Content for TS 23.271 Word version: 18.0.0
1…
5…
6…
6.2…
7…
8…
9…
9.1.1A…
9.1.2…
9.1.5…
9.1.6…
9.1.8…
9.1.9…
9.1.12…
9.1.13…
9.1.15…
9.1.19…
9.2…
9.2.2…
9.2.3…
9.3…
9.4…
9.5…
9.6…
10…
11…
A…
B…
E
F…
9.2.2 Mobile Originating Location Request, Packet Switched (PS-MO-LR)
9.2.2.1 Location Preparation Procedure
9.2.2.2 Positioning Measurement Establishment Procedure
9.2.2.3 Location Calculation and Release Procedure
...
...
9.2.2 Mobile Originating Location Request, Packet Switched (PS-MO-LR) p. 125
The following procedure shown in Figure 9.8 allows an UE to request either its own location and optionally, velocity; location assistance data or broadcast assistance data message ciphering keys from the network. Location assistance data may be used subsequently by the UE to compute its own location throughout an extended interval using a mobile based position method. A ciphering key enables the UE to decipher other location assistance data broadcast periodically by the network. The PS MO LR may be used to request ciphering keys or GNSS assistance data. The procedure may also be used to enable an UE to request that its own location be sent to an external LCS client.
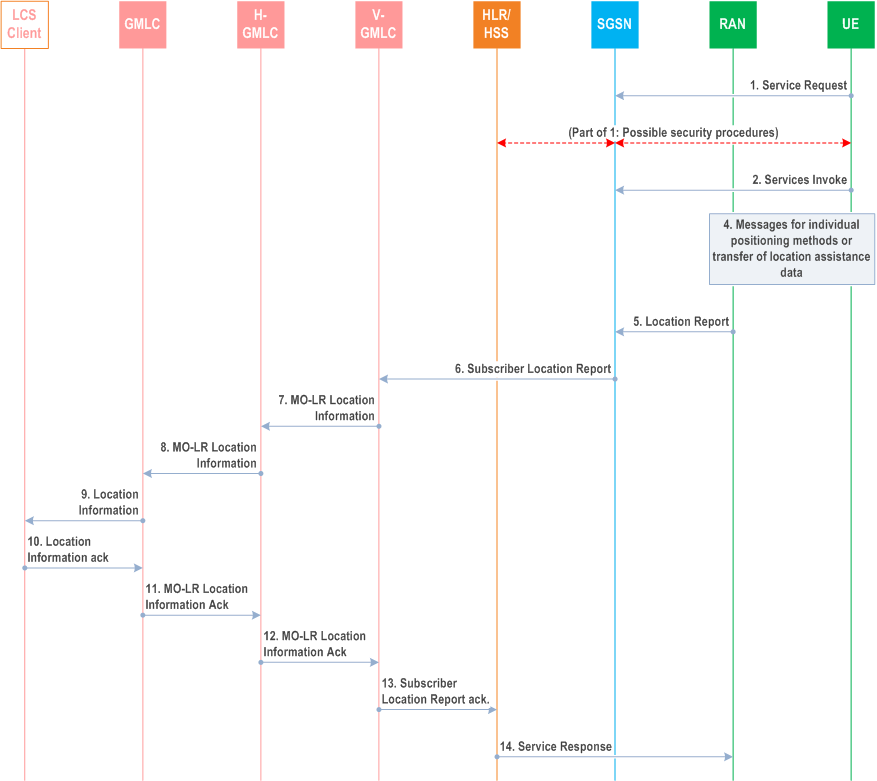
9.2.2.1 Location Preparation Procedure p. 125
Step 1.
In UMTS, if the UE is in idle mode, the UE requests a PS signalling connection and sends a Service request indicating signalling to the SGSN via the RAN. If the UE already has PS signalling connection, the UE does not need to send Service request. Security functions may be executed. These procedures are described in TS 23.060. In GSM this signalling step is not needed.
Step 2.
The UE sends a LCS PS-MO-LR Location Services invoke message to the SGSN. Different types of location services can be requested: location estimate of the UE, location estimate of the UE to be sent to an external LCS client, location assistance data or broadcast assistance data message ciphering keys. If the UE is requesting its own location or that its own location be sent to an external LCS client, this message carries LCS requested QoS information (e.g. accuracy, response time, LCS QoS Class), the requested maximum age of location and the requested type of location (e.g. "current location", "current or last known location"). If the UE is requesting that its location be sent to an external LCS client, the message shall include the identity of the LCS client and may include the address of the GMLC through which the LCS client should be accessed. In addition, a Service Identity indicates which MO-LR service of the LCS Client is requested by the UE may be included. The message also may include a pseudonym indicator to indicate a pseudonym should be assigned by the network and transferred to the LCS Client as the UE's identity. If the UE is instead requesting location assistance data or ciphering keys, the message specifies the type of assistance data or deciphering keys and the positioning method for which the assistance data or ciphering applies. For an LCS PS-MO-LR Location Services invoke, the SGSN shall assign a GMLC address, i.e. V-GMLC address, which is stored in the SGSN. If a V-GMLC address is not available, the SGSN may reject the location request. The SGSN verifies the subscription profile of the UE and decides if the requested service is allowed or not.
Step 3.
In case the requested type of location is "current or last known location" and the requested maximum age of location information is sent from UE, the SGSN verifies whether it stores the previously obtained location estimate of the target UE. If the SGSN stores the location estimate and the location estimate satisfies the requested maximum age of location, this step and steps 4 and 5 may be skipped. Otherwise the SGSN sends a Location Request message to the RAN associated with the Target UE's location. The message indicates whether a location estimate or location assistance data is requested. If the UE's location is requested, the message also includes the requested QoS. If location assistance data is requested, the message carries the requested types of location assistance data. The message carries also location parameters received in the Service Invoke message.
9.2.2.2 Positioning Measurement Establishment Procedure p. 126
Step 4.
If the UE is requesting its own location, the actions described in UTRAN Stage 2, TS 25.305 or GERAN stage 2 TS 43.059 are performed. If the UE is instead requesting location assistance data, the RAN transfers this data to the UE as described in subsequent clauses. The RAN determines the exact location assistance data to transfer according to the type of data specified by the UE, the UE location capabilities and the current cell.
9.2.2.3 Location Calculation and Release Procedure p. 126
Step 5.
When a location estimate best satisfying the requested QoS has been obtained or when the requested location assistance data has been transferred to the UE, the RAN returns a Location Report to the SGSN with an indication whether the obtained location estimate satisfies the requested accuracy or not. This message carries the location estimate or ciphering keys if this was obtained. If a location estimate or deciphering keys were not successfully obtained or if the requested location assistance data could not be transferred successfully to the UE, a failure cause is included in the Location Report.
Step 6.
If the location estimate was successfully obtained, the SGSN shall send a Subscriber Location Report to the V-GMLC assigned in the step 2, carrying the MSISDN/IMSI of the UE, the event causing the location estimate (PS-MO LR) and the location estimate, its age, obtained accuracy indication and the LCS QoS Class requested by the target UE. In addition, the Subscriber Location Report may include the pseudonym indicator, the identity of the LCS Client, the GMLC address and the Service Identity specified by the UE, if available.
Step 7.
Upon receipt of the Subscriber Location Report, the V-GMLC shall determine whether the UE requests transfer of its location estimate to an external LCS Client. If the identity of the LCS Client is not available, this step and steps 8 to 12 are skipped. Otherwise, the V-GMLC shall send the MO-LR Location Information to the H-GMLC (the V-GMLC may query the HLR/HSS of the UE to obtain the address of the H-GMLC), carrying the MSISDN/IMSI of the UE, the event causing the location estimate (PS MO-LR), the location estimate and its age, and the identity of the LCS Client. The pseudonym indicator and/or the GMLC address specified by the UE may also be included if available.
Step 8.
If the pseudonym indicator is included in the MO-LR Location Information, the H-GMLC assigns or asks the PMD to assign a pseudonym to the UE. If the identity of the LCS Client and the GMLC address access to the LCS Client are available, the H-GMLC shall send the MO-LR Location Information to the specified GMLC. If the identity of the LCS Client is available but the GMLC address access to the LCS Client is not available, the H-GMLC determines whether the specified LCS Client is accessible. If yes, the H-GMLC shall send the Location Information to the LCS Client, then the H-GMLC itself act as the specified GMLC, this step and step 11 are skipped. If not, according to the LCS Client identity, the H-GMLC shall determine a GMLC that can access the LCS Client, and send the MO-LR Location Information to the GMLC, carrying the MSISDN or the pseudonym of the UE, the identity of the LCS client, the event causing the location estimate (PS MO-LR), location estimate and its age.
Step 9.
If the identified LCS Client is not accessible, this step and step 10 are skipped. Otherwise the GMLC transfers the location information to the LCS client, carrying the MSISDN/IMSI or the pseudonym of the UE, the event causing the location estimate (PS-MO LR), the Service Identity, if available, and the location estimate and its age, in accordance with the LCS QoS Class requested by the target UE. If the UE requested LCS QoS class was Assured, GMLC sends the result to the LCS client only if the result has been indicated to fulfil the requested accuracy. If the UE requested LCS QoS class was Best Effort, GMLC sends whatever result it received to the LCS client with an appropriate indication if the requested accuracy was not met.
Step 10.
If the LCS Client does not support MO-LR (for temporary or permanent reasons) or can not handle the location estimate of the UE, e.g. the LCS Client does not know the Service Identity, or the UE does not register to the LCS Client, the LCS Client have no corresponding data of the UE, the LCS Client shall return the Location Information ack message to the GMLC or the H-GMLC (in case the LCS Client received Location Information is sent from H-GMLC) with a suitable error cause. Otherwise, the LCS Client handles the location estimate according to the Service Identity, sends the GMLC or the H-GMLC the Location Information ack message signalling that the location estimate of the UE has been handled successfully.
Step 11.
If the identified LCS Client is not accessible, the GMLC sends MO-LR Location Information Acknowledgement to the H-GMLC with an appropriate error cause. Otherwise, the GMLC shall send MO-LR Location Information Acknowledgement to the H-GMLC. The message shall specify whether the location estimate of the UE has been handled successfully by the identified LCS Client, and if not, the corresponding error cause obtained in step 10. The GMLC may record charging information both for the LCS Client and inter-operator revenue charges.
Step 12.
In case the H-GMLC receives the MO-LR Location Information Acknowledgement from the GMLC, it shall forward the MO-LR Location Information Acknowledgement from the GMLC to the V-GMLC, and record charging information both for the UE and inter-working revenue charges.
In case the H-GMLC receives the Location Information Acknowledgement from the LCS Client, it shall send MO-LR Location Information Acknowledgement to the V-GMLC. The message shall specify whether the location estimate of the UE has been handled successfully by the identified LCS Client, and if not, the corresponding error cause obtained in step 10. The H-GMLC shall record charging information both for the UE and inter-working revenue charges.
Step 13.
In case the V-GMLC receives the MO-LR Location Information Acknowledgement from the H-GMLC, the V-GMLC shall record charging information both for the UE and inter-working revenue charges and send the Subscriber Location Report Acknowledgement to the SGSN, carrying the information specifies whether the location estimate of the UE has been handled successfully by the identified LCS Client, and if not success, the corresponding error cause obtained in step 12.
In case the V-GMLC receives the Subscriber Location Report from the SGSN and it is not required to send to any LCS Client, the V-GMLC shall record charging information for the UE and response the Subscriber Location Report Acknowledgement to the SGSN.
Step 14.
The SGSN returns a Service Response message to the UE carrying any location estimate requested by the UE including the indication received from RAN whether the obtained location estimate satisfies the requested accuracy or not, ciphering keys or an indicator whether a location estimate was successfully transferred to the identified LCS client. If the location estimate was successfully transferred to the identified LCS Client, the Service Response message shall specify whether the location estimate of the UE has been handled successfully by the identified LCS Client, and if not, the corresponding error cause obtained in step 13. The SGSN may record charging information.