TS 38.470
NG-RAN — F1 interface –
General Aspects and Principles
V18.3.0 (PDF)
2024/09 25 p.
V17.6.0
2023/09 22 p.
V16.11.0
2023/09 19 p.
V15.8.0
2021/06 15 p.
- Rapporteur:
- Mr. Olofsson, Henrik
Huawei Technologies Co. Ltd.
Content for TS 38.470 Word version: 18.2.0
1 Scope
2 References
3 Definitions and abbreviations
4 General aspects
5 Functions of the F1 interface
6 Procedures of the F1 interface
7 F1 interface protocol structure
8 Other F1 interface specifications
$ Change history
1 Scope p. 6
The present document is an introduction to the 3GPP TS 38.47x series of technical specifications that define the F1 interface. The F1 interface provides means for interconnecting a gNB-CU and a gNB-DU of a gNB within an NG-RAN, or for interconnecting a gNB-CU and a gNB-DU of an en-gNB within an E-UTRAN.
2 References p. 6
The following documents contain provisions which, through reference in this text, constitute provisions of the present document.
- References are either specific (identified by date of publication, edition number, version number, etc.) or non-specific.
- For a specific reference, subsequent revisions do not apply.
- For a non-specific reference, the latest version applies. In the case of a reference to a 3GPP document (including a GSM document), a non-specific reference implicitly refers to the latest version of that document in the same Release as the present document.
[1]
TR 21.905: "Vocabulary for 3GPP Specifications".
[2]
TS 38.401: "NG-RAN; Architecture Description".
[3]
TS 38.471: "NG-RAN; F1 layer 1".
[4]
TS 38.472: "NG-RAN; F1 signalling transport".
[5]
TS 38.473: "NG-RAN; F1 Application Protocol (F1AP)".
[6]
TS 38.474: "NG-RAN; F1 data transport".
[7]
TS 38.425: "NG-RAN; Xn interface user plane protocol".
[8]
TS 38.300: "NR; Overall description; Stage-2".
[9]
TS 37.340: "NR; Multi-connectivity; Overall description; Stage-2".
[10]
TS 38.321: "NR; Medium Access Control (MAC) protocol specification".
[11]
TS 38.331: "NR; Radio Resource Control (RRC); Protocol specification".
[12]
TS 38.415: "NG-RAN; PDU Session User Plane Protocol".
3 Definitions and abbreviations p. 6
3.1 Definitions p. 6
For the purposes of the present document, the terms and definitions given in TR 21.905 and the following apply. A term defined in the present document takes precedence over the definition of the same term, if any, in TR 21.905.
BH RLC channel:
as defined in TS 38.300.
en-gNB:
as defined in TS 37.340.
gNB:
as defined in TS 38.300.
gNB-CU:
as defined in TS 38.401.
gNB-DU:
as defined in TS 38.401.
IAB-DU:
as defined in TS 38.300.
IAB-MT:
as defined in TS 38.300.
IAB-donor:
as defined in TS 38.300.
IAB-donor-CU:
as defined in TS 38.401.
IAB-donor-DU:
as defined in TS 38.401.
IAB-node:
as defined in TS 38.300.
Mobile IAB-DU:
as defined in TS 38.300.
Mobile IAB-MT:
as defined in TS 38.300.
MP Relay UE:
as defined in TS 38.300.
MP Remote UE:
as defined in TS 38.300.
Multi-path:
as defined in TS 38.300.
PC5 Relay RLC channel:
as defined in TS 38.300.
U2N Relay UE:
as defined in TS 38.300.
U2N Remote UE:
as defined in TS 38.300.
U2U Relay UE:
as defined in TS 38.300.
U2U Remote UE:
as defined in TS 38.300.
Uu Relay RLC channel:
as defined in TS 38.300.
3.2 Abbreviations p. 7
For the purposes of the present document, the abbreviations given in TR 21.905 and the following apply. An abbreviation defined in the present document takes precedence over the definition of the same abbreviation, if any, in TR 21.905.
BH
Backhaul
DRB
Data Radio Bearers
eDRX
extended Discontinuous Reception
eRedCap
Enhanced Reduced Capability
F1-C
F1 Control plane interface
F1-U
F1 User plane interface
F1AP
F1 Application Protocol
GTP-U
GPRS Tunnelling Protocol
IAB
Integrated Access and Backhaul
IP
Internet Protocol
L2
Layer-2
MBS
Multicast/Broadcast Service
MP
Multi-Path
N3C
Non-3GPP Connection
NR-MIB
NR-Master Information Block
NSAG
Network Slice AS Group
O&M
Operation and Maintenance
PA
Paging Area
PDC
Propagation Delay Compensation
PF
Paging Frame
PH
Paging Hyperframes
PO
Paging Occasion
PTP
Point to Point
PTM
Point to Multipoint
QMC
QoE Measurement Collection
QoE
Quality of Experience
QoS
Quality of Service
RedCap
Reduced Capability
RIM
Remote Interference Management
RLC
Radio Link Control
RRC
Radio Resource Control
SCTP
Stream Control Transmission Protocol
SIB1
System Information Block 1
SIB9
System Information Block 9
SIB10
System Information Block 10
SIB12
System Information Block 12
SIB13
System Information Block 13
SIB14
System Information Block 14
SIB15
System Information Block 15
SIB17
System Information Block 17
SIB18
System Information Block 18
SIB19
System Information Block 19
SIB20
System Information Block 20
SIB22
System Information Block 22
SIB23
System Information Block 23
SIB24
System Information Block 24
SL
Sidelink
SRB
Signalling Radio Bearers
TNL
Transport Network Layer
U2N
UE-to-Network
U2U
UE-to-UE
V2X
Vehicle-to-Everything
4 General aspects p. 8
This clause captures the F1 interface principles and characteristics.
4.1 F1 interface general principles p. 8
The general principles for the specification of the F1 interface are as follows:
- the F1 interface is open;
- the F1 interface supports the exchange of signalling information between the endpoints, in addition the interface supports data transmission to the respective endpoints;
- from a logical standpoint, the F1 is a point-to-point interface between the endpoints.
- the F1 interface supports control plane and user plane separation;
- the F1 interface separates Radio Network Layer and Transport Network Layer;
- the F1 interface enables exchange of UE associated information and non-UE associated information;
- the F1 interface is designed in a future proof way to fulfil different new requirements, support new services and new functions;
- one gNB-CU and a set of gNB-DUs are visible to other logical nodes as a gNB or an en-gNB where the gNB terminates the Xn and the NG interfaces, and the en-gNB terminates the X2 and the S1-U interfaces;
- the gNB-CU may be separated in control plane (CP) and user plane (UP).
4.2 F1 interface specification objectives p. 9
The F1 interface specifications facilitate the following:
- inter-connection of a gNB-CU and a gNB-DU supplied by different manufacturers.
4.3 F1 interface capabilities p. 9
The F1 interface supports:
- procedures to establish, maintain and release radio bearers for the NG-RAN part of PDU sessions and MBS Sessions, and for E-UTRAN Radio Access Bearers;
- procedures to establish, maintain and release BH RLC channels;
- the separation of each UE on the protocol level for user specific signalling management;
- the separation of each IAB-MT on the protocol level for IAB-MT specific signalling management;
- the transfer of RRC signalling messages between the UE and the gNB-CU;
- procedures to establish, maintain and release Uu Relay RLC channels and PC5 Relay RLC channels.
4.4 Void
5 Functions of the F1 interface p. 9
5.1 General p. 9
The following clauses describe the functions supported over F1-C and F1-U.
5.2 F1-C functions p. 9
5.2.1 F1 interface management function p. 9
The error indication function is used by the gNB-DU or gNB-CU to indicate to the gNB-CU or gNB-DU that an error has occurred.
The reset function is used to initialize the peer entity after node setup and after a failure event occurred. This procedure can be used by both the gNB-DU and the gNB-CU.
The F1 setup function allows to exchange application level data needed for the gNB-DU and gNB-CU to interoperate correctly on the F1 interface, and exchange the intended TDD DL-UL configuration originating from the gNB-DU or destined to the gNB-DU. The F1 setup is initiated by the gNB-DU. The F1 setup function also allows to send the information of a mobile IAB-MT from the co-located mobile IAB-DU to the gNB-CU.
The gNB-CU Configuration Update and gNB-DU Configuration Update functions allow to update application level configuration data needed between gNB-CU and gNB-DU to interoperate correctly over the F1 interface, and may activate or deactivate cells. The gNB-CU Configuration Update function may activate SSB beams of cells. The gNB-CU Configuration Update function may indicate the cells where the gNB-DU is allowed to deactivate the SSB beams. With the gNB-CU Configuration Update function, energy saving with cell activation and cell deactivation can be supported as defined in TS 38.300. For cross-link interference mitigation, the gNB-CU may coordinate the exchange of intended TDD DL-UL configuration by merging, forwarding and selective forwarding of intended TDD DL-UL configuration(s) between its gNB-DUs, or between its gNB-DUs and other gNBs, gNB-CUs. The gNB-DU Configuration Update function also allows to send the information of a mobile IAB-MT from the co-located mobile IAB-DU to the gNB-CU.
The F1 setup and gNB-DU Configuration Update functions allow to inform the S-NSSAI(s), NSAG(s), CAG ID(s) and NID(s) supported by the gNB-DU.
The F1 setup and gNB-DU Configuration Update functions allow to provide information on either RedCap access configuration, or eRedCap access configuration, or both at the gNB-DU.
The F1 setup and gNB-CU Configuration Update functions allow to inform the NID(s) available at the gNB-CU.
The F1 resource coordination function is used to transfer information about frequency resource sharing between gNB-CU and gNB-DU. In case of split gNB architecture, the gNB-CU may consolidate the outgoing messages from multiple gNB-DUs and distribute the incoming messages to the involved gNB-DUs, to perform resource coordination.
The gNB-DU status indication function allows the gNB-DU to indicate overload status to gNB-CU. In case of IAB, the IAB-donor-DU or IAB-DU can indicate the downlink congestion status to the IAB-donor-CU.
The network access rate reduction function is used to indicate to the gNB-DU that the rate at which UEs are accessing the network need to be reduced.
The F1 removal function is used to remove the interface instance and all related resources between the gNB-DU and the gNB-CU in a controlled manner.
The F1 TA information transfer function is used to transfer the TA information from the gNB-DU to the gNB-CU and the gNB-CU to the gNB-DU.
5.2.2 System Information management function p. 10
Scheduling of system broadcast information is carried out in the gNB-DU. The gNB-DU is responsible for transmitting the system information according to the scheduling parameters available.
The gNB-DU is responsible for the encoding of the NR-MIB message. In case broadcast of SIB1 and other SIBs is needed, the gNB-DU is responsible for the encoding of the SIB1 message, SIB10, SIB12, SIB13, SIB14, SIB15, SIB17, SIB18, SIB20, SIB22, SIB23 and SIB24, and the gNB-CU is responsible for the encoding of other SIBs. The gNB-DU may re-encode SIB9. The gNB-DU is responsible for the generation of the SystemInformation message.
The gNB-CU is responsible for receiving the positioning assistance information from LMF, e.g. the positioning related SIBs. The gNB-CU transparently sends the positioning assistance information to the gNB-DU. The gNB-DU is responsible for broadcasting the positioning assistance information in Positioning SI message(s).
To support Msg3 based on-demand SI and RRC Dedicated SIB Request as described in TS 38.331, the gNB-CU can confirm the received SI request from the UE by including the UE identity, and command the gNB-DU to broadcast the requested SystemInformation messages including the other SI.
To support UE RRC Positioning SI acquisition mechanism, as described in TS 38.331, the gNB-CU can confirm the received positioning SI request from the UE by including the UE identity, and command the gNB-DU to broadcast the requested positioning SI messages.
5.2.3 F1 UE context management function p. 10
The F1 UE context management function supports the establishment and modification of the necessary overall UE context.
The establishment of the F1 UE context is initiated by the gNB-CU and accepted or rejected by the gNB-DU based on admission control criteria (e.g., resource not available).
The modification of the F1 UE context can be initiated by either gNB-CU or gNB-DU. The receiving node can accept or reject the modification. The F1 UE context management function also supports the release of the context previously established in the gNB-DU. The release of the context is triggered by the gNB-CU either directly or following a request received from the gNB-DU. The gNB-CU request the gNB-DU to release the UE Context when the UE enters RRC_IDLE or RRC_INACTIVE. In case of configured grant small data transmission, this function allows the gNB-CU to request the gNB-DU to keep part of the UE context, including at least the lower layer configuration for SDT DRB(s)/SRB(s), C-RNTI, CS-RNTI, F1AP association, and F1 tunnel information, when the gNB-CU sends the UE into RRC_INACTIVE state. In case of positioning when the gNB-CU sends the UE into RRC_INACTIVE state, this function allows the gNB-CU to request the gNB-DU to keep part of the positioning context, including the SRS configuration for the UE.
This function can be also used to manage DRBs, SRBs and SL DRBs, i.e., establishing, modifying and releasing DRB, SRB and SL DRB resources. The establishment and modification of DRB, or SL DRB resources are triggered by the gNB-CU and accepted/rejected by the gNB-DU based on resource reservation information and QoS information to be provided to the gNB-DU. For each DRB to be setup or modified, the S-NSSAI may be provided by gNB-CU to the gNB-DU in the UE Context Setup procedure and the UE Context Modification procedure. In case of NG-RAN sharing, the gNB-CU includes the serving PLMN ID (for SNPNs the serving SNPN ID) in the UE Context Setup procedure.
This function is also used to manage a UE's configuration with multicast resources and to provide information about the multicast MRBs which are established for the multicast MBS Sessions the UE has joined.
For Uu, the mapping between QoS flows and radio bearers is performed by gNB-CU and the granularity of bearer related management over F1 is radio bearer level. For NG-RAN, the gNB-CU decides an aggregated DRB QoS profile for each radio bearer based on received QoS flow profile, and provides both aggregated DRB QoS profile and QoS flow profile to the gNB-DU, and the gNB-DU either accepts the request or rejects it with appropriate cause value. With this function, gNB-DU could also notify gNB-CU whether the QoS for already established DRBs is not fulfilled any longer or it is fulfilled again. The function can be also used to inform the gNB-DU the alternative QoS Parameters Sets when available for a QoS flow. To support packet duplication for intra-gNB-DU CA and packet split/duplication for intra-DU multi-path relay as described in TS 38.300, one data radio bearer should be configured with at least two GTP-U tunnels between gNB-CU and a gNB-DU.
For SL, the mapping between QoS flows and radio bearers is performed by gNB-CU and the granularity of bearer related management over F1 is radio bearer level. For NG-RAN, the gNB-CU decides an aggregated SL DRB QoS profile for each radio bearer based on received QoS flow profile, and provides both aggregated SL DRB QoS profile and QoS flow profile to the gNB-DU, and the gNB-DU either accepts the request or rejects it with appropriate cause value.
With this function, gNB-CU requests the gNB-DU to setup or change of the SpCell (as defined in TS 38.321) for the UE, and the gNB-DU either accepts or rejects the request with appropriate cause value. This function also enables the gNB-DU to inform the gNB-CU of which cell the UE has successfully accessed during conditional mobility.
With this function, the gNB-CU requests the setup of the SCell(s) at the gNB-DU side, and the gNB-DU accepts all, some or none of the SCell(s) and replies to the gNB-CU. The gNB-CU requests the removal of the SCell(s) for the UE.
With this function, the gNB-CU indicates the UL UE AMBR limit to the gNB-DU, and the gNB-DU enforces the indicated limit.
With this function, the gNB-DU indicates that a bearer, or a UE is inactive or active. The gNB-CU consolidates all the serving gNB-DUs for the UE and takes further action.
With this function, the gNB-CU indicates the gNB-DU that the UE context concerns mobility enhancement operation, and the gNB-DU takes corresponding actions.
In addition, for IAB-nodes and IAB-donors:
- The F1 UE context management function is used for managing BH RLC channels, i.e. establishing, modifying and releasing BH RLC channel resources. The establishment of BH RLC channels is triggered by the IAB-donor-CU. The establishment and modification is accepted/rejected by the IAB-node's parent, based on e.g. resource reservation information and QoS information provided to the IAB-node's parent.
- The DRB QoS profile framework is reused for BH RLC channels carrying DRBs. Prioritization of traffic on the F1-C interface is based on traffic type (e.g. UE-associated F1AP signalling, non-UE-associated F1AP signalling) and is enforced in the IAB-donor-DU and in IAB-nodes, considering that the traffic on the F1-C interface has higher priority than other traffic; in-sequence delivery over the signaling connection is always ensured.
- The IAB-donor-CU associates each BH RLC channel carrying control plane traffic with one of the signaled control plane traffic type values.
- The F1 UE context management function is used for managing Uu Relay RLC channels and PC5 Relay RLC channels for L2 U2N relay, i.e. establishing, modifying and releasing Uu Relay RLC channel and PC5 Relay RLC channel resources. The establishment of Uu Relay RLC channels and PC5 Relay RLC channels are triggered by the gNB-CU. The establishment and modification is accepted/rejected by the gNB-DU based on resource reservation information and QoS information provided to the gNB-DU. The modification of Uu/PC5 Relay RLC channels can be triggered by the gNB-CU or the gNB-DU.
- The gNB-CU determines the QoS for the PC5 Relay RLC channel and the QoS for the Uu Relay RLC channel based on the received QoS profile for the L2 U2N Remote UE, and provides the QoS information to the gNB-DU.
- The gNB-CU configures the gNB-DU about the SRB(s)/DRB(s) to Uu Relay RLC channel(s) mapping, which is used by the gNB-DU to perform data transfer of L2 U2N Remote UE. The mapping between DRB and Uu Relay RLC channel is configured at the granularity of GTP-U tunnel.
- The gNB-CU is responsible for the local ID allocation and update for L2 U2N Remote UE.
- The gNB-CU is responsible to determine the data split among two paths for a DRB for both intra-DU and inter-DU multi-path relay.
- The gNB-CU takes the responsibility to decide the addition/modification/release of a path.
- The functionality for the L2 U2N Relay can be applied to the L2 MP Relay using PC5 link.
-
Regarding the L2 MP Relay using N3C link,
- The F1 UE context management function is used for managing Uu Relay RLC channels for L2 MP Relay using N3C, i.e. establishing, modifying and releasing Uu Relay RLC channel resources. The establishment of Uu Relay RLC channels is triggered by the gNB-CU. The establishment or modification is accepted/rejected by the gNB-DU based on resource reservation information and QoS information provided to the gNB-DU. The modification of Uu Relay RLC channels can be triggered by the gNB-CU or the gNB-DU.
- The gNB-CU determines the QoS for the Uu Relay RLC channel based on the received QoS profile for the L2 MP Remote UE using N3C, and provides the QoS information to the gNB-DU.
- The gNB-CU configures the gNB-DU about the SRB(s)/DRB(s) to Uu Relay RLC channel(s) mapping, which is used by the gNB-DU to perform data transfer of L2 MP Remote UE using N3C. The mapping between DRB and Uu Relay RLC channel is configured at the granularity of GTP-U tunnel.
- The F1 UE context management function is used for managing PC5 Relay RLC channels for L2 U2U Remote UE and L2 U2U Relay UE, i.e. establishing, modifying and releasing PC5 Relay RLC channel resources. The establishment of PC5 Relay RLC channels are triggered by the gNB-CU. The establishment and modification is accepted/rejected by the gNB-DU based on resource reservation information and QoS information provided to the gNB-DU. The modification of PC5 Relay RLC channels can be triggered by the gNB-CU or the gNB-DU.
- The gNB-CU determines the QoS for the PC5 Relay RLC channel on the first hop or second hop of an end-to-end sidelink radio bearer based on the QoS profile received from L2 U2U Remote UE or L2 U2U Relay UE, and provides the QoS information to the gNB-DU.
5.2.4 RRC message transfer function p. 12
This function allows to transfer RRC messages between gNB-CU and gNB-DU. RRC messages are transferred over F1-C. The gNB-CU is responsible for the encoding of the dedicated RRC message with assistance information provided by gNB-DU. This function also allows gNB-DU to report to gNB-CU if the downlink RRC message has been successfully delivered to UE or not. The function also allows the gNB-DU to report to the gNB-CU if the accessing UE is a Reduced Capability UE as defined in TS 38.300. This function also allows the gNB-DU to duplicate the downlink RRC message according to the duplication information provided by gNB-CU.
For IAB-nodes, this function allows to transfer RRC messages for setting up and configuring the IAB-MT side of the BH RLC channel. These RRC messages are carried on F1-C between the IAB-donor-CU and the parent IAB-DU, i.e. the gNB-DU side of the BH RLC channel.
5.2.5 Paging function p. 13
The gNB-CU is responsible for filtering target cells for paging based on the UE Radio Capability for Paging. The gNB-CU may further send a list of recommended SSB beams to the gNB-DU for paging of UEs in RRC_INACTIVE.
The gNB-DU is responsible for transmitting the paging information according to the scheduling parameters provided. The gNB-DU also takes the UE paging capability into account for paging when provided by the gNB-CU.
The gNB-CU provides paging information to enable the gNB-DU to calculate the exact PH, if the eDRX is configured, PO and PF. The gNB-CU determines the PA. The gNB-DU consolidates all the paging records for a particular PH, PO, PF and PA, and encodes the final RRC message and broadcasts the paging message on the respective PH, PO, PF in the PA.
The paging function also supports CN controlled subgrouping paging for UE Power Saving.
5.2.6 Warning messages information transfer function p. 13
This function allows to cooperate with the warning message transmission procedures over NG interface. The gNB-CU is responsible for encoding the warning related SI message and sending it together with other warning related information for the gNB-DU to broadcast over the radio interface.
5.2.7 Remote Interference Management (RIM) message transfer function |R16| p. 13
This function enables the transfer of Remote Interference Management (RIM) backhaul messages between the gNB-CU and the gNB-DU. RIM messages are transferred over F1-C. The gNB-CU acts as a coordinator on behalf of its affiliated gNB-DUs, by merging the RIM information received from its gNB-DUs and forwarding the merged information to the target gNBs or gNB-CUs, transparently via the core network. Similarly, a gNB-CU distributes an incoming RIM backhaul message to all its concerned gNB-DUs.
5.2.8 Trace function |R16| p. 13
The Trace function provides means to control trace sessions for a UE over F1 interface.
5.2.9 Load management function |R16| p. 13
The load management function allows a gNB-CU to request the reporting of load measurements to gNB-DU and is used by gNB-DU to report the result of measurements admitted by gNB-DU.
5.2.10 Self-optimisation support function |R16| p. 13
This function allows the gNB-CU to provide information to the gNB-DU in order to support self-optimization functionality.
This function also allows the gNB-DU to provide information to the gNB-CU in order to support self-optimization functionality.
5.2.11 Positioning function |R16| p. 13
This function allows to transfer location management messages between gNB-CU and gNB-DU. With this function, gNB-CU request TRP information from gNB-DU, and gNB-DU response to gNB-CU with the TRP information. With this function, gNB-CU request positioning measurements from gNB-DU, and gNB-DU response to gNB-CU with the positioning measurements.
The function allows the gNB-CU to
- transfer the positioning assistance data to gNB-DU. The gNB-DU is responsible for broadcasting the positioning assistance data according to the scheduling parameters available;
- request the gNB-DU to configure SRS transmissions for UE;
- request the gNB-DU to configure PRS transmissions;
- request the gNB-DU to configure measurement gap or PRS processing window,
- request the gNB-DU to activate or deactivate preconfigured measurement gap or PRS processing window;
- request the gNB-DU to broadcast positioning system information;
- request the gNB-DU to reserve or release the SRS resources for area-specific SRS transmissions.
5.2.12 IAB support function |R16| p. 14
The support for IAB comprises several functions.
The BAP mapping configuration function allows the IAB-donor-CU to provide BAP mapping which includes the backhaul routing configuration and/or BH RLC channel mapping information for IAB-donor-DU or IAB-DU. This function also enables the IAB-donor-CU to provide the BAP header rewriting configuration, or other BAP related configurations to the IAB-DU. This function also enables the IAB-donor-CU to provide the BAP related configurations to the IAB-donor-DU.
The gNB-DU resource configuration function is used by the IAB-donor-CU to provide cell resource configuration for an IAB-donor-DU or an IAB-DU, and/or NA resource configuration of a parent node IAB-DU or IAB-donor-DU serving the co-located IAB-MT for an IAB-DU, and/or information about the child node's cell resource configuration and other periodic configurations to a parent IAB-node or an IAB-donor-DU. This function also allows the IAB-donor-CU to provide the semi-static cell resource configuration of a neighbour node or a peer parent-node of a child node, whereas this neighbor node or a peer parent can be an IAB-donor-DU or an IAB-DU.
The IAB TNL address configuration function enables the IAB-donor-CU to request IP address(es) to be used for IAB-node(s) from an IAB-donor-DU, or to request from an IAB-donor-DU the removal of IP address(es) used for IAB-node(s). This function is also used by the IAB-donor-CU to provide an IAB-donor-DU with the IP address information of the traffic to be transferred to a peer IAB-donor-DU via an inter-donor-DU tunnel.
The IAB UP configuration update function allows the update of BH information or the UP TNL information between the IAB-donor-CU and an IAB-DU.
The Mobile IAB F1 Setup Triggering function enables the IAB-donor-CU to trigger the new F1 interface establishment between a target logical mobile IAB-DU and a target F1-terminating IAB-donor-CU.
The Mobile IAB F1 Setup Outcome Notification function enables the mobile IAB-DU to report the outcome of the F1 interface setup between a target logical mobile IAB-DU and a target F1-terminating IAB-donor-CU.
5.2.13 NR MBS function |R17| p. 14
The NR MBS function supports establishing, modifying and releasing the MRB resources and the user data transport.
The multicast group paging function supports the sending of multicast group paging request to the gNB-DUs in order to group-page UEs that have joined the multicast MBS session.
5.2.14 PDC measurement function |R17| p. 14
The PDC measurement function allows the gNB-CU to request the gNB-DU to report measurements used for propagation delay compensation at the gNB-CU or UE.
5.2.15 QMC support function |R17| p. 14
This function enables the transfer of RAN visible QoE information from the gNB-CU to the gNB-DU, and the control thereof.
5.2.16 Timing Synchronisation Status Reporting function |R18| p. 14
The Timing Synchronisation Status Reporting function enables the gNB-CU to request the gNB-DU node to report the RAN timing synchronisation status information.
5.3 F1-U functions p. 15
5.3.1 Transfer of user data p. 15
This function allows to transfer of user data between gNB-CU and gNB-DU.
This function also allows to transfer PDU Set Information of a QoS flow, and indication of End of Data Burst to the gNB-DU. The detailed protocol is specified in TS 38.415.
5.3.2 Flow control function p. 15
This function allows to control the downlink user data flow to the gNB-DU. The detailed protocol is specified in TS 38.425.
5.4 TEIDs allocation p. 15
The gNB-DU is responsible for the allocation of the F1-U DL GTP TEID for each data radio bearer.
6 Procedures of the F1 interface p. 15
6.1 Control plane procedures p. 15
6.1.1 Interface Management procedures p. 15
The F1 Interface management procedures are listed below:
- Reset procedure;
- Error Indication procedure;
- F1 Setup procedure;
- gNB-DU Configuration Update procedure;
- gNB-CU Configuration Update procedure;
- gNB-DU Resource Coordination procedure;
- gNB-DU Status Indication procedure;
- F1 Removal procedure;
- Network Access Rate Reduction procedure;
- DU-CU TA Information Transfer procedure;
- CU-DU TA Information Transfer procedure.
6.1.2 Context Management procedures p. 15
The F1 Context management procedures are listed below:
- UE Context setup procedure;
- UE Context Release Request (gNB-DU initiated) procedure;
- UE Context Release (gNB-CU initiated) procedure;
- UE Context Modification (gNB-CU initiated) procedure;
- UE Context Modification Required (gNB-DU initiated) procedure;
- UE Inactivity Notification procedure;
- Notify procedure;
- Access Success procedure;
- DU-CU Cell Switch Notification procedure;
- CU-DU Cell Switch Notification procedure.
6.1.3 RRC Message Transfer procedures p. 16
The F1 RRC message transfer procedures are listed below:
- Initial UL RRC Message Transfer procedure;
- UL RRC Message Transfer procedure;
- DL RRC Message Transfer procedure;
- RRC Delivery Report procedure.
6.1.3A Warning Message Transmission procedures p. 16
The F1 Warning message transmission procedures are listed below:
- Write-Replace Warning procedure;
- PWS Cancel procedure;
- PWS Restart Indication procedure;
- PWS Failure Indication procedure.
6.1.4 System Information procedures p. 16
The F1 System information procedures are listed below:
- System Information Delivery procedure.
6.1.5 Paging procedures p. 16
The F1 Paging procedures are listed below:
- Paging procedure;
- QoE Information Transfer Control procedure.
6.1.6 Void
6.1.7 Radio information transfer procedures |R16| p. 16
The F1 Radio information transfer procedures are listed below:
- DU-CU Radio Information Transfer procedure;
- CU-DU Radio Information Transfer procedure.
6.1.8 UE Tracing procedures |R16| p. 17
The following procedures are used to trace the UE:
- Trace Start procedure;
- Deactivate Trace procedure;
- Cell Traffic Trace procedure.
6.1.9 Load management procedures |R16| p. 17
The load management procedures are listed as below:
- Resource Status Reporting Initiation procedure;
- Resource Status Reporting procedure.
6.1.10 Self-optimisation support procedure |R16| p. 17
The following procedures are used to transfer failure and mobility related information between the gNB-CU and the gNB-DU to support self-optimisation:
- Access and Mobility Indication procedure, from gNB-CU to gNB-DU;
- DU-CU Access and Mobility Indication procedure, from gNB-DU to gNB-CU.
- RACH Indication.
6.1.11 Positioning procedures |R16| p. 17
The F1 Positioning procedures are listed below:
- Positioning Assistance Information Control procedure;
- Positioning Assistance Information Feedback procedure;
- Positioning Measurement procedure;
- Positioning Measurement Report procedure;
- Positioning Measurement Abort procedure;
- Positioning Measurement Failure Indication procedure;
- Positioning Measurement Update procedure;
- TRP Information Exchange procedure;
- Positioning Information Update;
- Positioning Information Exchange procedure;
- Positioning Activation procedure;
- Positioning Deactivation procedure;
- E-CID Measurement Initiation;
- E-CID Measurement Failure Indication procedure;
- E-CID Measurement Report procedure;
- E-CID Measurement Termination procedure;
- PRS Configuration Exchange procedure;
- Measurement Preconfiguration;
- Measurement Activation;
- Positioning System Information Delivery procedure;
- SRS Information Reservation Notification procedure.
6.1.12 IAB procedures |R16| p. 18
The IAB procedures are listed below:
- BAP Mapping Configuration procedure;
- gNB-DU Resource Configuration procedure;
- IAB TNL Address Allocation procedure;
- IAB UP Configuration Update procedure;
- Mobile IAB F1 Setup Triggering procedure;
- Mobile IAB F1 Setup Outcome Notification procedure.
6.1.13 NR MBS procedures |R17| p. 18
The F1 MBS procedures are listed below:
- Broadcast Context Setup;
- Broadcast Context Release (gNB-CU initiated);
- Broadcast Context Modification;
- Broadcast Context Release Request (gNB-DU initiated);
- Multicast Group Paging procedure;
- Multicast Context Setup;
- Multicast Context Release (gNB-CU initiated);
- Multicast Context Modification;
- Multicast Context Release Request (gNB-DU initiated);
- Multicast Distribution Setup;
- Multicast Distribution Release;
- Multicast Context Notification;
- Broadcast Transport Resource Request;
- Multicast Common Configuration.
6.1.14 PDC Measurement procedures |R17| p. 18
The PDC measurement procedures are listed below:
- PDC Measurement Initiation procedure;
- PDC Measurement Report procedure.
6.1.15 QMC procedures |R17| p. 19
The QMC procedures are listed below:
- PDC Measurement Initiation procedure;
- PDC Measurement Report procedure.
6.1.16 Timing Synchronisation Status Reporting procedures |R18| p. 19
The following procedures are used to report the RAN timing synchronisation status information:
- Timing Synchronisation Status;
- Timing Synchronisation Status Report.
6.2 User plane procedures p. 19
Void
7 F1 interface protocol structure p. 19
7.1 F1 Control Plane Protocol (F1-C) p. 19
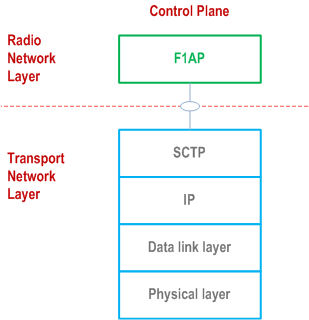
Figure 7.1-1 shows the protocol structure for F1-C. The TNL is based on IP transport, comprising the SCTP on top of IP. The application layer signalling protocol is referred to as F1AP (F1 Application Protocol).
7.2 F1 User Plane Protocol (F1-U) p. 19
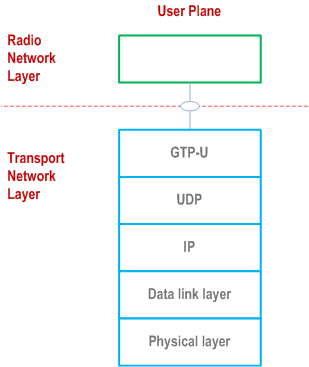
Figure 7.2-1 shows the protocol structure for F1-U. The TNL is based on IP transport, comprising the UDP and GTP-U on top of IP.
8 Other F1 interface specifications p. 20
This clause contains the description of the other related 3GPP specifications.
8.1 NG-RAN F1 interface: layer 1 (3GPP TS 38.471) p. 20
3GPP TS 38.471 specifies the physical layer technologies that may be used to support the F1 interface.
8.2 NG-RAN F1 interface: signalling transport (3GPP TS 38.472) p. 20
3GPP TS 38.472 specifies the signalling bearers for the F1AP for the F1-C interface.
8.3 NG-RAN F1 interface: F1AP specification (3GPP TS 38.473) p. 20
3GPP TS 38.473 specifies the F1AP protocol for radio network control plane signalling over the F1 interface.
8.4 NG-RAN F1 interface: data transport and transport signalling (3GPP TS 38.474) p. 20
3GPP TS 38.474 specifies the transport bearers for the user plane of the F1-U interface.
8.5 NG-RAN F1 interface: user plane protocol (3GPP TS 38.425) p. 20
3GPP TS 38.425 specifies the user plane protocol being used over the F1-U interface.
8.6 NG-RAN F1 interface: PDU Session user plane protocol (TS 38.415) |R18| p. 21
3GPP TS 38.415 specifies the PDU Set Information user plane protocol for sending PDU Set Information and indication of End of Data Burst over the F1-U interface.