Content for TR 22.826 Word version: 17.2.0
6 Security Aspects
6.1 Introduction
6.2 Actors and Responsibilities
6.3 Potential Requirements
7 Consolidated potential requirements
7.1 Security requirements
7.2 Network services performance requirements
7.3 Clock synchronization requirements
8 Conclusion and recommendations
A Security Considerations
$ Change history
6 Security Aspects p. 51
6.1 Introduction p. 51
The healthcare industry is currently undergoing many changes, not only in medicine but also in the information technology that serves as the underpinning of healthcare delivery. In fact, advancement in IT and electronic health records (EHRs), as well as reinforcement of professional collaboration (mentoring) and of telemedicine is leading to numerous new complexities. Electronic information is everywhere, often in more than one place at a time, and shall be accessed from everywhere thus making increasingly difficult to keep sensitive healthcare information well protected.
This has led regulatory bodies in every part of the world to iron out new regulatory texts which businesses in the healthcare industry shall be compliant with. Among them, one can cite the following regulations that already cover a broad range of rules impacting the privacy and security of healthcare data. e.g.:
A strong underlying principle in those regulations, is that natural persons, whatever their nationality or residence, have fundamental rights and freedoms, in particular the right to the protection of their personal data.
A good level of protection is provided when privacy is ensured by design or default, meaning that data protection measures are implemented across all data processing activities and endpoints and in accordance to the level of criticality of that data. As an example, "medical health," "genetic data" and "biometric data" are subject to a higher standard of protection than personal data in general.
Then, security traditionally includes the attributes of "Confidentiality", "Integrity" and "Availability" but recently has been also focused on "Auditability" to demonstrate to regulators that patient safety and privacy is maintained throughout entire processing and transporting chain. Compliance and regulatory expectations demand that data access and transfer be therefore well defined and documented.
6.2 Actors and Responsibilities p. 51
In the field of data security, the following roles are often defined:
- Controllers: natural or legal person that is responsible for handling the whole data life cycle and will have to establish or amend technical and organizational measures to ensure and prove that the processing of personal data fully complies with regulatory requirements. In practise, controllers can be e.g. hospitals, health houses or physicians…
- Processors: natural or legal person that processes medical data. A processor is required to maintain records of all its processing activities and to maintain disclosure readiness of this information to show compliance. A processor could be for instance a cloud provider offering services to a controller for data storage and processing.
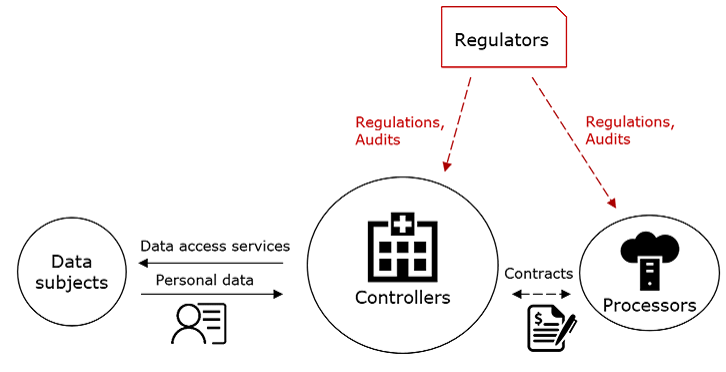
For more information on general data requirements from regulatory bodies, see Annex A.
6.3 Potential Requirements p. 52
6.3.1 Existing features partly or fully covering the functionality p. 52
| Reference number | Requirement text | Application / Transport | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|
| 8.9 | The 5G system shall support data integrity protection and confidentiality methods that serve URLLC and energy constrained devices. | T | Requirement taken from TS 22.261, however need to add "high data rates" to the requirement text. |
| 8.2, 8.3 | All requirements related to security management in private slices | T | See TS 22.261 |
6.3.2 Potential New Requirements p. 52
| Reference number | Requirement text | Application / Transport | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|
| 6.3.3-1 | The 5G system shall support security self-assessment of network functions involved in rendering communication services in order to detect malicious cyber activity or compromised systems in the operator's network. | T | |
| 6.3.3-2 | The 5G system shall provide suitable APIs to allow an authorized third party to consult security related metrics for the network slices dedicated to that third party, and any report on security breach or malicious activity that would have been self-detected. | T | |
| 6.3.3-3 | The 5G system shall allow the operator to authorize a 3rd party to create and modify network slices having appropriate security policies (e.g. user data privacy handling, slices isolation, enhanced logging …) subject to an agreement between the 3rd party and the network operator. | T |
7 Consolidated potential requirements p. 53
7.1 Security requirements p. 53
[7.1-1]
The 5G system shall provide suitable means to allow use of a trusted and authorized 3rd party provided integrity protection mechanism for data exchanged between an authorized UE served by a private slice and a core network entity in that private slice.
[7.1-2]
The 5G system shall provide suitable means to allow use of a trusted and authorized 3rd party provided integrity protection mechanism for data exchanged between an authorized UE served by a non-public network and a core network entity in that non-public network.
[7.1-3]
Based on operator policy, a 5G network shall provide suitable means to allow a trusted and authorized 3rd party to create and modify network slices used for the 3rd party with appropriate security policies (e.g. user data privacy handling, slices isolation, enhanced logging…).
[7.1-4]
Based on operator policy, the 5G system shall provide suitable means to allow a trusted and authorized 3rd party to consult security related logging information for the network slices dedicated to that 3rd party.
[7.1-5]
The 5G system shall support data integrity protection and confidentiality methods that serve URLLC, high data rates and energy constrained devices.
7.2 Network services performance requirements p. 54
| Requirement | Characteristic parameter | Influence quantity | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Communication service availability: target value in % | Communication service reliability: Mean Time Between Failure | End-to-end latency: maximum | Bit rate | Direction | Message Size [byte] | Survival time | UE speed | # of active UEs | Service Area | |
| 5.2.2 - 8K 120 fps HDR 10bits real-time video stream with lossless compression 5.2.3 - 4K 120 fps HDR 10bits real-time video stream with lossless compression | >99.99999 | >1 year | <1 ms | <50 Gbit/s | UE to Network | ~1500 - ~9000 (note 1) | ~8ms | stationary | 1 | Room |
| 5.2.4 - Stereoscopic 4K 120 fps HDR 10bits real-time video stream with lossless compression | >99.99999 | >1 year | <2 ms | <24 Gbit/s (note 2) | Network to UE; UE to Network | ~1500 - ~9000 (note 1) | ~8ms | stationary | 1 | Room |
| 5.2.2 - 8K 120 fps HDR 10bits real-time video stream with lossless compression 5.2.3 - 4K 120 fps HDR 10bits real-time video stream with lossless compression 5.2.4 - 4K 120 fps HDR 10bits real-time video stream with lossless compression | >99.99999 | >1 year | <1 ms | <50 Gbit/s | Network to UEs | ~1500 - ~9000 (note 1) | ~8ms | stationary | <10 | Room |
| 5.2.3 3D 256 x 256 x 256 voxels 24 bits 10 fps ultrasound unicast data stream | >99.9999 | >1 year | <10ms | <4 Gbit/s | UE to Network | ~1500 | ~100 ms | stationary | 1 | Room |
| 5.2.4 - Motion control data stream | >99.999999 | >10 year | <2 ms | <16 Mbit/s | Network to UE; UE to Network | <2000 | ~1 ms | Stationary | 1 | Room |
| 5.2.4 - Haptic feedback data stream | >99.999999 | >10 year | <2 ms | <16 Mbit/s | Network to UE; UE to Network | <2000 | ~1 ms | Stationary | 1 | Room |
|
NOTE 1:
MTU size of 1500 bytes is not generally suitable to gigabits connections as it induces many interruptions and loads on CPUs. On the other hand, Ethernet jumbo frames of up to 9000 bytes require all equipment on the forwarding path to support that size in order to avoid fragmentation.
NOTE 2:
No subsampling considered for the generation of the stereoscopic view
|
||||||||||
| Requirement | Characteristic parameter | Influence quantity | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Communication service availability: target value in % | Communication service reliability: Mean Time Between Failure | End-to-end latency: maximum | Bit rate | Direction | Message Size [byte] | Survival time | UE speed | # of active UEs | Service Area | |
| 5.3.2 - Compressed 4K (3840x2160 pixels) 60 fps 12 bits per pixel color coded (e.g. YUV 4:1:1) real-time video stream 5.3.4 - Compressed 4K video stream | >99.99 | >1 month | <20 ms | <25 Mbit/s | UE to Network; Network to UE | ~1500 | ~100 ms | stationary | <20 per 100 km2 | Regional |
| 5.3.2 - Uncompressed 512x512 pixels 32 bits 20 fps video stream from ultra-sound probe 5.3.4 - Uncompressed 512x512 pixels 32 bits 20 fps video stream from ultra-sound probe | 99.999 | >>1 month (<1 year) | <20 ms | 160 Mbits/s | UE to Network | ~1500 | ~50 ms | stationary | <20 per 100 km2 | Regional |
| 5.3.3 - Stereoscopic 4K 60 fps HDR 10bits frame packed real time video (loss less compressed) 5.3.4 - Stereoscopic 4K 60 fps 12 bits per pixel color coded (e.g. YUV 4:1:1) real time video (loss less compressed) | 99.99 - 99.9999 (note 2) | >1 month (<1 year) (note 2) | < 250 ms | <6 Gbit/s | Network to UE; UE to Network | ~1500 - ~9000 (note 1) | ~16 ms | stationary | <20 per 100 km2 | National; Regional |
| 5.3.3 - 4K 60 fps 12 bits per pixel color coded (e.g. YUV 4:1:1) real time video (loss less compressed) | >99.999 | >>1 month (<1 year) | < 250 ms | <2 Gbit/s | Network to UEs | ~1500 - ~9000 (note 1) | ~16 ms | stationary | <5 per 100m2 (note 3) | National |
| 5.3.3 - Haptic feedback 5.3.4 - Haptic feedback data stream | >99.9999 | > 1 year | <20 ms | <16 Mbit/s | Network to UE; UE to Network | <2000 | ~1 ms | stationary | <20 per 100 km2 | National; Regional |
|
NOTE 1:
MTU size of 1500 bytes is not generally suitable to gigabits connections as it induces many interruptions and loads on CPUs. On the other hand, Ethernet jumbo frames of up to 9000 bytes require all equipment on the forwarding path to support that size in order to avoid fragmentation.
NOTE 2:
Higher values are needed for telesurgery systems.
NOTE 3:
This comprises a maximum of 5 displays gathered in the same 100m2 room considering a room density <2 per 1000km2
|
||||||||||
| Requirement | Characteristic parameter | Influence quantity | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Communication service availability: target value in % | Communication service reliability: Mean Time Between Failure | End-to-end latency: maximum | Bit rate | Direction | Message Size [byte] | Survival time | UE speed | # of active UEs | Service Area | |
| 5.5.2 - Uncompressed 2048x2048 pixels 16 bits per pixel 10 fps real-time video scan stream | 99.99 | >>1 month (<1 year) | < 100ms | 670 Mbit/s | UE to Network | ~1500 | <100 ms | <150 | <20 per 100 km2 | Regional |
| 5.5.2 - Compressed 4K (3840x2160 pixels) 12 bits per pixel (e.g. YV12) 60 fps real time video stream | 99.99 | >1 month | < 100ms | 25 Mbits/s | UE to Network | ~1500 | <100 ms | <150 | <20 per 100 km2 | Regional |
| 5.5.2 - Physical vital signs monitoring data stream | >99.999 | >>1 month (<1 year) | <100 ms | <1 Mbit/s | UE to Network | ~80 | - | <150 | <20 per 100 km2 | Regional |
| 5.5.2 - High quality audio stream | >99.99 | >1 month | <100 ms | <128 kbit/s | Network to UE; UE to Network | ~300 | ~16 ms | <150 | <20 per 100 km2 | Regional |
| 5.5.3 - Cardiac telemetry outside the hospital (note 2) | >99.9999 | <1 year (>>1 month) | <100 ms | 0.5 Mbit/s | UEs to Network | <1000 | <1 s | <500 | 10/km2 - 1000/km2 | Country wide including rural areas; Deep Indoor (note 1) |
|
NOTE 1:
In this context, "deep indoor" term is meant to be places like e.g. elevators, building's basement, underground parking lot, …
NOTE 2:
These performance requirements aim energy-efficient transmissions performed using a device powered with a 3.3V battery of capacity <1000 mAh that can last at least 1 month without recharging and whereby the peak current for transmit operations stays below 50 mA.
|
||||||||||
7.3 Clock synchronization requirements p. 57
| Use case reference | Number of devices for clock synchronisation | Clock synchronicity requirement | Service area |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5.3.3 - Communication QoS requirement for robotic telesurgery | Up to 10 UEs | < 50 μs | 400 km |
8 Conclusion and recommendations p. 58
The current TR provides a number of use cases for communication services related to critical medical applications in the following categories:
Image Assisted Surgery inside hybrid operating rooms equipped with high quality and augmented imaging systems
Robotic Aided Surgery inside hybrid operating rooms or in remote medical facilities
Tele-diagnosis and monitoring in ambulances, hospitals or remote healthcare facilities
For the above listed areas, the document identifies potential performances requirements for 3GPP communication systems involved in the delivery of care or surgery to patients so that considered medical procedures are carried out with adequate level of safety and efficiency.
In addition, the document also proposes potential requirements needed to ensure handling of medical related data in 3GPP communication systems while fulfilling confidentiality, integrity and auditability principles set forth in regulatory texts.
It is proposed that those requirements are considered for development of normative requirements.
A Security Considerations p. 59
A.1 Regulatory texts' analysis p. 59
As a general rule, organizations involved in controlling and/or processing the data have to be careful with the data and exact in knowing where it is being stored, how it is being processed and whether consent has been given. Parsing national regulations along those lines for general data management requirements in light of the role models explained in clause 6.2, leads to the following mapping of high-level requirements on the involved actors.
| Requirements | Controllers | Processors | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Explicit Consent: data subjects to explicitly give their consent (declaratory statement or opt-in tick box) for processing their medical, genetic or biometric data | X | ||
| Right to Data Portability: data subjects to have their personal data sent back to them to transmit elsewhere more easily | X | ||
| Right to Be Forgotten: data subjects to have their personal data erased without undue delay | X | ||
| Right to rectification: data subjects to obtain from the controller without undue delay the rectification of inaccurate personal data concerning him or her | X | ||
| Right to restriction of processing: data subjects to obtain from the controller restriction of processing under certain circumstances | X | ||
| Subject Access Rights, the request to access data must be addressed quickly (less than one month) | X | ||
| Appointment of a Data Protection Officer where medical, genetic or biometric data is processed in a large scale | X | X | |
| Data Protection Impact Assessment: risk assessment of the impact of anticipated processing activities on personal, medical, genetic or biometric data | X | X | For telcos, this implies a certain level of security policies parametrization in order to cope with different type of data |
| Mandatory data breach reporting: breaches must be reported to a data protection regulator within 72 hours, and those affected by the breach must also be informed. | X | X | |
| Anonymization: the method of processing personal data in order to irreversibly prevent identification. | X | X | |
| Data confidentiality: protection of data from being accessed by unauthorised parties through e.g. pseudonymization and/or encryption of personal data | X | X | |
| Data Integrity: maintenance of the accuracy and consistency of data throughout its entire life cycle | X | X | |
| Integrity, availability and resilience of processing systems and services against accidental loss, destruction or malicious actions that compromise the availability, authenticity, integrity and confidentiality of stored or transmitted personal data | X | X | For telcos, this requirement leads to the need of having self-assessment of systems related to their ability to process the data according to regulatory rules |
| Existence of a process for regularly testing, assessing and evaluating the effectiveness of technical and organisational measures for ensuring the security of the processing | X | X | For telcos this means the ability to monitor and assess security policies and their efficiency |
| Traceability: care providers to determine the initial source of the data, and what happened to it through its various locations and transformations. | X | X | For telcos this implies enhanced logging capabilities for highly secured communication services |