broadcast/Multicast Service".
[3]
TS 26.140: "Multimedia Messaging Service (MMS): Media formats and Codecs".
[4]
TS 26.134: "Transparent end-to-end Packet-switched Streaming Service (PSS) Protocols and codecs".
→ to date, withdrawn by 3GPP
[5]
→ to date, withdrawn by 3GPP
TS 22.240: "Service requirement for the 3GPP Generic User Profile (GUP)".
[6]
TS 22.242: "Digital Rights Management".
[7]
TS 24.002: "GSM-UMTS Public Land Mobile Network (PLMN) Access Reference Configuration".
3 Definitions and abbreviations p. 5
3.1 Definitions p. 5
For the purposes of the present document, the definitions in TR 21.905 as well as the following definitions apply.
Broadcast service area:
see TS 22.146: "Multimedia Broadcast/Multicast Service".
Local Broadcast Area:
see TS 22.146: "Multimedia Broadcast/Multicast Service".
Broadcast mode:
see TS 22.146: "Multimedia Broadcast/Multicast Service".
Broadcast service:
see TS 22.146: "Multimedia Broadcast/Multicast Service".
Broadcast session:
see TS 22.146: "Multimedia Broadcast/Multicast Service".
MBMS transport service:
A MBMS transport service is either a broadcast service or a multicast service as defined in TS 22.146.
MBMS User Services:
Services that are intended to be delivered to multiple users simultaneously. MBMS User Services use the capabilities of the MBMS application independent transport.
Media types:
a media type refers to one form of presenting information to a user, e.g. voice or fax.
Mobile Station (MS):
see TS 22.146: "Multimedia Broadcast/Multicast Service".
Multicast transmission activation:
see TS 22.146: "Multimedia Broadcast/Multicast Service".
Multicast service area:
see TS 22.146: "Multimedia Broadcast/Multicast Service".
Local multicast area:
see TS 22.146: "Multimedia Broadcast/Multicast Service".
Multicast mode:
see TS 22.146: "Multimedia Broadcast/Multicast Service".
Multicast joining:
see TS 22.146: "Multimedia Broadcast/Multicast Service".
Multicast session:
see TS 22.146: "Multimedia Broadcast/Multicast Service".
Multimedia Broadcast/Multicast Service (MBMS):
see TS 22.146: "Multimedia Broadcast/Multicast Service".
Multicast group:
see TS 22.146: "Multimedia Broadcast/Multicast Service".
Multicast service:
see TS 22.146: "Multimedia Broadcast/Multicast Service".
Multicast subscription:
see TS 22.146: "Multimedia Broadcast/Multicast Service".
Multicast Subscription Group:
see TS 22.146: "Multimedia Broadcast/Multicast Service".
User Equipment:
3.2 Abbreviations p. 6
For the purposes of the present document, the following abbreviations apply:
MBMS
Multimedia Broadcast/Multicast Service
MS
Mobile Station
PSS
Packet-switched Streaming Service
UE
User Equipment
4 Classification of MBMS User Services p. 6
There exist many services and applications that can be provided over the application independent MBMS transport [2]. It is not necessary to standardise specific end user services because the deployment of particular applications and services over the capabilities provided by the 3GPP system is operator specific and outside the scope of standardisation. However, it is possible to classify MBMS User Services according to the method used to distribute these services.
There are four types of MBMS User Service considered within this specification.
- Streaming services A continuous data flow providing a stream of continuous media (i.e. audio and video) is a basic MBMS User Service. Like digital video broadcasting, supplementary information of text and/or still images (static media) is also important. For example, if text includes URLs of some content on the Internet, a user can easily access the content without entering the URL for herself. Still images may also be used for banner images that advertise some product or service. These static media need to be synchronized and displayed with audio/video streams.
- File download services This service delivers binary data (file data) over an MBMS bearer. An MBMS client (i.e. UE) activates an appropriate application, and utilises the delivered data. The most important functionality for this service is reliability. In other words, it is necessary that the user receive all the data sent in order to experience the service.
- Carousel services Carousel is a service that combines aspects of both the Streaming and File download services described above. Similar to the streaming service this service includes time synchronisation. However, the target media of this service is only static media (e.g. text and/or still images). Time synchronization with other media is also required. For example, text objects are delivered and updated from time to time. Still images may also be collated to display low frame-rate video. In common with the download service this service also includes reliability (typically 100% reliability is not always necessary). The benefit of this service is that it is possible over a low bit-rate bearer. An example of an application utilising the Carousel service is a 'ticker-tape' type service in which the data is provided to the user repetitively and updated at certain times to reflect changing circumstances.
- Television (TV) service The Television service is an MBMS service consisting of synchronised streaming audio and visual components.
5 High level requirements p. 7
5.0 General p. 7
MBMS user services are services an operator may provide to subscribers. MBMS user services use the capabilities of MBMS. The operator may provide such services on his own or in collaboration with third party service providers. In addition, an MBMS user service may be provided to the operator's own subscribers and/or to inbound roaming subscribers from other operators.
MBMS User Services
MBMS user services are based on broadcast- or multicast services, which are defined in TS 22.146.
MBMS user services shall be bearer agnostic to enable access via generic IP access systems.
An MBMS user service may use one or more broadcast- or multicast services at a time within the MBMS service area bound to this user service.
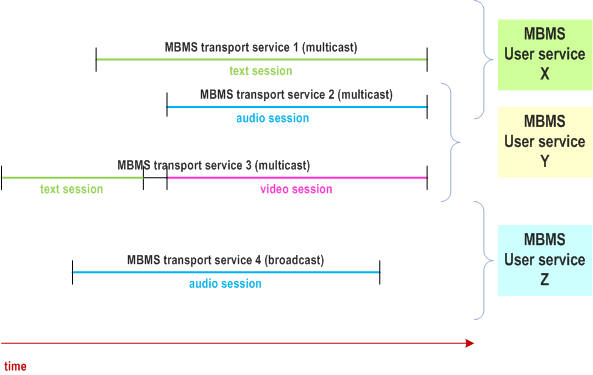 It shall be possible for an MBMS user service to make use of different application independent MBMS transport services at different times or in parallel. The MBMS transport services used may vary for instance in QoS parameters or target broadcast or multicast area.
It shall be possible for one application independent MBMS transport service to be used by more than one MBMS user service at a time.
If an MBMS user service makes use of several application independent MBMS transport services then these may only consist of either broadcast or multicast services, but not of a combination of both.
When necessary, within a single MBMS user service, it shall be possible to synchronize the media sessions.
The UTRAN, GERAN and E-UTRAN accesses shall provide protection against normal transmission errors (eg interference not related to cell changes and handovers).
Non 3GPP access system used to transport MBMS user services should provide protection against normal transmission errors (e.g. interference not related to cell changes and handovers).
The BM-SC is responsible for providing protection e.g. FEC, long interleaving and/or point to point repairing the transmission, against errors (eg those caused by cell changes and longer breaks in transmission).
Service examples
MBMS user services may be classified according to the table within Annex A of this specification into several service examples, which are characterized by
MBMS user services may be provided for many purposes to the user and may convey information of various kinds. E.g. some services may be used for traffic information, others for entertainment or for news services. Service classes denote a classification of MBMS user services according to their usage. However, service class values are not in the scope of 3GPP standardisation but may be subject of inter-operator service arrangements.
It shall be possible for an MBMS user service to make use of different application independent MBMS transport services at different times or in parallel. The MBMS transport services used may vary for instance in QoS parameters or target broadcast or multicast area.
It shall be possible for one application independent MBMS transport service to be used by more than one MBMS user service at a time.
If an MBMS user service makes use of several application independent MBMS transport services then these may only consist of either broadcast or multicast services, but not of a combination of both.
When necessary, within a single MBMS user service, it shall be possible to synchronize the media sessions.
The UTRAN, GERAN and E-UTRAN accesses shall provide protection against normal transmission errors (eg interference not related to cell changes and handovers).
Non 3GPP access system used to transport MBMS user services should provide protection against normal transmission errors (e.g. interference not related to cell changes and handovers).
The BM-SC is responsible for providing protection e.g. FEC, long interleaving and/or point to point repairing the transmission, against errors (eg those caused by cell changes and longer breaks in transmission).
Service examples
MBMS user services may be classified according to the table within Annex A of this specification into several service examples, which are characterized by
MBMS user services may be provided for many purposes to the user and may convey information of various kinds. E.g. some services may be used for traffic information, others for entertainment or for news services. Service classes denote a classification of MBMS user services according to their usage. However, service class values are not in the scope of 3GPP standardisation but may be subject of inter-operator service arrangements.

- Their predominant broadcast- or multicast service, that constitutes this MBMS user service together with its reliability (QoS) and data transfer rate requirements
- Media types that are transmitted via this broadcast- or multicast service
- Type of the service, which implies handling of the distributed media by the UE (e.g. download for subsequent presentation, streaming for instant presentation or carousel downloading)
- Charging characteristics
- A potential requirement for point-to-point delivery verification for delivered content.
5.1 Common requirements to broadcast and multicast p. 9
The following list describes requirements on an application level:
-
Service classes
In case of roaming a user shall be able to enjoy services as follows:
- A user shall be able to activate services that are provided locally in the visited network, as allowed by the user's home environment (e.g. local tourist information).
- A user subscribed to a service class in the HPLMN shall be able to enjoy equivalent services in the same service class as provided by a visited PLMN without explicit subscription in the VPLMN (e.g. weather forecast).
- Service Interworking The user shall be able to manipulate content delivered over MBMS and forward it using other services (e.g. MMS, Speech Call- and IMS signalling, Hyperlinks, …). Care should be taken in order to fulfil requirements concerning DRM and respective barring and charging capabilities. When interacting with user profiles, MBMS User Services shall use the mechanisms described in TS 22.240 (Generic User Profile).
- Content storage in the UE It shall be possible for the UE to store content delivered to it over MBMS and provide it to the user at a later time. Care should be taken in order to fulfil requirements concerning DRM and respective charging capabilities.
-
Data formats and types
Media types shall be supported independent of specific data types and formats behind..
As a minimum MBMS User Services shall support the following media types:
- Text It shall be possible to embed hyperlinks and to decorate text within content provided by MBMS User Services.
- Still Images
- Video
- Speech
- Mono/Stereo Audio
- Digital Rights Management The MBMS User Service shall be able to control content distribution as defined in TS 22.242. MBMS content providers shall be able to invoke DRM to prevent unauthorized copying and forwarding of content.
- Notification of required capabilities The capabilities (e.g. memory size) required to receive a particular transmission shall be notified in advance by the network or service centre.
- MBMS Television Service It shall be possible for a user to select between different content within the MBMS Television Service. The MBMS service shall add no more than 1 second when switching between different TV streams to any delay introduced with regards to the coding of the TV stream. It shall be possible for an operator to configure the MBMS Television service so that the typical switching time, from the end user's perspective, does not exceed 2 seconds. Handover within the same radio access technology shall be transparent to the user. Handover between different radio access technologies should be performed without any user perceived interruption.
5.2 Interoperability p. 10
MBMS User Services shall ensure service interoperability with respect to media formats and codecs, at the same time being able to re-use existing multimedia capabilities in the UE as far as possible.
Therefore MBMS User Services shall support a minimum set of media formats and codecs. This minimum set should be aligned with the set of media formats and codecs required for MMS [3] and PSS [4].
5.2a Pre-Delivery verification p. 10
It is required that the operator can verify the number of active MBMS users when service commences.
The UE shall provide a secure means to inform the network of the start of services by pre-delivery verification transmitted over a point-to-point connection to the home/visited network. This pre-delivery verification may be relayed to the service provider. The pre-delivery verification shall also support the carriage of bearer specific non-real time information, i.e. previously stored in the UE, to the BM-SC. Such bearer specific information may, for example, include historic C/I measurements for the serving cell.
It should be noted that pre-delivery verification by point-to-point mechanisms partially reduces the resource-efficiency of the underlying broadcast services. Sacrificing resource-efficiency due to requirements of UE reporting may be necessary but should be kept as minimal as possible to minimize congestion.
5.3 Delivery verification p. 11
For some MBMS user services it is required that the operator can verify that the content conveyed by the service has been received by the UE.
The UE shall provide a secure means to provide such delivery verification transmitted over a point-to-point connection to the home/visited network. This delivery verification may be relayed to the service provider.
The delivery verification shall also support the carriage of bearer specific non-real time information, i.e. previously stored in the UE, to the BM-SC. Such bearer specific information may, for example, include historic C/I measurements for the serving cell.
It should be noted that delivery verification by point-to-point mechanisms partially reduces the resource-efficiency of the underlying broadcast services. Sacrificing resource-efficiency due to requirements of UE reporting may be necessary but should be kept as minimal as possible to minimize congestion.
6 MBMS User Service requirements p. 11
6.1 Charging p. 11
The MBMS User Service shall support standardized mechanisms to transfer charging related information.
It shall be possible to charge for MBMS content the user receives while roaming in a VPLMN.
As indicated in Annex A some services will require an indication that MBMS content has been received. Therefore it shall be possible for the UE to provide such an indication.
The MBMS User Service shall support the following charging mechanisms :
- Charging on a subscription basis
- Charging for keys that that allow the user access to the data
6.2 Security p. 11
The following security aspects shall be taken into account:
Any user modifiable MBMS service data (e.g. storage of deliveries in the UE, data type and format specific behaviours etc) shall only be modified by the authenticated user (see also 4.1.1 above).
6.3 Privacy p. 11
Third parties and VASP should not be aware about user IDs for MBMS subscriptions unless explicitly allowed by the operator.
6.4 Quality of service p. 11
It should be possible for the operator to collect statistical data such as lost frames, assigned resources, bit-rates achieved etc.
It shall be possible for the operator to adapt the distribution of a MBMS user service consisting of different MBMS transport services to provide multiple QoS levels according to the QoS resources provided by the access network(s), while maintaining the resource efficiency of the underlying MBMS transport services.
It shall be possible to base the adaptation of the distribution of a MBMS user service to the QoS resources provided by the access network(s) on:
- the QoS resources within the same access network (e.g. UTRAN).
- the QoS resources provided by different access networks (e.g. UTRAN and GERAN).
6.5 Subscription p. 12
During the lifetime of subscription to a Multicast Service it shall be possible for the user to declare the service preferences. It shall be possible for the network to store the user settings e.g. using GUP.
6.6 Availability p. 12
The user should be able to receive MBMS user services via generic IP access systems.
A Use Cases p. 13
| Service Example | Media | Distribution Scope | MBMS User Service Classification | ApplicationBit rate (Note 1) | Delivery Verification Required (Note 3) | User Charging (Note 4) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reliable text distribution (eg Local news) | Text | Multicast | Download | Up to 10 kbps | Yes | Event |
| Unverified text distribution | Text | Multicast, Broadcast | Carousel, download | Up to 10 kbps | No | - |
| Text distribution with still images and/or low quality video | Text, Still images, Video (e.g. 3fps) | Multicast, Broadcast | Carousel, download | Up to 32 kbps | Service dependent | User service dependent (Note 2) |
| Audio streaming | Stereo Audio | Multicast | Streaming | Up to 48kbps | Service dependent | - |
| Audio streaming | Stereo Audio | Broadcast | Streaming | Up to 48kbps | No | - |
| Audio download | Stereo Audio | Broadcast | Download | Up to 48kbps | Service dependent | - |
| Audio download | Stereo Audio | Multicast | Download | Up to 48kbps | Yes | Event |
| Audio distribution with low quality video | Stereo Audio, Video (e.g. 3fps) | Broadcast | Streaming | Up to 128kbps (Note 5) | No | - |
| Audio distribution with low quality video | Stereo Audio, Video (e.g. 3fps) | Multicast | Streaming | Up to 128kbps (Note 5) | Service dependent | - |
| Audio distribution with low quality video | Stereo Audio, Video (e.g. 3fps) | Broadcast | Download | Up to 128kbps (Note 5) | Service dependent | - |
| Audio distribution with low quality video | Stereo Audio, Video (e.g. 3fps) | Multicast | Download | Up to 128kbps (Note 5) | Yes | Event |
| Video streaming | Video & supplementary data (e.g. text, still images) | Broadcast | Streaming | Up to 384 kbps (Note 5) | No | - |
| Video streaming | Video & supplementary data (e.g. text, still images) | Multicast | Streaming | Up to 384 kbps (Note 5) | Service dependent | - |
| Video distribution | Video & supplementary data (e.g. text, still images) | Broadcast | Download | Up to 384 kbps (Note 5) | Service dependent | - |
| Video distribution | Video & supplementary data (e.g. text, still images) | Multicast | Download | Up to 384 kbps (Note 5) | Yes | Event |
| General Content Distribution | Video, Audio, File Data (binary data) | Broadcast | Carousel, download | Up to 384 kbps (Note 5) | Service dependent | - |
| General Content Distribution | Video, Audio, File Data (binary data) | Multicast | Carousel, download | Up to 384 kbps (Note 5) | Yes | Event |
| Secure data download | File; eg UE type specific and/or application specific software | Multicast | Carousel, download | Up to 10kbps | - | - |
|
NOTE 1:
Bit rate of the user data at the application layer.
NOTE 2:
If User Charging is Event based then Delivery Verification is required.
NOTE 3:
Delivery Verification relates only to verification itself. Quality assessments may be required in addition.
NOTE 4:
DRM may be applicable to User Charging.
NOTE 5:
For GERAN lower bandwidth availability may constrain some applications. In such cases it may be possible to provide the same content via different delivery methods.
NOTE 6:
The ' - ' mark indicates that no applicable information has been identified.
|
||||||
B Example service scenarios p. 15
This annex provides a non-exhaustive list of potential service scenarios for MBMS User Services.
B.1 Text notification service p. 15
Media:
Text
Precondition:
The user is a member of a MBMS Multicast group supplying text alerts.
Actions:
At an appropriate time an alert is sent to the user's mobile handset using the MBMS Multicast service.
Post condition:
The user receives the alert using her mobile handset and takes appropriate action.
B.2 Local Area Information distribution (Case A) p. 15
Media:
Text & Text with low quality video
Precondition:
The user is a registered with an MBMS Broadcast service providing information to the local area such as local news and weather reports.
Actions:
Information in the form of text & text with low quality video is distributed to the user's mobile handset by the MBMS Broadcast service. The text may be scrolled on the mobile handset. The information distributed by the MBMS Broadcast Service may be repeated periodically and updated at appropriate intervals.
Post condition:
The user is aware of events that have taken place within the local area and can view appropriate images.
B.3 Local Area Information distribution (Case B) p. 15
Media:
Video & Audio
Precondition:
The user is a registered with an MBMS Broadcast service providing streaming audio and/or visual content related to a local area, such as audio and visual guides to local attractions, traffic reports etc…
Actions:
Audio and/or visual information is distributed to the user's mobile handset by the MBMS Broadcast service. The user is able experience the content on her mobile device. The user is able to receive the MBMS broadcast service continuously throughout the local area. At some points the user is able to interact with the content of the MBMS Broadcast service in order to access specific information regarding items being presented within the content. The user is able to activate/deactivate reception of the MBMS service at any time.
Post condition:
The user experiences and interacts with the content provided and is therefore able to obtain information regarding the local area and act accordingly.
B.4 Multicast distribution p. 15
Media:
Text & Text with still images
Precondition:
The user is a member if a MBMS multicast group providing personally tailored content such as targeted advertising etc…
Actions:
Information is provided by the MBMS Multicast service in the form of text & text with still images, to the user's mobile handset based on her subscription to the Multicast group and current location.
Post condition:
The user receives tailored content and is able to utilize this as appropriate.
B.5 Audio Distribution p. 16
Media:
Stereo Audio
Precondition:
The user is registered with an MBMS Broadcast service providing stereo quality streaming audio content.
Actions:
Audio content is distributed to the user's mobile handset by the MBMS Broadcast service. Whilst listening to the audio content the user is able to interact with the service using the capabilities of the mobile handset (e.g. messaging).
Post condition:
The user is able to enjoy the stereo quality audio content and interacts with the service as appropriate.
B.6 General Content Distribution p. 16
Media:
Video, Audio & File Data
Precondition:
The user is registered with a MBMS Broadcast service providing a variety of content.
Actions:
Content is periodically distributed to a particular area by the MBMS Broadcast service. When the user activates reception of the MBMS Broadcast service she is able to receive the content being distributed at that time.
Post condition:
The user is able to receive and enjoy the content being distributed.
B.7 Software Download p. 16
Media:
File
Preconditions:
Need to update/download software in UE, the User is subscribed to MBMS User Service, OTA download is supported in UE
Actions:
The operator compiles a list of affected users and sends them a text message (using MBMS) explaining the problem and that the user should select the MBMS application on their handset. The user sees a message inviting her to activate the Enable Upgrade, selects 'yes' and the software patch transferred by the MBMS User Service, including verification parameters.
Postcondition:
The software once installed allows the user to view the MMs that she couldn't see before.