Content for TS 23.417 Word version: 7.0.0
1 Scope p. 6
The present document describes the IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS) core component of the TISPAN NGN functional architecture and its relationships to other subsystems and components.
Use of IMS functional entities in support of transit scenarios is incompletely described. Completion of this description is dependent on ongoing work in 3GPP.
2 References p. 6
The following documents contain provisions which, through reference in this text, constitute provisions of the present document.
- References are either specific (identified by date of publication, edition number, version number, etc.) or non specific.
- For a specific reference, subsequent revisions do not apply.
- For a non-specific reference, the latest version applies. In the case of a reference to a 3GPP document (including a GSM document), a non-specific reference implicitly refers to the latest version of that document in the same Release as the present document.
[1]
ETSI ES 282 001: "Telecommunications and Internet converged Services and Protocols for Advanced Networking (TISPAN); NGN Functional Architecture Release 1".
[2]
ETSI TS 182 006: "Telecommunications and Internet converged Services and Protocols for Advanced Networking (TISPAN); IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS); Stage 2 description (3GPP TS 23.228 v7.2.0, modified)".
[3]
ETSI TS 123 218: "Digital cellular telecommunications system (Phase 2+); Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS); IP Multimedia (IM) session handling; IM call model; Stage 2 (3GPP TS 23.218)".
[4]
ETSI ES 282 010: "Telecommunications and Internet Converged Services and Protocols for Advanced Networking (TISPAN); Charging [Endorsement of 3GPP TS 32.240 v6.3.0, 3GPP TS 32.260 v6.3.0, 3GPP TS 32.297 v6.1.0, 3GPP TS 32.298 v6.1.0 and 3GPP TS 32.299 v6.4.0 modified]".
[5]
ETSI ES 283 024: "Telecommunications and Internet converged Services and Protocols for Advanced Networking (TISPAN); PSTN/ISDN Emulation: H.248 Profile for controlling Trunking Media Gateways in the PSTN/ISDN Emulation Subsystem (PES); Protocol specification".
[6]
ETSI ES 283 027: "Telecommunications and Internet converged Services and Protocols for Advanced Networking (TISPAN); Endorsement of the SIP-ISUP Interworking between the IP Multimedia (IM) Core Network (CN) subsystem and Circuit Switched (CS) networks [3GPP TS 29.163 (Release 7), modified]".
[7]
ETSI TS 183 021: "Telecommunications and Internet converged Services and Protocols for Advanced Networking (TISPAN); NGN Release 1; Endorsement of 3GPP TS 29.162 Interworking between IM CN Sub-system and IP networks".
[8]
ETSI EN 301 931: "Intelligent Network (IN); Intelligent Network Capability Set 3 (CS3); Intelligent Network Application Protocol (INAP); Protocol specification".
[9]
ETSI ES 201 915-1: "Open Service Access (OSA); Application Programming Interface (API); Part 1: Overview (Parlay 3)".
[10]
ETSI TS 123 002: "Digital cellular telecommunications system (Phase 2+); Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS); Network architecture (3GPP TS 23.002)".
[11]
ETSI TS 123 278: "Digital cellular telecommunications system (Phase 2+); Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS); Customised Applications for Mobile network Enhanced Logic (CAMEL) Phase 4; Stage 2; IM CN Interworking (3GPP TS 23.278)".
[12]
ETSI TS 129 278: "Digital cellular telecommunications system (Phase 2+); Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS); customized Applications for Mobile network Enhanced Logic (CAMEL); CAMEL Application Part (CAP) specification for IP Multimedia Subsystems (IMS) (3GPP TS 29.278)".
[13]
RFC 3136 (2001): "The SPIRITS Architecture".
[14]
RFC 3261 (2002): "SIP: Session Initiation Protocol".
[15]
ITU-T Recommendation H.248: "Gateway control protocol".
[xvi]
ETSI ES 282 007 v1.1.1: "Telecommunications and Internet converged Services and Protocols for Advanced Networking (TISPAN); IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS); Functional architecture".
3 Definitions and abbreviations p. 7
3.1 Definitions p. 7
For the purposes of the present document, the following terms and definitions apply:
IP Multimedia Subsystem:
As defined in TS 123 002 [10].
NGN IP Multimedia Subsystem:
IMS that supports the provision of SIP-based multimedia services and PSTN/ISDN simulation services to NGN terminals
User Equipment (UE):
one or more devices allowing a user to access services delivered by TISPAN NGN networks
3.2 Abbreviations p. 7
For the purposes of the present document, the following abbreviations apply:
AF
Application Function
ALG
Application Layer Gateway
AS
Application Server
ASF
Application Server Function
BCSM
Basic Call State Model
BGF
Border Gateway Function
CAMEL
Customised Application for Mobile Enhanced Logic
CCBS
Call Control on Busy Subscriber
CSCF
Call Session Control Function
IBCF
Intermediate Breakout Control Function
I-BGF
Interconnection-Border Gateway Function
I-CSCF
Interrogating-Call Session Control Function
IM-MGW
IP Multimedia - Media GateWay
IMS
IP Multimedia Subsystem
IN
Intelligent Network
INAP
IN Application Part
IN-SCF
Intelligent Network Switching Control Function
IP-CAN
IP-Connectivity Access Network
ISDN
Integrated Services Digital Network
MGCF
Media Gateway Control Function
MGF
Media Gateway Function
MM
MultiMedia
MRFC
Multimedia Resource Function Controller
MRFP
Multimedia Resource Function Processor
NAPT
Network Address and Port Translation
NASS
Network Attachment SubSystem
NGN
Next Generation Network
OSA
Open Service Access
P-CSCF
Proxy-Call Session Control Function
PDF
Policy Decision Function
PES
PSTN/ISDN Emulation Subsystem
PSTN
Public Switched Telephony Network
RACS
Resource and Admission Control Subsystem
SCF
Switching Control Function
SCIM
Service Capability Interaction Manager
S-CSCF
Serving-Call Session Control Function
SGF
Signalling Gateway Function
SIP
Session Initiation Protocol
SLF
Subscription Locator Function
SPIRITS
Service in the PSTN/IN Requesting InTernet Services
SSF
Service Switching Function
TCAP
Transaction Capabilities Application Part
T-MGF
Trunking-Media Gateway Function
UE
User Equipment
UPSF
User Profile Server Function
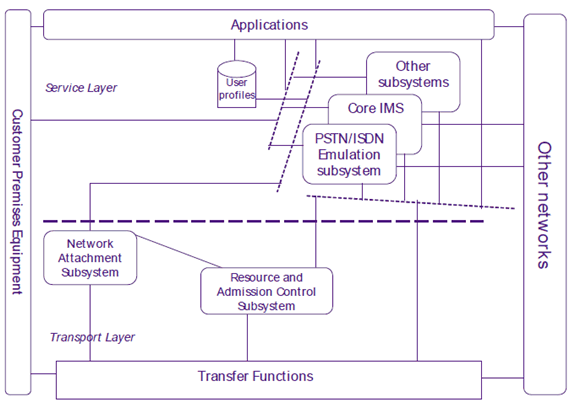
4 Overall architecture p. 8
The TISPAN NGN functional architecture ES 282 001 [1] is structured according to a service layer and an IP-based transport layer (see Figure 1).
The service layer comprises the following components:
- The IP Multimedia Subsystem core component (IMS).
- The PSTN/ISDN Emulation Subsystem (PES).
- Other multimedia subsystems (e.g. streaming subsystem, content broadcasting subsystem etc.) and applications.
- Common components (i.e. used by several subsystems) such as those required for accessing applications, charging functions, user profile management, security management, routing data bases (e.g. ENUM), etc.