Content for TS 23.216 Word version: 18.0.0
6.4 CS to PS SRVCC
6.4.1 GPRS Attach procedure for SRVCC
6.4.2 E-UTRAN Attach procedure for SRVCC
6.4.3 Call flows for SRVCC to E-UTRAN/UTRAN (HSPA)
6.4.3.1 SRVCC to E-UTRAN/UTRAN (HSPA) from GERAN without DTM/PS HO support
6.4.3.2 SRVCC to E-UTRAN/UTRAN (HSPA) from GERAN with DTM support but without DTM HO support and SRVCC to E-UTRAN from UTRAN without PS HO support
6.4.3.3 SRVCC to E-UTRAN/UTRAN (HSPA) with DTM/PS HO support
...
...
6.4 CS to PS SRVCC |R11| p. 61
6.4.1 GPRS Attach procedure for SRVCC p. 61
GPRS attach procedure is performed as follows:
- If the subscriber is allowed to have CS to PS SRVCC, the HSS shall include the "CS to PS SRVCC allowed" indication in the Insert Subscriber Data sent to the MSC Server. The "CS to PS SRVCC allowed" indication may be specific for each VPLMN.
6.4.2 E-UTRAN Attach procedure for SRVCC p. 61
E-UTRAN attach procedure for 3GPP CS to PS SRVCC UE is performed as defined in TS 23.401.
6.4.3 Call flows for SRVCC to E-UTRAN/UTRAN (HSPA) p. 61
6.4.3.1 SRVCC to E-UTRAN/UTRAN (HSPA) from GERAN without DTM/PS HO support p. 61
Depicted in Figure 6.4.3.1-1 is an overview call flow for SRVCC to E-UTRAN/UTRAN (HSPA) from GERAN without DTM/PS HO support. The flow is based on the assumption that the source is GERAN without DTM/PS HO support or that the UE is without DTM/PS HO support and that all PS bearers are suspended.
The CS to PS SRVCC procedure will only be successfully performed under the following conditions:
- the UE has indicated to be CS to PS capable,
- the CS to PS allowed indication was part of the subscriber data received from HSS,
- the UE is IMS registered; and
- the UE has at least one PS bearer (usable for SIP signalling).
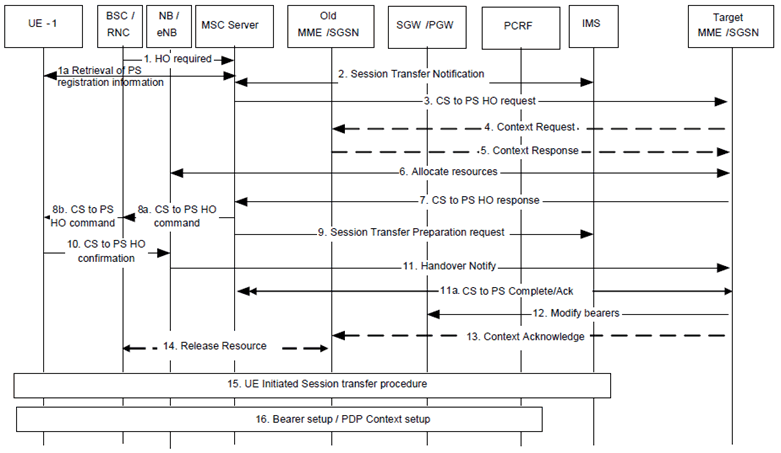
Figure 6.4.3.1-1: SRVCC to E-UTRAN/UTRAN (HSPA) from GERAN without DTM / PS HO and SRVCC to E-UTRAN from UTRAN
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
Step 1.
The RNC/BSC sends a HO required to the MSC Server including an indication this HO is for CS to PS. If an inter-MSC CS HO has occurred prior to the CS to PS HO procedure, the MSC Server forwards the HO required to the anchor MSC Server.
Step 1a.
The MSC retrieves P-TMSI+RAI+P-TMSI signature or GUTI from the UE.
Step 2.
The MSC Server sends an Session Transfer Notification to IMS, which indicates that IMS should prepare for the transfer of media to PS. IMS allocates media ports in the network for the transfer. The media ports and codec information allocated by IMS are provided to the MSC Server in the response message
Step 3.
The MSC Server selects the target MME/SGSN based on Target ID contained in the HO required and sends a SRVCC CS to PS HO request to the target MME/SGSN. If required, the IMSI is provided for identifying the UE, and the GUTI or P-TMSI, P-TMSI signature and RAI as provided by the UE (see clause 5.3.4.3) are provided to the target MME/SGSN.
Step 4.
If the target MME/SGSN has no UE context it sends Context Request using GUTI or P-TMSI, P-TMSI signature and RAI to find the old MME/SGSN.
Step 5.
The old MME/SGSN responds with Context Response message including all UE contexts.
Step 6.
The target MME/SGSN allocates resources for all PS bearers in E-UTRAN or UTRAN (HSPA). The target MME/SGSN determines if the Serving-GW is to be relocated, e.g. due to PLMN change.
Step 7.
A SRVCC CS to PS HO response is returned from the target MME/SGSN to the MSC Server.
Step 8.
MSC Server sends CS to PS command to the RAN, possibly via the target MSC, and the RAN send HO command to UE, indicating CS to PS handover. The MSC Server also includes in that message the IP address/ports and selected codec for the IMS media anchoring.
Step 9.
A Session Transfer Preparation Request is sent to IMS to trigger IMS to have the media path switched to the IP address/port of the UE on the target access.
Step 10.
The UE sends Handover confirmation to the eNodeB/NodeB.
Step 11.
The eNodeB send Handover Notify to the MME/SGSN.
Step 11a.
The MME/SGSN sends a SRVCC CS to PS Complete Notification message to the MSC Server to confirm the completion of the handover. The source MSC Server acknowledges the information by sending a SRVCC CS to PS Complete Acknowledge message to the MME/SGSN. When receiving the SRVCC CS to PS Complete Notification message, the MSC Server may release the local resource toward the BSS/RAN but not for the resources toward IMS (i.e. will not send any session release towards IMS).
Step 12.
The MME/S4-SGSN sends Modify Bearer Request to the SGW, which may be forwarded to the PGW to update PS bearer contexts according to IRAT HO procedure as specified in TS 23.401. At this stage the user plane path is established for all bearers between the UE, target eNodeB/NodeB, Serving-GW (for Serving-GW relocation this will be the Target Serving-GW) and PDN-GW and the voice session may continue temporarily on the default bearer until the dedicated bearer has been setup.
In this procedure, the MME/SGSN includes the CS to PS SRVCC indication. When dynamic PCC is deployed and PCRF has subscribed to the corresponding event as specified in TS 23.203, the CS to PS indication is provided to the PCRF. This causes PCRF to make policy decisions to permit traffic towards the ATGW on the default bearer. Otherwise, when GTP is used, the PGW can install the filters locally to allow the default bearer to temporarily permit traffic towards the configured ATGWs.
Step 13.
If the target MME/SGSN has received Context Response from the old SGSN/MME, the target MME/SGSN sends the Context Acknowledge to the Context Response to the old SGSN/MME. A timer in the old SGSN is started to supervise when resources in the old BSC/RNC and the old Serving-GW (for Serving-GW relocation) shall be released according to IRAT HO procedure as specified in TS 23.401.
Step 14.
When the timer at the old SGSN started in step 13 expires, the old SGSN will clean-up all its resources towards old BSC/RNC if the UE is Iu/Gb Connected.
Step 15.
The UE initiates the Session transfer procedures according to TS 23.237.
Step 16.
As a result of the Session transfer procedures, the setup of a dedicated bearer or PDP Context for voice is performed according to the dedicated bearer/PDP Context activation procedure as specified in TS 23.401 or TS 23.060. After the setup of a dedicated bearer for voice and the respective filters in UE and PGW, the default bearer is not longer used for voice media and the PCRF revert any policy decision made in step 12 for the purpose of CS to PS SRVCC procedures.
6.4.3.2 SRVCC to E-UTRAN/UTRAN (HSPA) from GERAN with DTM support but without DTM HO support and SRVCC to E-UTRAN from UTRAN without PS HO support p. 64
The call flow for this scenario is similar to the call flow depicted in Figure 6.4.3.1-1, except that the old PS node in this case is an SGSN and step 4 is performed towards the old SGSN which is in the same routing area as the BSC/RNC. The target MME/SGSN shall send Context Request using P-TMSI and RAI to find the old SGSN to obtain the bearer contexts of the UE.
6.4.3.3 SRVCC to E-UTRAN/UTRAN (HSPA) with DTM/PS HO support p. 64
The call flow for this scenario is similar to the call flow depicted in Figure 6.4.3.1-1, with the clarification that the BSC/RNC shall only send CS to PS HO required to MSC Server when CS to PS HO is supposed to be triggered. The PS to PS HO required shall not be sent to the old SGSN. Hence, no PS HO signalling is initiated. The target MME/SGSN shall send Context Request using P-TMSI and RAI to find the old SGSN to obtain the bearer contexts of the UE.