Content for TS 29.163 Word version: 18.1.0
4 General
4.1 General interworking overview
5 Network characteristics
5.1 Key characteristics of ISUP/BICC based CS networks
5.2 Key characteristics of IM CN subsystem
6 Interworking with CS networks
6.1 Interworking reference model
6.2 Control plane interworking model
6.3 User plane interworking model
...
...
4 General p. 28
4.1 General interworking overview p. 28
The IM CN subsystem shall interwork with BICC and ISUP based legacy CS networks, e.g. PSTN, ISDN, CS PLMNs, in order to provide the ability to support basic voice calls (see TS 22.228), between a UE located in the IM CN subsystem and user equipment located in a CS network.
For the ability to support the delivery of basic voice calls between the IM CN subsystem and CS networks, basic protocol interworking between SIP (as specified in TS 24.229) and BICC or ISUP (as specified in ITU-T Recommendations Q.1902.1-6 [30] and ITU-T Recommendations Q761 to Q764 [4] respectively) has to occur at a control plane level, in order that call setup, call maintenance and call release procedures can be supported. The MGCF shall provide this protocol mapping functionality within the IM CN subsystem.
User plane interworking between the IM CN subsystem and CS network bearers (e.g. 64k TDM, ATM/AAL2 circuit or IP bearer) are supported by the functions within the IM-MGW. The IM-MGW resides in the IM CN subsystem and shall provide the bearer channel interconnection. The MGCF shall provide the call control to bearer setup association.
The IM CN subsystem shall interwork, at the control and user plane, with BICC and ISUP based legacy CS networks. The support of supplementary services shall be as defined in TS 22.228. The MGCF and IM-MGW shall support the interworking of the IM CN subsystem to an external ISUP based CS network. They may also support interworking to a BICC based CS network where no 3GPP specific extension is applied. The MGCF and the IM-MGW may also support interworking to a BICC based CS network where 3GPP specific extensions in accordance with TS 29.205 are applied.
5 Network characteristics p. 29
5.1 Key characteristics of ISUP/BICC based CS networks p. 29
This signalling interface to a PSTN is either based on BICC Capability Set 2 as specified in ITU-T Recommendations Q.1902.1 to Q.1902.6 [30], or on ISUP (see ITU-T Recommendations Q.761 to Q.764 [4]).
The interface towards a CS-PLMN may either be one of the interfaces mentioned in the paragraph above or a signalling interface based on BICC with 3GPP specific extensions, as specified for the 3GPP Nc interface in TS 29.205, and the IM-MGW may support the 3GPP Nb interface, as specified in TS 29.414 and TS 29.415. If the 3GPP Nc interface is applied as signalling interface, the 3GPP Nb interface is used as user plane interface and the Nb UP Framing protocol is applied.
5.2 Key characteristics of IM CN subsystem p. 29
The IM CN subsystem uses SIP to manage IP multimedia sessions in a 3GPP environment, it also uses Ipv6, as defined in RFC 2460, as the transport mechanism for both SIP session signalling and media transport. The 3GPP profile of SIP defining the usage of SIP within the IM CN subsystem is specified in TS 24.229. Example callflows are provided in TS 24.228.
6 Interworking with CS networks p. 29
6.1 Interworking reference model p. 29
Figure 1 details the reference model required to support interworking between the 3GPP IM CN subsystem and CS networks for IM basic voice calls.
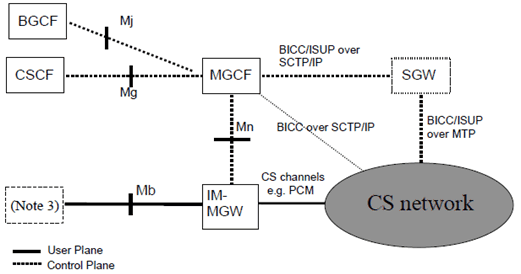
Figure 1: IM CN subsystem to CS network logical interworking reference model
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
6.1.1 Interworking reference points and interfaces p. 30
The reference points and network interfaces shown in figure 1 are as described:
Protocol for Mg reference point: The single call control protocol applied across the Mg reference point (i.e. between CSCF and MGCF) will be based on the 3GPP profile of SIP as defined in accordance with TS 24.229.
Protocol for Mn reference point: The Mn reference point describes the interfaces between the MGCF and IM-MGW, and has the properties as detailed in TS 29.332.
Protocol for Mj reference point: The single call control protocol applied across the Mj reference point (i.e. between BGCF and MGCF) will be based on the 3GPP profile of SIP as defined in accordance with TS 24.229.
Protocol for Mb reference point: The Mb reference point is defined in accordance with TS 23.002 and is Ipv6 based.
6.1.2 Interworking functional entities p. 30
6.1.2.1 Signalling Gateway Function (SGW) p. 30
This component performs the call related signalling conversion to or from BICC/ISUP based MTP transport networks to BICC/ISUP based SCTP/IP transport networks, and forwards the converted signalling to or from the MGCF. The functionality within SGW shall be in accordance with TS 23.002.
6.1.2.2 Media Gateway Control Function (MGCF) p. 30
This is the component within the IM CN subsystem, which controls the IM-MGW, and also performs SIP to BICC or SIP to ISUP call related signalling interworking.
The functionality defined within MGCF shall be defined in accordance with TS 23.002.
6.1.2.3 IP Multimedia - Media Gateway Function (IM-MGW) p. 31
This is the component within the IM CN subsystem, which provides the interface between the PS domain and the CS domain, and it shall support the functions as defined in accordance with TS 23.002.
6.2 Control plane interworking model p. 31
Within the IM CN subsystem, the 3GPP profile of SIP is used to originate and terminate IM sessions to and from the UE.
External CS networks use BICC or ISUP to originate and terminate voice calls to and from the IM CN subsystem.
Therefore, in order to provide the required interworking to enable inter network session control, the control plane protocols shall be interworked within the IM CN subsystem. This function is performed within the MGCF (see clause 6.1.2).
6.3 User plane interworking model p. 31
Within the IM CN subsystem, Ipv6, and framing protocols such as RTP, are used to transport media packets to and from the IM CN subsystem entity like UE or MRFP.
External legacy CS networks use circuit switched bearer channels like TDM circuits (e.g. 64 kbits PCM), ATM/AAL2 circuit or IP bearers to carry encoded voice frames, to and from the IM CN subsystem.
Other CN networks use ATM/AAL 1 or AAL 2 or IP as a backbone, with different framing protocols.
Therefore, in order to provide the required interworking to enable media data exchange, the user plane protocols shall be translated within the IM CN subsystem. This function is performed within the IM-MGW (see clause 6.1.2).