Content for TR 22.822 Word version: 16.0.0
5.6 Satellite transborder service continuity
5.7 Global satellite overlay
5.8 Indirect connection through a 5G satellite access network
5.9 5G Fixed Backhaul between NR and the 5G Core
5.10 5G Moving Platform Backhaul
5.11 5G to Premises
5.12 Satellite connection of remote service centre to off-shore wind farm
...
...
5.6 Satellite transborder service continuity p. 15
5.6.1 Description p. 15
The radio coverage of a 5G terrestrial network associated to operator TA in country A. is made of a number of areas matching its deployment schedule. The same approach is followed by network operator TB in country B.
A satellite SA, which radio coverage partially overlaps the coverage of TA & TB, is deployed.
A satellite SB, which radio coverage partially overlaps the coverage of TA & TB, is deployed.
UEs having access to TA & TB can also have access to SA and SB.
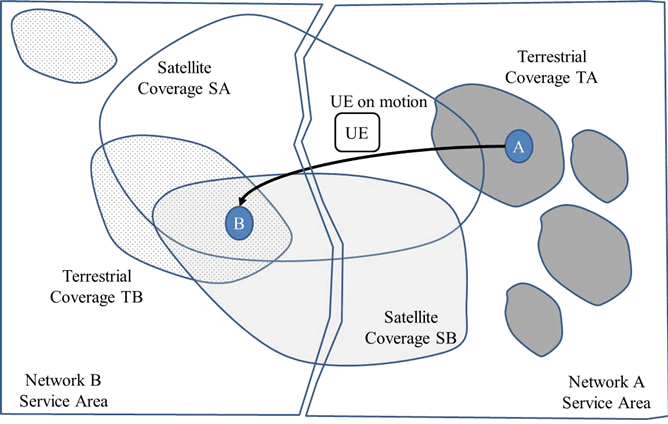
Figure 5.6.1-1: Multiple countries and multiple terrestrial networks that include satellite access
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
The satellite component may be a satellite access network with one of the following configurations:
- A 5G satellite RAT, providing a radio coverage extension of an available 5G access network of TA or TB.
- A satellite access network providing connection to 5G CN of TA or TB.
- A stand-alone 5G network, with independent access network and core capabilities, with roaming agreements with TA and TB.
5.6.2 Pre-conditions p. 16
Alice leaves home in the capital city of A to go visiting her dear friend Bob in the capital city of B.
Alice and Bob are well known experts from the 5G industry. Alice wants to report to Bob on the last updates of the sector, and she wants to takes the opportunity of the travel to download the latest news from the 3GPP web site, as well as from other technical and scientific electronic libraries.
5.6.3 Service Flows p. 16
- During the trip of Alice, her UE is connected first to the 5G terrestrial network of TA.
- Then, since TA has established an agreement to use also a satellite component, Alice's UE is connected to TA's network through the SA satellite component when the terrestrial component of TA becomes unavailable. This connectivity of Alice's UE can be achieved through a relay node UE located on board the train platform;
- Following, the train leaves the Service Area of Operator A and enters the Service Area of Network B. Still, no terrestrial coverage is available, and Satellite coverage of SA is the only one available. The UE of Alice is still connected through SA.
- Following, terrestrial coverage is still not available; satellite coverages SA and SB are available to Network operator B. The UE of Alice is connected through either of these.
- Following, Alice's UE can be covered by both of Satellite SB and a terrestrial network, the latest is selected.
- Finally, Alice's arrives in capital city of B and is welcomed by Bob when leaving the train.
5.6.4 Post-conditions p. 16
Bob is very pleased with the report on the 5G evolution as provided by Alice.
5.6.5 Potential Impacts or Interactions with Existing Services/Features p. 17
In a 5G system with satellite access, mobility management shall take into account satellite radio access network(s).
5.6.6 Potential Requirements p. 17
[PR 5.6.6.001]
In a 5G system with satellite access network, a 5G satellite access network shall support 5G access network sharing
[PR 5.6.6.002]
In a 5G system with satellite access network, a 5G satellite access network shall support 5G CN sharing and it shall support MNOs of different countries attached to the same 5G satellite network.
[PR 5.6.6.003]
A satellite access network belonging to different 5G systems of different countries shall be able to meet the corresponding regulatory requirements (e.g. LI).
[PR 5.6.6.004]
A 5G system with satellite access shall support the management of a 5G satellite network as a radio extension of the 5G terrestrial network with QoS capability.
[PR 5.6.6.005]
A 5G system with satellite access network shall support roaming between a 5G satellite network and a 5G terrestrial network.
[PR 5.6.6.006]
A 5G system with satellite access can appear in different configurations including the following ones:
- A 5G satellite RAT.
- A 5G satellite RAN.
- A 5G satellite access network.
- A 5G satellite network
5.7 Global satellite overlay p. 17
5.7.1 Description p. 17
As indicated in TR 22.891, the propagation delay is limited by physics, i.e. the speed of light (299 792 458 meters per second) in air and 2/3 of the speed of light in fibre connection. With these limits, 1ms one way transmission latency can be mapped to 300 km air propagation or 200 km for fibre based transmission.
When the distance between 2 sites increases (several thousands of kilometres), the difference in latency between air and optical fibre transmission media may become critical for such applications and hence it is worth considering alternative network options compared to optical fibre based network.
A constellation of Low-Earth orbiting satellites, where each spacecraft is equipped with a gNB and interconnected with other neighbouring spacecraft's via Inter Satellite Links, provides access to UEs. Such a type of constellation system would provide an overlay mesh network for users that have a need for long distance connectivity with improved latency performance or specific end to end security.
The constellation of satellites can be considered as contributing to a single overlay 5G system, or as contributing a many 5G systems as many countries covered by the Constellations for instance.
Global organisations with distributed sites around the world may require long distance connectivity between the sites with critical requirements including low latency, reliability and/or end-to-end security to support critical application domains such as High Frequency Trading (HFT), Banking or Corporate communications.
An organisation is structured on a set of distributed sites throughout the globe that needs to be interconnected. This organisation has strong requirements with respect to security as well as with respect to Quality of Service (QoS), both for bandwidth and latency, since operations are related to these metrics: for mining or oil & gas exploitation, for trading, etc. The case of High Frequency Trading is addressed here.
5.7.2 Pre-conditions p. 18
The organisation purchases services with a network operator, with a number of UE's:
- UE A is located in Paris Stock Exchange. Computers are connected to UE A for HFT.
- UE B is located in Tokyo Stock Exchange. UEs including Computers are connected to UE B for HFT.
- UE C is located in New York City Stock Exchange. Computers are connected to UE C for HFT.
- UEs for other Stock Exchanges London, Chicago, etc. are also connected to the network.
5.7.3 Service Flows p. 18
The operator has access to a number of routes, whether terrestrial or satellite-based, in order to guarantee an end-to-end performance for its customers. Based on the monitoring of the performances (latency influenced by the delay as well as the network load) of the different routes, the satellite network overlay is selected for some UE to UE connectivity case (for instance Paris SE to Tokyo SE, Paris SE to Chicago SE). For other shorter distance cases (Paris SE to London SE), the terrestrial routes may be preferred.
5.7.4 Post-conditions p. 18
The organisation is offered the highest end-to-end QoS performance for global connectivity, with optimal routes that can be established for each path, including through the satellite overlay.
5.7.5 Potential Impacts or Interactions with Existing Services/Features p. 18
When considering the delivery of services, with the possibility of global extension of coverage considering some QoS constraints, a satellite global overlay may be considered.
5.7.6 Potential Requirements p. 18
[PR 5.7.6.001]
A 5G system with global satellite overlay access shall be able to select the communication link providing the UEs with the suitable quality with respect to latency, jitter and required bit rates.
[PR 5.7.6.002]
Two 5G systems with satellite access connected to each other shall be able to select the communication link(s) providing the UEs with the suitable quality with respect to latency, jitter and required bit rates.
[PR 5.7.6.003]
A 5G system shall be able to support meshed connectivity between satellites based on 5G RAT.
5.8 Indirect connection through a 5G satellite access network p. 18
5.8.1 Description p. 18
When considering the class of "service continuity" use cases as described in the existing version of TR 22.822, a number of potential remote users could be located in areas with no connectivity to 5G services through any 5G terrestrial access networks, either temporarily due to the motion of the platform (aeronautical, maritime or land - car, train -) or due to economic circumstances. These platforms could also be moving platforms, such as command cards, when considering mission critical communications.
To cope with this situation, a 5G satellite network could offer an answer to the connectivity requirement: Remote UE's, either on motion, or on station or fixed, possibly with no satellite access capability or out of reach of a satellite access (due to blocking of the direct access), would be interconnected with a satellite enabled UE that would be also a Relay UE.
The Relay UE would provide indirect connectivity between associated Remote UEs and the 5G Core Network through the 5G satellite access.
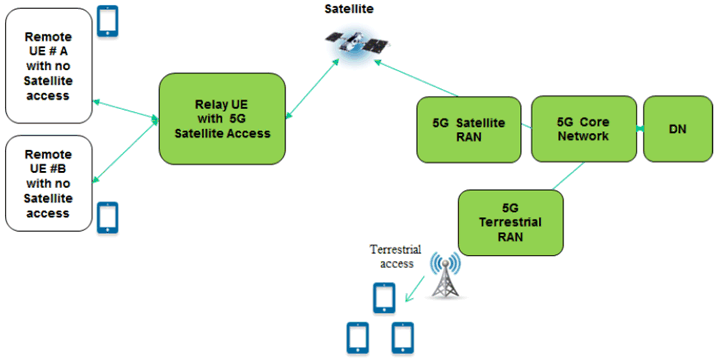
Figure 5.8.1-1: Interconnection of UE to a 5G network through a bent pipe satellite enabled and relay enabled UE
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
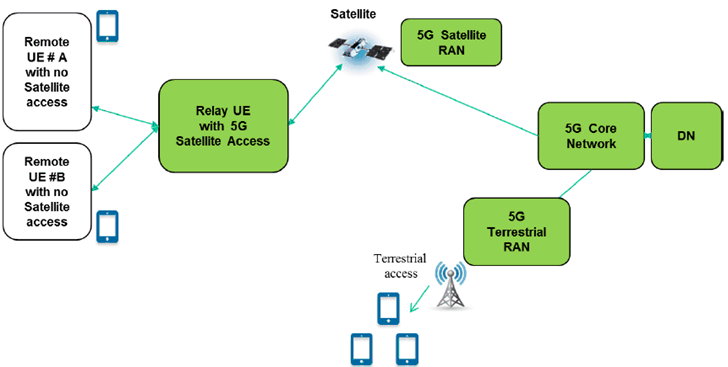
Figure 5.8.1-2: Interconnection of UE to a 5G network through a 5G satellite enabled and relay enabled UE
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
Some Relay UEs may be located in different countries, some other Relay UEs, due to the motion of the associated platform (long haul aircraft or ships) could be moving from one country to the other during the connectivity session of the associated remote UEs.
The number of remote UEs attached to a single Relay UEs is related to the local conditions: from a few is a remote area, to several hundred (commercial jet) or thousands (maritime cruise vessel) for instance.
5.8.2 Pre-conditions p. 19
Subscribers of remote UEs attached to the Relay UEs are expecting similar connectivity services as if they were located within direct reach of a 5G terrestrial access.
5.8.3 Service Flows p. 20
Alix purchases a 5G subscription together with a UE. Her subscription includes a service coverage extension within designated areas (commercial, jets, commercial cruise lines). When Alix embarked on a flight from Paris to Tokyo, she checked that she could browse with her smartphone through the Internet, she was guaranteed she would be able to do so.
Pauline, a civil servant for the civil protection is also provided a UE. Pauline can be asked to operate far in the forest to support of Mr S.C. who can get lost and needs help, in particular in winter time. When requested to intervene, Pauline boards on a snow car equipped with a satellite enabled UE. Her smartphone gets connected directly with the satellite enabling her satellite UE to act as a relay UE.
Alix and Pauline UEs are not satellite enabled.
A minimum list of services (data transfer, messaging, voice, low rate video) and associated QoS are designated by the service providers of Alix and Pauline for their corresponding service subscriptions.
5.8.4 Post-conditions p. 20
Whenever within reach of a relay UE that is satellite capable and that is associated with the 5G system with satellite access, Pauline and Alix have been offered connectivity to the subscribed list of services which include:
- Alix embarked in aircraft with a relay UE that is satellite capable. During the flight, the relay UE has been capable to access to several satellites, and the connectivity of the relay of the UE has been managed accordingly with no interruption.
- This is also the case for the connectivity of Pauline UE's with her 5G network. Pauline could help Mr S.C as she was tasked correctly by her commander to head in the right direction avoiding in real time potential difficult weather conditions. She could also report in real time on the local situation of Mr S.C..
- Providing mission critical services subscribed with appropriate priority, pre-emption, and Quality of Service (QoS).
5.8.5 Potential Impacts or Interactions with Existing Services/Features p. 20
The following interaction with or impact to the following aspects need to be highlighted:
- Roaming functions can be impacted since UE's can be roaming during the motion of the Relay UE from one country to another one, while the UE is attached to the Relay UE. This is FFS.
- The impact on charging should also be addressed in conjunction with the roaming topic as above.
- The Relay UE that is shared among several UEs could be in view at the same time of more than one 5G terrestrial systems with satellite access. Conditions on the Relay UE with satellite access may be restricted by the number of simultaneous 5G terrestrial systems it is connected with and the associated selection criteria.
- The definition of the minimum set of services to be provided through a Relay with 5G Satellite Access should be defined, as the delay performances for 5G satellite access are different from a 5G terrestrial access. In some cases the requirements could be relaxed, in some other cases access to these services may not be possible. The impact should be addressed from the point of view of the different interfaces and functions of the 5G system.
- Security mechanisms of the 5G system shall be implemented seamlessly all the way through the 5G satellite network to ensure that the remote UEs are offered the same security performances as for any other UEs served within the same 5G system. This is FFS.
5.8.6 Potential Requirements p. 20
[PR 5.8.6.001]
A 5G system with satellite access shall be able to support Relay UE's with 5G satellite access.
[PR 5.8.6.002]
A 5G system with satellite access shall support roaming of Relay UEs and the remote UEs connected to the relay UE between 5G networks.
[PR 5.8.6.003]
A 5G system with satellite RAT shall support service continuity for Relay UEs and the remote UEs connected to the relay UE when a Relay UE is moving between different 5G RANs in the same 5G network.
5.9 5G Fixed Backhaul between NR and the 5G Core p. 21
5.9.1 Description p. 21
Alice and Barbara live in Aville and Bville, two small villages in the country about 5km apart connected by a main road. The surrounding area has a low population density, just farms and a disused quarry.
The two villages do not currently enjoy modern communication services. DSL connectivity is poor because of the distance to the next small town, Cville, where the mobile operators also have good coverage, but it hardly reaches the two villages. The mobile operators have decided to place a shared cell tower between the villages. They are home to 300 families, with more in the summer due to holiday accommodation. The road can occasionally be busy with holiday traffic but is usually quiet.
Alice and Barbara enjoy using their mobile phones when they leave school in Cville, but the signal becomes unusable before they arrive home.
5.9.2 Pre-conditions p. 21
The satellite operator S has been working with one of the mobile operators on another project and has excellent coverage of Aville and Bville.
The mobile operators have decided to start up by using a satellite backhaul to the new cell tower. This can be arranged quickly and there is no need for any construction work, beyond the site of the cell tower.
5.9.3 Service Flows p. 21
The two cells on the new tower provide all the usual services of the mobile operators, using the satellite network of S to provide the connectivity between the cell tower and the mobile operator's core networks.
The interfaces between the 5G Core and NR are transported directly over the satellite link.
Network functions delocalization could improve overall quality of service in certain scenarios (e.g. AMF/SMF delocalization to improve/enhance local communications within the backhauled area where significant user density is foreseen).
5.9.4 Post Conditions p. 21
Alice and Barbara are able to use their phones in their own villages just as well as in Cville.
The operators of the mobile and satellite networks are happy with the solution and are working on copying it for five other locations. From the end user's point of view, the response of the network is now far better than the poor DSL or the distance terrestrial mobile cells.
One of the larger farms close to Bville has run a successful mMTC trial.
5.9.5 Potential Impacts or Interactions with Existing Services/Features p. 21
The main advantage of using satellite for backhaul is that locations which are otherwise difficult to provide with terrestrial network coverage for geographical or economic reasons can easily be reached. This comes at a cost of propagation delay, which has to be mitigated as far as possible, and is detailed in Figure A.4 in the Annex.
It is anticipated that there will be some changes needed to handle these latencies between the NR radio base stations and the core network.
5.9.6 Potential Requirements p. 22
[PR 5.9.6.001]
The 5G system shall support the use of satellite links between the radio access network and core network and within the core network, by enhancing the 3GPP system to handle the latencies introduced by satellite backhaul.
5.10 5G Moving Platform Backhaul p. 22
5.10.1 Description p. 22
A train operator TO is opening a new 1000 km high speed line across the country. TO wishes to provide specific entertainment services (with no or low uplink traffic and high downlink) for all passengers and general internet services for those passengers who pay a supplement. It is also necessary to provide non-critical operational data for TO's internal use.
5.10.2 Pre-conditions p. 22
TO has good arrangements with the terrestrial mobile operators in the country.
The coverage of the mobile operators is excellent in urban and most sub-urban areas throughout the country. In the densely populated areas of the country the mobile networks can be overloaded at certain times of day at specific locations.
However, in the middle of the country there is about 200 km of track with no coverage at all.
TO has started to work together with a satellite operator SO that is able to provide good coverage throughout the country and an exceptionally good throughput in the downlink. SO also has good reciprocal cooperation with all of the mobile operators to ensure good service is available to TO's customers.
TO will work with the mobile operators to place 5G base stations on the trains.
5.10.3 Service Flows p. 22
The terrestrial mobile operators can unicast / multicast / broadcast entertainment content over their existing terrestrial base stations and or/and over the base stations on the train.
When the train passes through the middle of the country there will be a long period where only the satellite connectivity can be used.
Frequently used content can be stored in TO's local infrastructure and updated as needed.
UEs entitled to general internet services can also use both access networks, combined or singly.
TO's internal services can use the networks as necessary.
5.10.4 Post-conditions p. 22
UEs using TO's entertainment services are served efficiently, independent of their location. Frequently consumed services are stored locally, enabling almost instantaneous delivery
Entitled UEs can use general internet services as required.
5.10.5 Potential Impacts or Interactions with Existing Services/Features p. 22
5.10.6 Potential Requirements p. 22
[PR 5.10.6.001]
The 5G system shall support the use of satellite links between the radio access network and core network and within the core network, by enhancing the 3GPP system to handle the latencies introduced by satellite backhaul.
5.11 5G to Premises p. 23
5.11.1 Description p. 23
Neudorf is a village built in the foothills of the alps in the 1970s. There are about 80 dwellings. At the time it was built as a holiday village, the location chosen because of the nearby ski lift. With global warming the lift went bankrupt, but the area is now popular (as a primary residence) because of the alternative lifestyle away from the city. When it was built telecommunications meant having a phone and nothing else. Today the old exchange is too far away to give good DSL and cellular coverage varies greatly because of the hills and is not really very good in general. The inhabitants are divided, some want modern communications and others show little interest.
There are no cable companies operating at this rather remote location and many of the premises have been using Satellite for Broadcast TV reception for a long time.
5.11.2 Pre-conditions p. 23
A new satellite operator S has deployed a component operating in this geographical area and beyond. The satellite component can be used to optimise access to available spectrum and network resources.
The Terrestrial cellular operator T decides to work with S to provide better services for its customers in the area, using a new home/office gateway unit to combine the available signals from S and T, and to present good WIFI coverage within the premises.
5.11.3 Service Flows p. 23
Terrestrial operator T broadcasts and multicasts media content over its satellite component. Caching can be done on the gateway and T has a flexible means of organising this to provide excellent performance for frequently accessed content.
In general, unicast will use the cellular route. If low latency is not needed for a service, the satellite component should be used.
T is also investigating how gateways in a favourable geographical position could provide coverage for subscribers close by, but in an unfavourable position due to the lay of the land.
5.11.4 Post-conditions p. 23
The customers of T have greatly improved service.
5.11.5 Potential Impacts or Interactions with Existing Services/Features p. 23
The 5G system needs to have the capability to implement broadcast/multicast service through a satellite component.
5.11.6 Potential Requirements p. 23
[PR 5.11.6.001]
The 5G system shall support the use of satellite links between the radio access network and core network and within the core network, by enhancing the 3GPP system to handle the latencies introduced by satellite backhaul.
[PR 5.11.6.002]
UEs shall have the capability for simultaneous dual mode of operation, supporting a 5G satellite access and a terrestrial access at the same time.
[PR 5.11.6.003]
A 5G system supporting a 5G satellite access and a 5G terrestrial access shall be able to optimally distribute user traffic over both types of access.
5.12 Satellite connection of remote service centre to off-shore wind farm p. 24
5.12.1 Description p. 24
The wind power plant communication network at an off-shore wind farm connects to the on-shore and inland remote service centre via 5G satellite connection (see Figure 5.L.1-1).
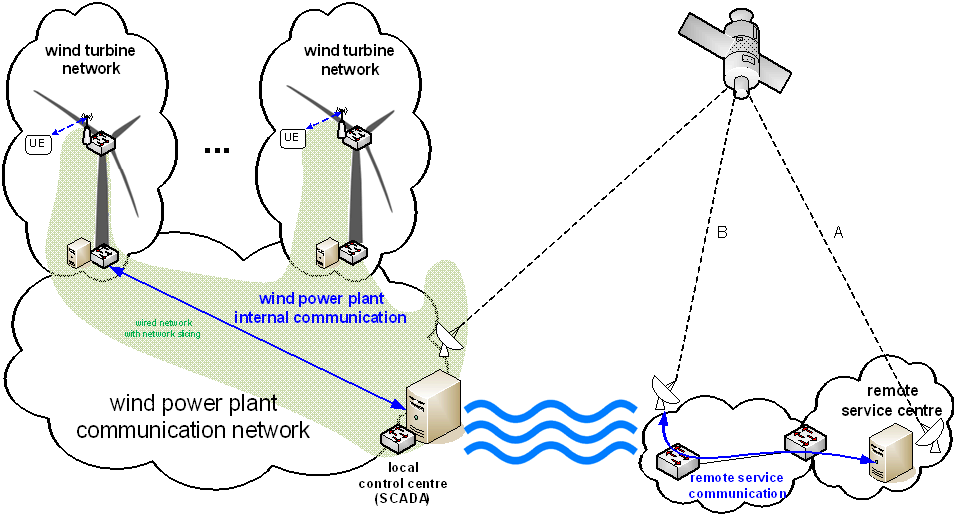
Figure 5.12.1-1: Example of off-shore wind power plant communication network connected to inland remote service centre via 5G satellite connection
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
Figure 4 shows two settings of how the remote service centre can connect to the satellite:
- The remote service centre uses a 5G satellite UE directly (on-shore satellite connection A).
- The remote service centre connects to a PLMN that includes a 5G satellite connection (on-shore satellite connection B).
5.12.2 Pre-conditions p. 24
The local control centre in the wind power plant communication network includes a 5G satellite UE. A LEO satellite 5G network is available.
5.12.3 Service Flows p. 24
The 5G satellite connection is used for remote service communication between the off-shore wind farm and the remote service centre. Examples of included communication services are:
- Remote monitoring and non-time-critical control of wind farm operation: moderate data volume, low satellite communication latency (LEO satellites);
- Continuous data upload for, e.g., data analytics at remote service centre: high uplink data volume (from wind power plant communication network to satellite), no restriction on satellite communication latency;
- Video surveillance during on-demand maintenance at wind turbine: high-definition video transmission (uplink from wind power plant communication network to satellite), low satellite communication latency (LEO satellites);
- On-demand download of bulk sensor data for remote analysis: high uplink data volume (from wind power plant communication network to satellite), no restriction on satellite communication latency;
- On-demand provision of support information from remote service centre to on-site service personnel by remote service centre: high downlink data volume (from satellite to wind power plant communication network), no restriction on satellite communication latency.
5.12.4 Post-conditions p. 25
Same as before service flows.
5.12.5 Potential Impacts or Interactions with Existing Services/Features p. 25
Communication service continuity between 5G satellite connection and terrestrial PLMN (especially with on-shore satellite connection A).
5.12.6 Potential Requirements p. 25
[PR 5.12.6.001]
The 5G system with satellite access shall support high uplink data rates for 5G satellite UEs.
[PR 5.12.6.002]
The 5G system with satellite access shall support high downlink data rates for 5G satellite UEs.
[PR 5.12.6.003]
The 5G system with satellite access shall provide suitable interfaces for QoS monitoring of the 5G satellite connection at the 5G satellite UE.
[PR 5.12.6.004]
The 5G system with satellite access shall enable the selection of the satellite access per communication service based on QoS requirements (e.g. latency).
[PR 5.12.6.005]
The 5G system with satellite access shall support communication service availabilities of at least 99.99%.