Content for TS 23.283 Word version: 18.1.0
1…
10…
10.2…
10.2.2…
10.2.3…
10.3…
10.3.3…
10.3.3.7…
10.3.4…
10.3.4.4…
10.3.5…
10.3.5.8…
10.3.6…
10.3.7…
10.3.7.5…
10.3.8…
10.4…
10.4.4…
10.5…
10.5.7…
10.6…
10.6.2…
10.6.2.3…
10.6.3…
10.6.4…
10.7…
10.8…
10.11…
10.11.4…
10.12…
10.14…
10.15…
10 Procedures and information flows
10.1 Affiliation
10.1.1 Information flows for affiliation
10.1.1.1 General
10.1.1.2 IWF group affiliation request
10.1.1.3 IWF group affiliation response
10.1.1.4 IWF group de-affiliation request
10.1.1.5 IWF group de-affiliation response
10.1.2 Affiliation procedures
10.1.2.1 General
10.1.2.2 Group affiliation to a group defined in the MC system
10.1.2.3 Group de-affiliation from a group defined in the MC system
10.1.2.4 Group affiliation to group defined in the LMR system
10.1.2.5 Group de-affiliation from a group defined in the LMR system
...
...
10 Procedures and information flows p. 16
10.1 Affiliation p. 16
10.1.1 Information flows for affiliation p. 16
10.1.1.1 General p. 16
The following subclauses define information flows for affiliation on the IWF-1 interface. Affiliation related information flows on reference points other than IWF-1 are defined in TS 23.280.
10.1.1.2 IWF group affiliation request p. 16
Table 10.1.1.2-1 describes the information flow IWF group affiliation request between the IWF and an MC service server and between an MC service server and the IWF.
| Information Element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| MC service ID | M | The MC service ID of the originator (LMR user or MC service user) who triggers the MC service group affiliation request. (see NOTE) |
| MC service group ID list | M | A list of one or more MC service group IDs to which the originator intends to affiliate and is defined in the destination MC system. |
| MC service type M | M | The type(s) of service(s) for which the request is intended (e.g. MCData or MCPTT or both) |
10.1.1.3 IWF group affiliation response p. 16
Table 10.1.1.3-1 describes the information flow IWF group affiliation response between the IWF and an MC service server and between an MC service server and the IWF.
| Information Element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| MC service ID | M | The MC service ID of the originator (LMR user or MC service user) who triggered the MC service group affiliation request. |
| MC service group ID list | M | A list of one or more MC service group IDs to which the originator intends to affiliate and is defined in the destination MC system. |
| Affiliation status per MC service group ID | M | Indicates the affiliation result for every MC service group ID in the list. |
10.1.1.4 IWF group de-affiliation request p. 16
Table 10.1.1.4-1 describes the information flow IWF group de-affiliation request between the IWF and an MC service server and between an MC service server and the IWF.
| Information Element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| MC service ID | M | The MC service ID of the originator (LMR user or MC service user) who triggers the MC service group de-affiliation request. (see NOTE) |
| MC service group ID list | M | A list of one or more MC service group IDs to which the originator intends to de-affiliate. |
| MC service type | M | The type(s) of service(s) for which the request is intended (e.g. MCData or MCPTT or both) |
10.1.1.5 IWF group de-affiliation response p. 17
Table 10.1.1.5-1 describes the information flow IWF group de-affiliation response between the IWF and an MC service server and between an MC service server and the IWF.
| Information Element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| MC service ID | M | The MC service ID of the originator (LMR user or MC service user) who triggers the MC service group de-affiliation request. |
| MC service group ID list | M | A list of one or more MC service group IDs to which the originator intends to de-affiliate. |
| De-affiliation status per MC service group ID | M | Indicates the de-affiliation result for every MC service group ID in the list. |
10.1.2 Affiliation procedures p. 17
10.1.2.1 General p. 17
When an interworking group is defined in the MCPTT system, the LMR system (via the IWF) informs the MCPTT system of group affiliations in one of the following ways:
- Every group affiliation in the LMR system results in an affiliation sent to the MCPTT system, which contains the identity (with appropriate translation by the IWF) of the affiliating group member; or
- A group affiliation is sent on behalf of the group's LMR users (via the IWF) to the MCPTT system when the first group member affiliates to the designated group in the LMR system, and a group de-affiliation is sent on behalf of the group's LMR users (via the IWF) to the MCPTT system when the last group member de-affiliates, and no other group affiliation signalling is sent.
- the group list in the MCPTT system contains the IWF's MCPTT ID. This ID is recognized (through configuration) as having the ability to affiliate on behalf of the group's LMR users associated with this IWF;
- the IWF affiliates with its MCPTT ID to the group defined in the MCPTT system;
- the MCPTT system recognizes the affiliation as being from an IWF on behalf of the group's LMR users;
-
when the IWF has affiliated to the group, the MCPTT system:
- considers any LMR user associated with the IWF to be affiliated to the group on which the IWF has affiliated. The IWF's users need not be listed ahead of time in the group list for this group in the MCPTT system;
- allows requests such as call setup or floor request, from MCPTT IDs,with or without functional alias, representing LMR users associated with the IWF for actions on the group to which the IWF has affiliated;
- does not carry out an additional affiliation on behalf of LMR users when those users make call requests, and therefore does not send additional messages to those users (e.g. release messages to both the IWF affiliated identity and the LMR user identity performing the action), via the IWF, during call processing;
- recognizes which LMR users are associated with the IWF because their MCPTT IDs belong to the same system as the IWF; and,
- uses special rules for the IWF for limits such as "Limitation of number of affiliations per user (N2)".
-
requests from LMR users to the MCPTT system are identified with their individual MCPTT IDs (as translated by the IWF):
- a user in the LMR system can affiliate on its own (via the IWF) as long as the user is a group member (i.e. in the group list), even if the IWF has affiliated to the group.
- the IWF may make requests on behalf of a group's LMR users using the IWF MCPTT ID like a normal group member including, for example, group join requests for groups using the chat model;
- the IWF is not allowed to affiliate to a group that is not configured with the IWF's MCPTT ID in the group member list; and,
- if the IWF has not affiliated to an MCPTT group, then call requests to this group from LMR users on the system associated with the IWF, can only be accepted if the LMR user's MCPTT ID is in the group list, and has already affiliated.
10.1.2.2 Group affiliation to a group defined in the MC system p. 18
The LMR system may affiliate its group members to an interworking group defined in the MC system via the IWF.
For group regroup, the affiliated group members are automatically affiliated to the temporary group.
The signalling procedure of interworking group affiliation is described in Figure 10.1.2.2-1.
Pre-conditions:
- The group to be affiliated to is defined in the MC system.
- The IWF is connected to and is authorized to interwork with the MC system.
- The interworking group information is available at the IWF.
- The mapping relationship of group and user identities between MC system and the LMR system has been configured at the IWF.
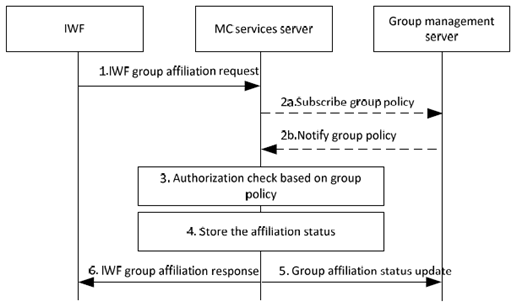
Figure 10.1.2.2-1: Group affiliation to a group defined in the MC system
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
Step 1.
The IWF sends an IWF group affiliation request to the MC service server on behalf of the LMR system.
Step 2a.
The MC service server checks if the group policy is locally cached. If the group policy is not locally cached on the MC service server then the MC service server requests the group policy from the group management server.
Step 2b.
The MC service server receives the group policy from the group management server.
Step 3.
Based on the group policy, the MC service server checks if the MC service group(s) is not disabled and if the user identified by the MCPTT ID supplied by the IWF is authorised to affiliate to the requested MC service group(s).
Step 4.
Based on the group policy and user subscription, the MC service server affiliates the IWF to the group. If a separate affiliation for each LMR user is expected, the status of the affiliating user is stored by the MC service server as the status associated with an MC service ID provided by the IWF that corresponds to the identity of that LMR user. If a separate affiliation for each LMR user is not expected, an affiliation status for the group using the MC service ID provided by the IWF is stored.
Step 5.
The MCPTT server sends the group affiliation status update message to the group management server, the group management server stores and updates the group affiliation status.
Step 6.
The MC service server returns an IWF group affiliation response to the IWF.
10.1.2.3 Group de-affiliation from a group defined in the MC system p. 19
The signalling procedure of interworking group de-affiliation from a group defined in the MC system is described in Figure 10.1.2.3-1.
The LMR system manages the individual de-affiliation requests from the LMR users. The LMR system can de-affiliate its group members from the interworking group via the IWF.
Pre-conditions:
- The mapping relationship of group and user identities between the MC system and the LMR system has been configured at the IWF.
- The affiliation procedure described in subclause 10.1.2.2 was previously performed.
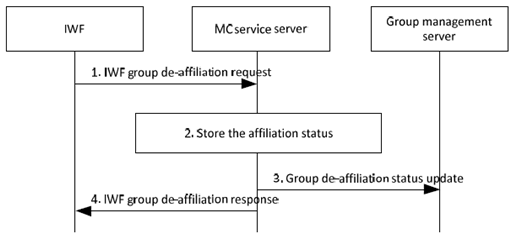
Figure 10.1.2.3-1: Group de-affiliation from group defined in the MC system
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
Step 1.
The IWF sends an IWF group de-affiliation request to the MC service server on behalf of the LMR system.
Step 2.
If a separate de-affiliation from each LMR user is expected and based on the group policy and user subscription, the MC service server may de-affiliate the LMR group member from the group. Further, the MC service server may store the affiliation status of the user(s) for the requested MC service group(s). If a separate de-affiliation from each LMR user is not expected, the de-affiliation signalling de-affiliates the IWF and therefore the entire LMR system from the group.
Step 3.
The MC service server sends the group de-affiliation status update message to the group management server, the group management server stores and updates the group affiliation status.
Step 4.
The MC service server returns an IWF group de-affiliation response to the IWF.
10.1.2.4 Group affiliation to group defined in the LMR system p. 20
The MC system may affiliate its group members to an interworking group defined in the LMR system via the IWF.
The signalling procedure of group affiliation via the IWF is described in Figure 10.1.2.4-1.
Pre-conditions:
- The group to be affiliated to is defined in the LMR system.
- The IWF is connected to and is authorized to work with the MC system.
- The mapping relationship of group and user identities between the MC system and the LMR system has been configured at the IWF.
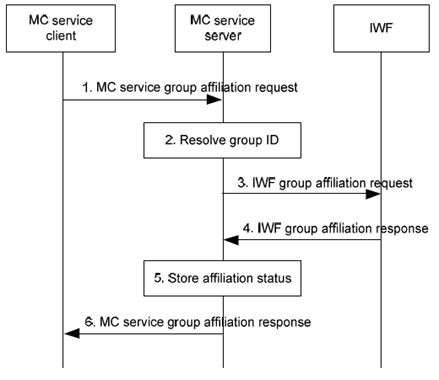
Figure 10.1.2.4-1: Group affiliation to group defined in the LMR system
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
Step 1.
The MC service client sends a MC service group affiliation request, including the MC service group ID(s), to the MC service server.
Step 2.
The MC service server checks if the MC service group ID(s) is an interworking group defined in the LMR system.
Step 3.
The MC service server sends an IWF group affiliation request to the IWF.
Step 4.
The IWF returns an IWF group affiliation response to the MC service server, informing the successful affiliation to the LMR group.
Step 5.
The MC service server stores the group affiliation status of the MC service client for the requested interworking group.
Step 6.
The MC service server sends an MC service group affiliation response to the MC service client.
10.1.2.5 Group de-affiliation from a group defined in the LMR system p. 21
The signalling procedure of interworking group de-affiliation from a group defined in the LMR system is described in Figure 10.1.2.5-1.
The MC system manages the individual de-affiliation requests from the MC service users. The MC system may de-affiliate its group members from the interworking group via the IWF.
Pre-conditions:
- The mapping relationship of group and user identities between the MC system and the LMR system has been configured at the IWF.
- The affiliation procedure described in subclause 10.1.2.4 was previously performed.
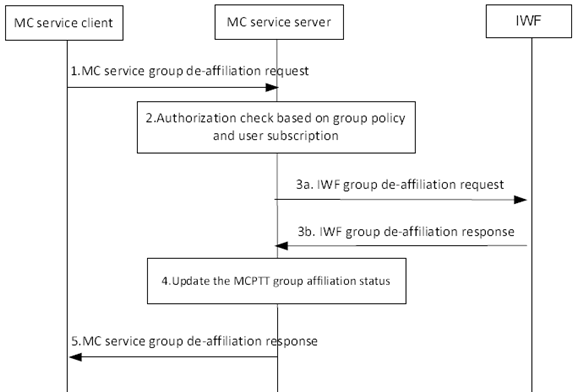
Figure 10.1.2.5-1: Group de-affiliation from a group defined in the LMR system
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
Step 1.
The MC service client of the MC service user sends an MC service group de-affiliation request to the MC service server. The MC service client shall provide the initiating MC service ID and the MC service group ID(s) being de-affiliated from.
Step 2.
Based on the user subscription and stored group policy, the MC service server checks if the user of the MC service client is affiliated to the requested MC service group(s). The MC service server checks if the MC service group(s) is an interworking group.
Step 3a.
If the MC service group(s) is an interworking group, the MC service server sends an IWF group de-affiliation request to the IWF.
Step 3b.
The IWF returns an IWF group de-affiliation response to the MC service server.
Step 4.
If the user of the MC service client is authorized to de-affiliate from the requested MC service group(s), the MC service server removes the affiliation status of the user for the requested MC service group(s).
Step 5.
The MC service server returns an MC service group de-affiliation response to the MC service client.