Content for TS 26.150 Word version: 18.0.0
5 Protocols and procedures for optimized feed reception
5.1 Introduction
5.2 Syndicated Feed Discovery
5.2.1 Feed Discovery using an external UE application
5.2.2 Feed Discovery using the SFR enabled Feed Reader
...
...
5 Protocols and procedures for optimized feed reception p. 9
5.1 Introduction p. 9
SFR is a profile of the DCD enabler [5] dedicated to ATOM, RSS content delivery and reception.
5.2 Syndicated Feed Discovery p. 9
Syndicated feed discovery refers to methods for the UE to obtain a list of available syndicated feeds with the intent to activate the reception of one or more syndicated feeds. As part of the optimized delivery of SFR, two methods for discovering a feed (internal discovery and external discovery) are specified.
The UE may discover syndicated feeds either through the SFR enabled Feed Reader, an external UE application (such as the browser) or an external device (such as a browser on a PC). Syndicated feeds can also be discovered through an external device (such as a PC browser) and the syndicated feed reader in the UE may be notified to initiate the reception. This external reception initiation is further defined in section 5.4.3.
Using an external UE application for syndicated feed discovery is defined in 5.2.1. The syndicated feed URI is given to the SFR enabled Feed Reader.
Using the SFR enabled Feed Reader for syndicated feed discovery is defined in section 5.2.2. The Syndicated Feed reader retrieves information about all available feeds from the SFR server.
5.2.1 Feed Discovery using an external UE application p. 9
The user discovers available syndicated feeds using an external UE application such as a UE browser. The external UE application makes the feed URI available to the SFR enabled feed reader.
The SFR enabled Feed Reader gets the feed URI as input and then needs to determine if it is an SFR optimized feed or if it is a regular ATOM/RSS feed. Details for the syndicated feed subscription are defined in clause 5.4.
An example of feed discovery using an external UE application is described in clause A.1 and clause A.4.
The feed can be available at a new SFR server with which the SFR enabled Feed Reader is not configured. In such case the SFR enabled feed reader needs to activate to the new SFR server in order to receive feeds. This activation process is specified in sections 5.3.2.2, 5.3.3 and 6.1.1 of [5].
5.2.2 Feed Discovery using the SFR enabled Feed Reader p. 9
The SFR enabled Feed Reader includes methods for feed discovery. The SFR enabled Feed Reader is already activated and registered to an existing SFR server. The syndicated feed reader receives a list of available syndicated feeds from the SFR server. An initial list, the Channel-Guide List, of syndicated feeds is received with the ApplicationRegistrationResponse message (see clause 5.3).
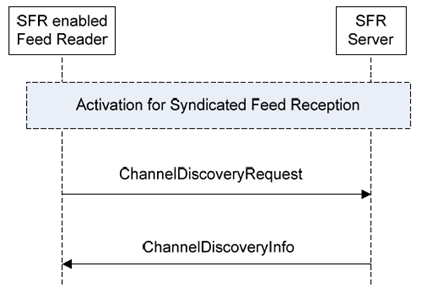
The SFR enabled Feed Reader uses a subset of Channel Discovery methods defined in section 7.1.3.10 of [5].
Information Elements (IE) of the ChannelDiscoveryRequest Message:
- Message-ID: Mandatory in OMA DCD and SFR.
- Session-ID; Mandatory in OMA DCD and SFR.
- Channel-Metadata: Mandatory in OMA DCD and SFR. The relevant subset for SFR is defined in clause 5.7.
- Session-ID; Mandatory in OMA DCD and SFR.
- Message-ID: Mandatory in OMA DCD and SFR.
- Channels-added: Conditional in OMA DCD and SFR.
- Channels-removed: Conditional in OMA DCD and SFR.
- Channels-updated: Conditional in OMA DCD and SFR.