Content for TS 23.334 Word version: 17.2.0
1…
4…
5…
5.11…
5.12…
5.14…
5.18…
5.19…
5.20…
5.21…
6…
6.1.6…
6.1.11…
6.2…
6.2.10…
6.2.10.3.1.2
6.2.10.3.2
6.2.10.4…
6.2.10.4.3…
6.2.10.5
6.2.10.6…
6.2.10A…
6.2.13…
6.2.14…
6.2.14.3
6.2.14.4…
6.2.15…
6.2.17…
6.2.17.3…
6.2.17.5…
6.2.18…
6.2.20
6.2.21…
6.2.22…
6.2.22.3…
6.2.22.3.2
6.2.23
6.2.24
6.2.25
7
8…
8.3
8.4
8.5…
8.23…
6.2.10.3.2 End-to-access-edge security for conferencing (BFCP) p. 103
6.2.10.3.2.1 IMS UE originating procedures for e2ae p. 103
Figure 6.2.10.3.2.1.1.1 shows the originating session set-up procedures for one or more BFCP media stream(s) using e2ae security.
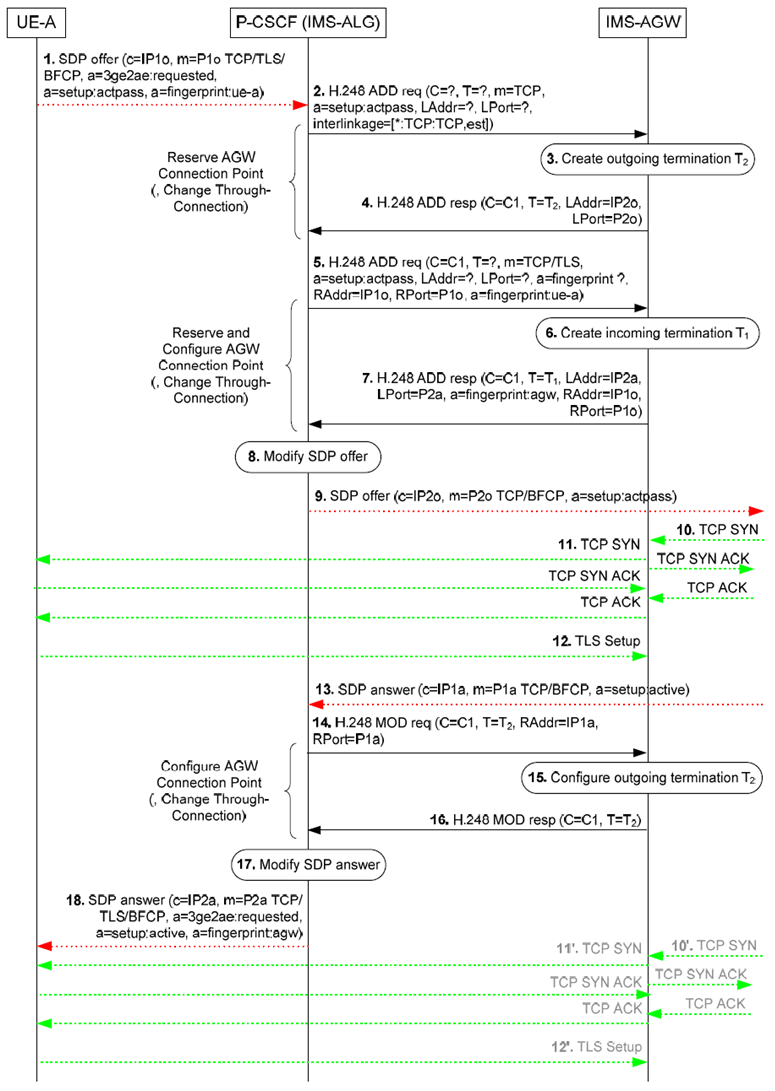
Figure 6.2.10.3.2.1.1.1: Originating example call flow for e2ae security for BFCP where an incoming TCP bearer establishment triggers an outgoing TCP bearer establishment
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
The IMS UE A performs an IMS originating session set-up according to TS 23.228, with modifications as described in TS 33.328.
The procedure in the above Figure for requesting e2ae security for a media stream is described step-by-step with an emphasis on the additional aspects for IMS-ALG and IMS-AGW of media protection using TLS.
Step 1.
IMS UE A sends an SDP offer for a media stream containing cryptographic information, together with an "a=3ge2ae:requested" SDP attribute for the BFCP-related SDP m-line, to the P CSCF (IMS ALG). For e2ae protection of BFCP the cryptographic information contained in the SDP offer consists of the fingerprint of the certificate of IMS UE A in accordance to RFC 4975. For each media stream that uses transport "TCP/TLS/BFCP", the P CSCF (IMS ALG) checks for the presence of the "a=3ge2ae:requested" SDP attribute. If that indication is present and the P CSCF (IMS ALG) indicated support of e2ae-security for BFCP during registration, the P CSCF (IMS ALG) allocates the required resources, includes the IMS AGW in the media path and proceeds as specified in this clause.
Step 2.-4.
The IMS-ALG uses the "Reserve AGW Connection Point" procedure to request a termination for "TCP" media towards the core network. To indicate that the IMS-AGW shall operate in TCP Proxy mode, the IMS-ALG provides "a=setup:actpass" attribute. The IMS-ALG sets the interlinkage topology on the termination T2 to configure the IMS-AGW to use the TCP connection establishment request (TCP SYN) received at the termination T2 as a trigger to send a TCP connection establishment on the termination T1.
Step 5.-7.
The IMS-ALG uses the "Reserve And Configure AGW Connection Point" procedure to request a termination for "TCP/TLS" media towards the access network. In the remote descriptor, it provides the IP address, port and fingerprint attribute received from the UE containing the fingerprint of the UE's certificate in accordance to RFC 4975. This instructs the IMS AGW to verify during the subsequent TLS handshake with the IMS UE that the fingerprint of the certificate passed by the IMS UE during this TLS handshake matches the fingerprint passed by the P CSCF (IMS ALG) to the IMS AGW. In turn, the IMS AGW communicates the fingerprint of the certificate it is going to use for setting up protection for this media stream to the P CSCF (IMS ALG). To indicate that the IMS-AGW shall operate in TCP Proxy mode, the IMS-ALG provides "a=setup:actpass" attribute.
Step 8.
The P CSCF (IMS ALG) changes the transport from "TCP/TLS/BFCP" to "TCP/BFCP" in the SDP offer, removes the "a=3ge2ae:requested" SDP attribute and the fingerprint SDP attribute, and inserts the address information received from the IMS-AGW.
Step 9.
The P CSCF (IMS ALG) forwards the SDP offer.
Step 10.
The remote peer chooses to become the active party in the TCP connection establishment and sends a TCP SYN to establish the TCP connection. If the P-CSCF (IMS-ALG) indicated to the IMS-AGW at step 2 that it shall ignore any incoming TCP connection establishment requests (TCP SYN), e.g. to enable a remote source transport address filtering, or if the P-CSCF (IMS-ALG) did not indicate to the IMS-AGW at step 2 that it shall latch onto the required destination address via the source address/port of the incoming media, the IMS-AGW shall drop the TCP SYN received from the remote peer.
If the TCP SYN is not answered before a timer expiry, the remote peer will send the TCP SYN a second time (step 10'). The IMS AGW will answer a repeated TCP SYN if it is received after step 14 (step 10').
The IMS-AGW answers the TCP SYN and the remote peer completes the TCP connection establishment.
Step 11.
The IMS-AGW uses the TCP SYN received at the termination T2 (at step 10 or step 10' if the TCP SYN is dropped at step 10) as a trigger to send a TCP SYN towards the UE to establish a TCP connection (effectively making the IMS-AGW acting as the TCP client towards the UE). The UE answers the TCP SYN and the IMS-AGW completes the TCP connection establishment.
Step 12.
Upon completion of the TCP connection establishment, the UE B starts the establishment of the TLS session. The IMS-AGW needs to wait until step 14 to verify the received fingerprint.
Step 13.
The P CSCF (IMS ALG) receives the SDP answer.
Step 14.-16.
The IMS-ALG uses the "Configure AGW Connection Point" procedure to configure the termination towards the core network with remote address information. If the P-CSCF (IMS-ALG) indicated to the IMS-AGW at step 2 that it shall ignore any incoming TCP connection establishment requests (TCP SYN), the IMS-ALG indicates to the IMS-AGW to accept incoming TCP connection establishment (TCP SYN) only from the indicated remote transport address.
Step 17.
The P CSCF (IMS ALG) modifies the SDP answer before sending it to the UE A. The P CSCF (IMS ALG) sets the transport to "TCP/TLS/BFCP" and includes the fingerprint of the IMS AGW's certificate in accordance to RFC 4975.
Step 18.
The P-CSCF (IMA-ALG) then sends the updated SDP answer to IMS UE A. After receiving this message IMS UE A completes the media security setup.
6.2.10.3.2.2 IMS UE terminating procedures for e2ae p. 106
Figure 6.2.10.3.2.2.1.1 shows the terminating session set-up procedures for one or more BFCP media stream(s) using e2ae security.
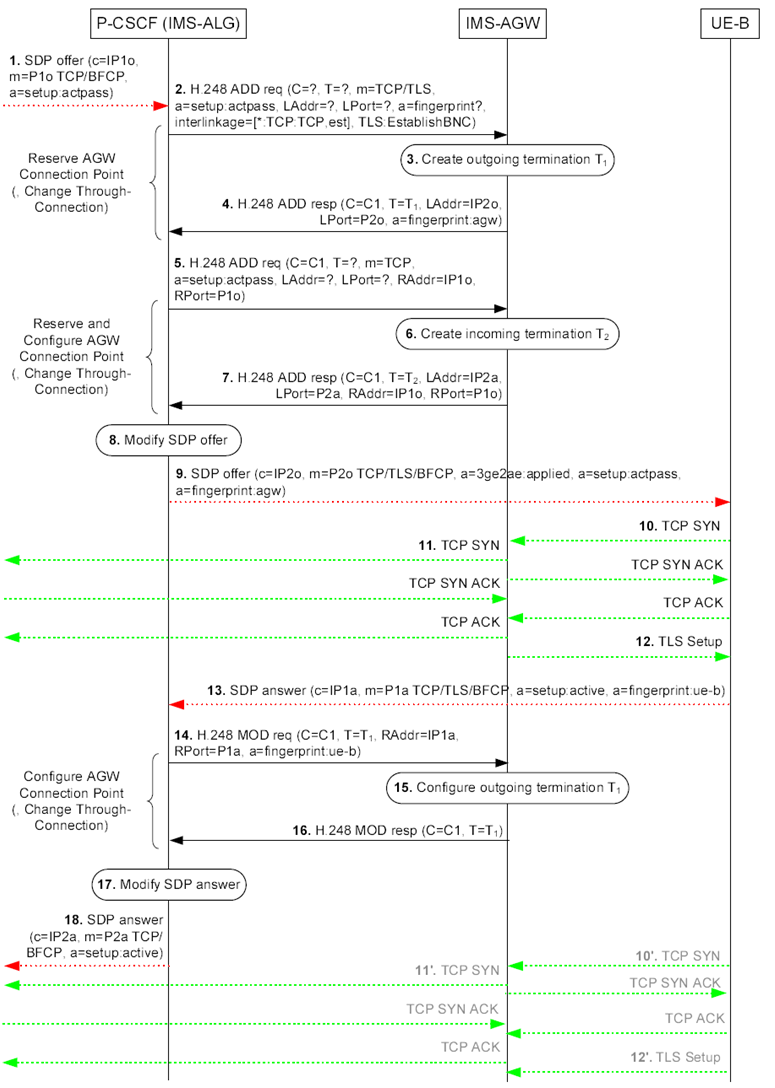
Figure 6.2.10.3.2.2.1.1: Terminating example call flow for e2ae security for MSRP where an incoming TCP bearer establishment triggers an outgoing TCP bearer establishment
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
The IMS UE B performs an IMS terminating session set-up according to TS 23.228, with modifications as described in TS 33.328.
The procedure in the above Figure for requesting e2ae security for a media stream is described step-by-step with an emphasis on the additional aspects for IMS-ALG and IMS-AGW of media protection using TLS.
Step 1.
The P CSCF (IMS ALG) receives an SDP offer for an MSRP media stream. For each BFCP media stream offered with transport "TCP/BFCP", if both the IMS UE and P CSCF (IMS ALG) indicated support for e2ae-security for BFCP during registration, the P CSCF (IMS ALG) allocates the required resources, includes the IMS AGW in the media path and proceeds as specified in this clause.
Step 2.-4.
The IMS-ALG uses the "Reserve AGW Connection Point" procedure to request a termination for "TCP/TLS" media towards the access network. The IMS-ALG configures the IMS-AGW with the request to start the establishment of the TLS session once the TCP connection is established (effectively making the IMS-AGW acting as the TLS client). . To indicate that the IMS-AGW shall operate in TCP Proxy mode, the IMS-ALG provides "a=setup:actpass" attribute. The IMS-ALG sets the interlinkage topology on the termination T1 to configure the IMS-AGW to use the TCP connection establishment request (TCP SYN) received at the termination T1 as a trigger to send a TCP connection establishment on the termination T2.
The IMS AGW communicates the fingerprint of the certificate it is going to use for setting up protection for this media stream to the P CSCF (IMS ALG).
Step 5.-7.
The IMS-ALG uses the "Reserve And Configure AGW Connection Point" procedure to request a termination for "TCP" media towards the core network. To indicate that the IMS-AGW shall operate in TCP Proxy mode, the IMS-ALG provides "a=setup:actpass" attribute.
Step 8.
The P CSCF (IMS ALG) changes the transport from "TCP/ BFCP" to "TCP/TLS/BFCP" in the SDP offer, adds the "a=3ge2ae:applied" SDP attribute and the fingerprint SDP attribute received from the IMS-AGW, and inserts the address information received from the IMS-AGW.
Step 9.
The P CSCF (IMS ALG) forwards the SDP offer.
Step 10.
The UE B chooses to become the active party in the TCP connection establishment and sends a TCP SYN to establish the TCP connection. If the P-CSCF (IMS-ALG) indicated to the IMS-AGW at step 2 that it shall ignore any incoming TCP connection establishment requests (TCP SYN), e.g. to enable a remote source transport address filtering, or if the P-CSCF (IMS-ALG) did not indicate to the IMS-AGW at step 2 that it shall latch onto the required destination address via the source address/port of the incoming media, the IMS-AGW shall drop the TCP SYN received from the UE.
If the TCP SYN is not answered before a timer expiry, the UE will send the TCP SYN a second time (step 10'). The IMS AGW will answer a repeated TCP SYN if it is received after step 14 (step 10').
The IMS-AGW answers the TCP SYN and the remote peer completes the TCP connection establishment.
Step 11.
The IMS-AGW sends a TCP SYN towards the core network to establish a TCP connection. The remote peer answers the TCP SYN and the IMS-AGW completes the TCP connection establishment.
Step 12.
Upon completion of the TCP connection establishment, the IMS-AGW starts the establishment of the TLS session. The IMS-AGW needs to wait until step 14 to verify the received fingerprint.
Step 13.
The P CSCF (IMS ALG) receives the SDP answer. It contains the fingerprint attribute with the UE's certificate in accordance to RFC 4975.
Step 14.-16.
The IMS-ALG uses the "Configure AGW Connection Point" procedure to configure the termination towards the UE B with remote address information. In the remote descriptor, it also provides fingerprint attribute received from the UE. This instructs the IMS AGW to verify during the TLS handshake with the IMS UE (see step 12) that the fingerprint of the certificate passed by the IMS UE during this TLS handshake matches the fingerprint passed by the P CSCF (IMS ALG) to the IMS AGW. If the P-CSCF (IMS-ALG) indicated to the IMS-AGW at step 2 that it shall ignore any incoming TCP connection establishment requests (TCP SYN), the IMS-ALG indicates to the IMS-AGW to accept incoming TCP connection establishment (TCP SYN) only from the indicated remote transport address.
Step 17.
The P CSCF (IMS ALG) modifies the SDP answer before sending it to the core network. The P CSCF (IMS ALG) sets the transport to "TCP/ BFCP" and removes the SDP fingerprint attribute.
Step 18.
The P CSCF (IMS ALG) then sends the updated SDP answer to core network.