Content for TS 23.161 Word version: 18.0.0
1…
5…
6…
6.2…
6.2.4
6.3…
6.3.2.2…
6.3.3…
6.3.3.2…
6.4…
6.4.2.2…
6.5…
6.5.2…
6.5.3…
6.6…
6.6.1.3…
6.6.2…
6.7…
6.7.2…
6.8…
6.2.4 Addition of an access using S2b p. 25
6.2.4.1 Addition of Untrusted WLAN access p. 25
This procedure is used to add untrusted WLAN access to an existing PDN Connection.
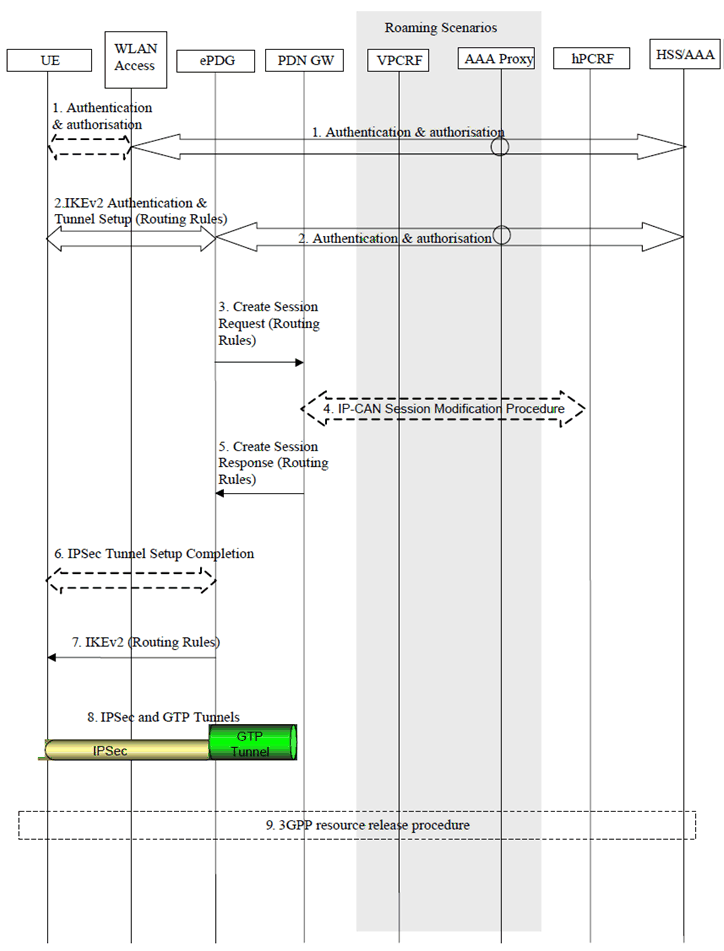
Figure 6.2.4.1-1 shows the particular case when the UE is first connected to a 3GPP access and then it requests addition of a WLAN access.
It is assumed that the UE has successfully attached to 3GPP access and established a PDN connection over 3GPP access using GTP as described in clause 6.1.1 and that the UE has received from the network an indication that NBIFOM is supported for this PDN connection.
Subsequently the UE performs the untrusted WLAN attachment, and requests to establish a PDN connection using the same APN, and attempts to use both accesses for the same PDN connection simultaneously.
Step 1.
The UE discovers a WLAN and performs the authentication and authorization procedure with 3GPP EPC via the WLAN access as specified in TS 23.402, clause 7.2.1 step 1.
Step 2.
IKEv2 authentication and tunnel setup procedure are performed via the WLAN access between the UE, ePDG and 3GPP AAA Server/HSS as specified in TS 33.402. For IP address preservation, the UE includes the same address (IPv4 address or IPv6 prefix/address or both) that was allocated during its attachment to 3GPP access. A new access can be added to a multi-access PDN connection without an associated routing rule.
If UE-initiated NBIFOM mode was selected at initial PDN Connection establishment, the UE may include Routing Rules in this step, as well as an indication for default access for the PDN Connection.
Step 3.
Since the handover indication is included, the TWAN selects the same PDN GW as is already allocated for the PDN Connection. The ePDG includes an NBIFOM indication in the Create Session Request message to the PDN GW. The ePDG also includes Routing Rules(s) and the indication for default access if provided by the UE in step 2.
Step 4.
When the PDN GW receives the Create Session Request with NBIFOM indication, the PDN GW does not remove the bearers over 3GPP access for the corresponding PDN connection. The same IP address is allocated for the PDN connection as the one used in 3GPP access network. If dynamic PCC is applied, the PDN GW initiates the IP-CAN Session Modification Procedure with the PCRF. The PDN GW indicates to the PCRF the addition of an access for the PDN connection and informs the PCRF about the additional RAT type. The PCRF may reject the addition of the access if the multi-access IP-CAN session would correspond to an invalid combination of IP-CAN and RAT Types or is not allowed by the subscription.
If routing rules were received, the PDN GW provides the PCRF with notification of the UE requested IP flow mapping to an Access Type. The PCRF may accept or reject the routing rules. . If network-initiated NBIFOM mode was selected at initial PDN Connection establishment, the PCRF shall indicate the default access for the PDN Connection to the PDN GW.
If UE-initiated NBIFOM mode was selected at initial PDN Connection establishment, the UE indicates the default access to the PCRF via PDN GW during this procedure. The PCRF takes a final decision on the default access based on the subscription, and indicate the default access for the PDN Connection to the PDN GW. The default access replied by the network may be different than the default access requested by the UE.
Step 5.
The PDN GW sends a Create Session Response message to the ePDG that includes the routing rules. The PDN GW generates a Charging Id for the Default Bearer and includes the Charging Ids for the PDN Connection and the Default Bearer in the Create Session Response to the ePDG. The PDN GW also indicates the default access for the PDN Connection to the ePDG.
Step 6.
The ePDG indicates to the UE that the authentication and authorization with the external AAA server is successful.
Step 7.
If routing rules were included in step 2 above, the ePDG notifies the UE whether the routing rules were accepted or rejected. In network-initiated NBIFOM procedure, the network does not provide any routing rules to the UE during this procedure. The ePDG indicates the default access to the UE as part of the IKEv2 signalling.
Step 8.
IP connectivity from the UE to the PDN GW is now setup. Any packet in the uplink direction complying with the routing rules is tunnelled to the ePDG by the UE using the IPSec tunnel. The ePDG then tunnels the packet to the PDN GW. From the PDN GW normal IP-based routing takes place. In the downlink direction, the packet for UE arrives at the PDN GW. The PDN GW tunnels the packet to the ePDG based on the routing rules. The ePDG then tunnels the packet to the UE via the IPsec tunnel.
Step 9.
If routing rules were included in step 2 above, the appropriate 3GPP resource release procedures are executed for the resources associated with the flows that were moved onto the WLAN access as specified in TS 23.402.