Content for TS 23.161 Word version: 18.0.0
1…
5…
6…
6.2…
6.2.4
6.3…
6.3.2.2…
6.3.3…
6.3.3.2…
6.4…
6.4.2.2…
6.5…
6.5.2…
6.5.3…
6.6…
6.6.1.3…
6.6.2…
6.7…
6.7.2…
6.8…
6.3.2.2 Routing Rules signalled via Trusted WLAN access
6.3.2.3 Routing Rules signalled via Untrusted WLAN access
...
...
6.3.2.2 Routing Rules signalled via Trusted WLAN access p. 30
6.3.2.2.1 Single-connection mode p. 30
In single-connection mode, the PDN GW sends the routing rules over 3GPP access independent of access type, as described in clause 6.3.2.1.
6.3.2.2.2 Multi-connection mode p. 30
In the following signalling flow, the PDN GW provides new or updated Routing Rule(s) with access type WLAN via GTP and WLCP procedures. The routing rule is sent via TWAN access in this case. This may result in that IP flows routed over 3GPP access are now routed over WLAN, or vice versa.
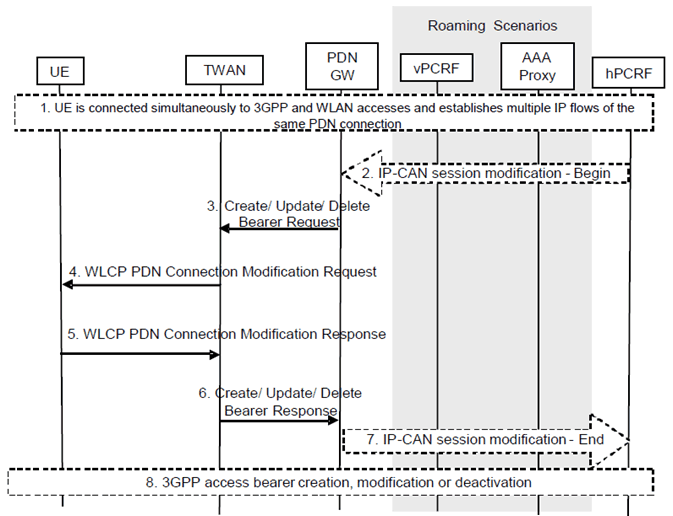
Figure 6.3.2.2.2-1: Network-initiated IP flow mobility within a PDN connection over TWAN access using GTP
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
Step 1.
The PDN Connection is active simultaneously over 3GPP access and TWAN access.
Step 2.
If dynamic PCC is applied for the PDN Connection the PCRF determines based on policy information and current UE state that session modification should be initiated to move specific flows. The PCRF provides PCC Rules with access type information to the PDN GW during an IP-CAN session modification procedure. The PDN GW determines that new Routing Rules / Modified Routing Rules need to be sent to the UE based on the received PCC Rules.
If dynamic PCC is not applied the PDN GW may determine based on local policies that new Routing Rules / Modified Routing Rules need to be sent to the UE.
Step 3.
The PDN GW sends the new or updated Routing Rules within Create/Update/Delete Bearer Request to the TWAN. If bearer resources need to be established or modified due to the PCC rules received in step 2, the bearer operations may be performed in this step.
Step 4.
The TWAN sends a WLCP PDN Connection Modification Request message to the UE, including the Routing Rules.
Step 5.
The UE may decide to accept or reject the Routing Rules. When the UE rejects the Routing Rules the UE provides a cause value indicating why the request was rejected. This cause value may be used by the network to determine when/if this IP flow mobility operation can be requested again. The UE applies the accepted routing rules and acknowledges the applied rules in a WLCP PDN Connection Modification Response message to the TWAN.
Step 6.
The TWAN sends Create/Update/Delete Bearer Response to the PDN GW.
Step 7.
The PDN GW indicates to the PCRF whether the PCC Rules could be enforced or not. This corresponds to the completion of the PCEF-initiated IP CAN session modification procedure as defined in TS 23.203.
Step 8.
Appropriate 3GPP resource release/modification procedures are executed as described in TS 23.401 for the resources (bearers) associated with the Routing Rules that were removed from 3GPP access.
6.3.2.3 Routing Rules signalled via Untrusted WLAN access p. 32
In the following signalling flow, the PCRF identifies and moves specific flows from 3GPP to WLAN.
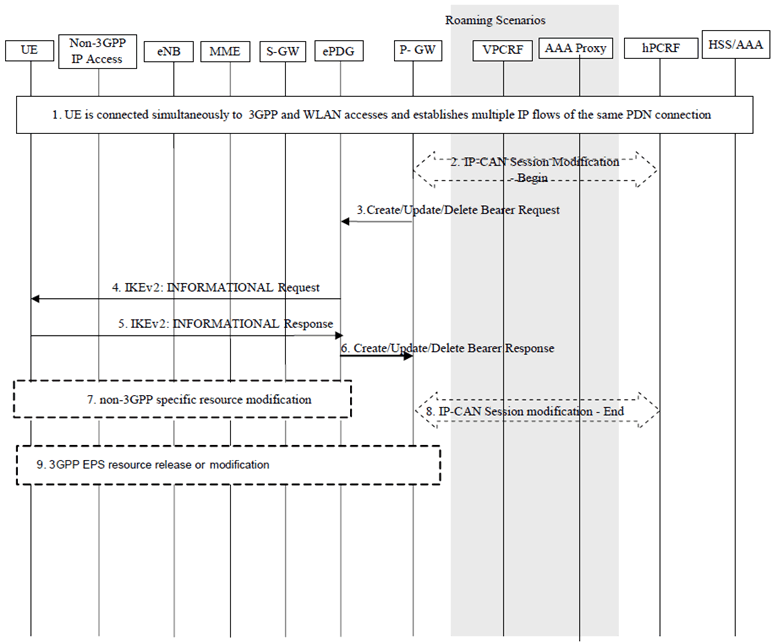
Figure 6.3.2.3-1: IP flow mobility within a PDN connection with negotiation via untrusted WLAN access
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
Step 1.
The UE is connected simultaneously to 3GPP and WLAN accesses and establishes multiple IP flows of the same PDN connection.
Step 2.
If dynamic PCC is applied for the PDN Connection, the PCRF determines based on policy information and current UE state that session modification should be initiated to move specific flows. The PCRF provides PCC Rules with access type information to the PDN GW during an IP-CAN session modification procedure.
Step 3.
The PDN GW determines that new or modified Routing Rules need to be sent to the UE based on the received PCC Rules. The PDN GW sends the new or updated Routing Rules within Create/Update/Delete Bearer Request to the TWAN. If bearer resources need to be established or modified due to the PCC rules received in step 2, the bearer operations may be performed in this step.
Step 4.
The ePDG initiates an IKEv2 INFORMATIONAL request, which includes the modified routing rule to indicate the updated routing rule to be used by the UE. The UE may accept or reject the Routing Rules. When the UE rejects the Routing Rules the UE provides a cause value indicating why the request was rejected. This cause value may be used by the network to determine when/if this IP flow mobility operation can be requested again.
Step 5.
The UE responds with a IKEv2 INFORMATIONAL response, acknowledging the new routing rules and applies the corresponding filters
Step 6.
The ePDG sends a Create/Update/Delete Bearer Response to the PDN GW.
Step 7.
The WLAN access specific resource release, setup or modification may be performed based on the modified traffic selector in WLAN access network.
Step 8.
The PDN GW indicates to the PCRF whether the Routing Rules could be enforced or not.
Step 9.
Appropriate 3GPP resource release/modification procedures are executed for the resources associated with the new or updated PCC rules.