Content for TS 23.283 Word version: 18.1.0
1…
10…
10.2…
10.2.2…
10.2.3…
10.3…
10.3.3…
10.3.3.7…
10.3.4…
10.3.4.4…
10.3.5…
10.3.5.8…
10.3.6…
10.3.7…
10.3.7.5…
10.3.8…
10.4…
10.4.4…
10.5…
10.5.7…
10.6…
10.6.2…
10.6.2.3…
10.6.3…
10.6.4…
10.7…
10.8…
10.11…
10.11.4…
10.12…
10.14…
10.15…
10.2.2 Group regrouping
10.2.2.1 General
10.2.2.2 MC system initiates the group regroup
10.2.2.3 IWF initiates the group regroup
10.2.2.4 Ownership of the group regroup
10.2.2.5 Simultaneous group regroup requests from each side of the IWF-1 interface
10.2.2.6 Resolution of vocoder and encryption mode for the group regroup
...
...
10.2.2 Group regrouping p. 26
10.2.2.1 General p. 26
The procedures in TS 23.280 are followed, but with changes required for interworking. The IWF will behave on the interface as if it is a peer MC service server with a peer group management client and peer group management server.
Exceptions to the TS 23.280 procedures are detailed in the subclauses below.
10.2.2.2 MC system initiates the group regroup p. 26
The MC system can initiate a group regroup that includes groups defined at the IWF. The IWF is informed and may reject the regroup if conditions do not allow it to support the regroup. This is described in Figure 10.2.2.2-1.
Pre-conditions:
- The group management client has retrieved the group configurations of the groups to be regrouped.
- At least one MC service group has been defined in the MC system.
- At least one MC service group has been defined in the IWF.
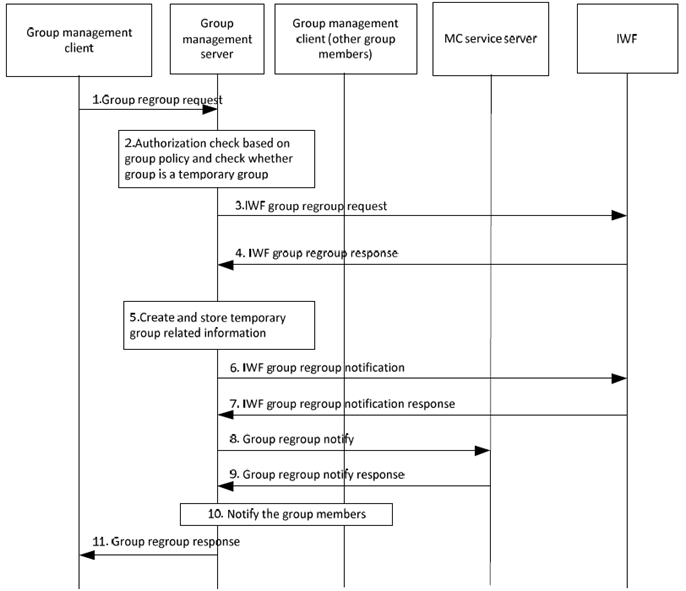
Step 1.
The group management client of the MC service user (e.g. dispatcher) requests group regroup operation to the group management server (which is the group management server of one of the MC service groups to be regrouped). The identities of the groups being combined shall be included in this message. The group management client may indicate the security level required for the temporary group. The group management client may indicate the priority level required for the temporary group.
Step 2.
The group management server checks whether group regroup operation is performed by an authorised MC service user, based on group policy. The group management server checks whether the group is a temporary group. If the group is a temporary group, then the group regrouping will be rejected, otherwise the group regrouping can proceed.
Step 3.
The group management server forwards the IWF group regroup request to the IWF with the information about the IWF's groups.
Step 4.
The IWF provides an IWF group regroup response. Due to security aspects concerning sharing information among different MC systems, the IWF does not share the users' information of the groups under its management to the group management server. The IWF may reject the IWF group regroup response. (e.g. if one of its constituent groups is in the emergency state or is already in a regroup, if the IWF does not support temporary groups or the IWF does not support group regrouping)
Step 5.
The group management server creates and stores the information of the temporary group, including the temporary MC service group ID, off-network information, and the MC service IDs of the groups being combined, the priority level of the temporary group, and the security level of the temporary group. If the authorised MC service user does not specify the security level and the priority level, the group management server shall set the lower security level and the higher priority of the constituent groups.
Step 6.
The group management server notifies the IWF about its group regroup operation.
Step 7.
The IWF acknowledges the group management server.
Step 8.
The group management server notifies the MC service server of the temporary group creation with the information of the constituent groups.
Step 9.
The MC service server acknowledges the notification from the group management server.
Step 10.
The group management server notifies the MC service group members of the constituent MC service groups of the group management server, possibly with an indication of lower security level.
Step 11.
The group management server provides a group regroup response to the group management client of the authorised MC service user (e.g. dispatcher).
10.2.2.3 IWF initiates the group regroup p. 28
The procedure in TS 23.280 is followed, except for steps 1 and 2. The IWF will behave on the interface as if it is a peer MC service server with a peer group management server. This is described in Figure 10.2.2.3-1.
Pre-conditions:
- At least one MC service group has been defined in the MC system.
- At least one MC service group has been defined in the IWF.
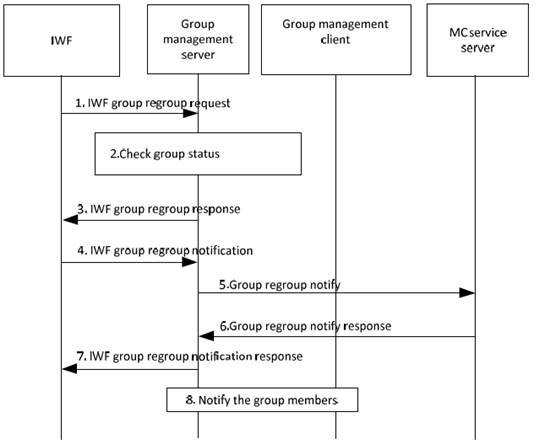
Step 1.
The IWF sends an IWF group regroup request to the group management server.
Step 2.
The group management server checks whether the group can be included in a temporary group.
Step 3.
The group management server provides an IWF group regroup response.
Step 4.
The IWF notifies the group management server regarding the temporary group creation with information of the constituent groups.
Step 5.
The group management server notifies the MC service server regarding the temporary group creation with the information of the constituent groups.
Step 6.
The MC service server acknowledges the notification from the group management server. The MC service server may reject the IWF group regroup, e.g. if one of its constituent groups is already in a regroup.
Step 7.
The group management server acknowledges the notification from the IWF.
Step 8.
The group management server notifies the MC service group members of the constituent MC service groups of the group management server, possibly with an indication of a lower security level.
10.2.2.4 Ownership of the group regroup p. 29
The group management server that performs the group regroup operation owns the temporary group created by the regroup, as implied in TS 23.280.
10.2.2.5 Simultaneous group regroup requests from each side of the IWF-1 interface p. 29
To prevent routing issues and complexity that could result from regrouping the same users from both sides of the interface, the following rules can be applied:
- If group regrouping signalling using temporary groups is used on the MC system, the IWF must prevent the regroup signalling from propagating to the LMR system if the LMR system does not support regrouping;
- the IWF must handle the translation between temporary group identities on the MC system and the original interworking group identities used on the LMR system; and
- the regrouping rules in subclause 10.2.4.4 of TS 23.280 also apply.
10.2.2.6 Resolution of vocoder and encryption mode for the group regroup p. 29
If one of the LMR groups to be included in a group regroup requires the use of LMR E2EE the preferred voice codecs for an MCPTT temporary group should be LMR codecs. If any of the mission critical users to be included in this MCPTT temporary group do not support LMR E2EE or the preferred LMR codecs, voice calls using LMR E2EE will fail for those users.