Content for TS 23.285 Word version: 18.0.0
4 Architecture model and concepts
4.1 General concept
4.2 Architectural reference model
4.2.1 PC5 and LTE-Uu based V2X architecture reference model
4.2.1.1 Non-roaming architecture for PC5 and LTE-Uu based V2X communication
4.2.1.2 Roaming architecture for PC5 and LTE-Uu based V2X communication
4.2.1.3 Inter-PLMN architecture for PC5 and LTE-Uu based V2X communication
4.2.2 MBMS for LTE-Uu based V2X architecture reference model
4.2.3 Reference points
4.3 Functional entities
4.3.1 V2X Control Function
4.3.2 UE
4.3.3 V2X Application Server
4.3.4 MME
4.3.5 BM-SC
4.3.6 MBMS-GW
...
...
4 Architecture model and concepts p. 8
4.1 General concept p. 8
There are two modes of operation for V2X communication, namely over the PC5 and over LTE-Uu. LTE-Uu can be unicast and/or MBMS. These two operation modes may be used by a UE independently for transmission and reception, e.g. a UE can use MBMS for reception without using LTE-Uu for transmission. A UE may also receive V2X messages via LTE-Uu unicast downlink.
For both operation modes, the following principles apply:
- V2X Application Servers e.g. in different domains can communicate with each other for the exchange of V2X messages. The interface between V2X Application Servers and the methods of the exchange of messages between V2X Application Servers is out of scope of 3GPP.
- ProSe discovery feature (clause 5.3 of TS 23.303 ProSe Direct Discovery) is not required for V2X Services.
- Subject to regional regulations, lawful interception requirements apply to V2X Services.
- An RSU is not an architectural entity, but an implementation option. This is achieved by collocating a V2X application logic/server with some entities of the 3GPP system, as shown in examples in Annex A.
4.2 Architectural reference model p. 9
4.2.1 PC5 and LTE-Uu based V2X architecture reference model p. 9
4.2.1.1 Non-roaming architecture for PC5 and LTE-Uu based V2X communication p. 9
Figure 4.2.1.1-1 shows the high level view of the non-roaming architecture for PC5 and LTE-Uu based V2X communication.
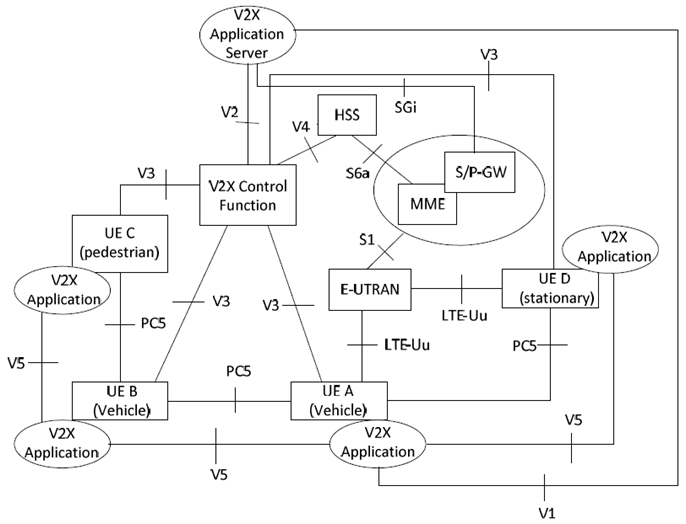
Figure 4.2.1.1-1: Non-roaming reference architecture for PC5 and LTE-Uu based V2X communication
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
4.2.1.2 Roaming architecture for PC5 and LTE-Uu based V2X communication p. 9
Figure 4.2.1.2-1 shows the high level view of the roaming architecture for PC5 and LTE-Uu based V2X communication. In this Figure, UE A uses a subscription of PLMN A and UE B uses a subscription of PLMN B; UE A is roaming in PLMN B while UE B is not roaming.
A V2X Application Server may connect to multiple PLMNs, e.g. one V2X Application Server can connect with the V2X Control Function in PLMN A and the V2X Control Function in PLMN B in the Figure.
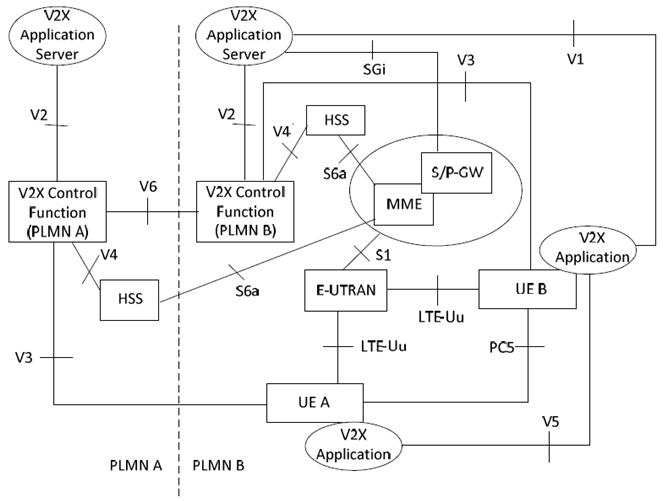
Figure 4.2.1.2-1: Roaming reference architecture for PC5 and LTE-Uu based V2X communication
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
4.2.1.3 Inter-PLMN architecture for PC5 and LTE-Uu based V2X communication p. 10
Figure 4.2.1.3-1 shows the high level view of the inter-PLMN architecture for PC5 and LTE-Uu based V2X communication. In this Figure, UE A uses a subscription of PLMN A and UE B uses a subscription of PLMN B; UE A is roaming in PLMN C while UE B is not roaming.
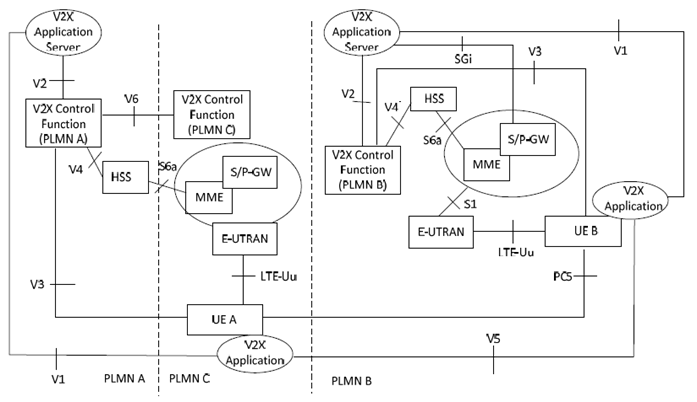
Figure 4.2.1.3-1: Inter-PLMN reference architecture for PC5 and LTE-Uu based V2X communication
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
4.2.2 MBMS for LTE-Uu based V2X architecture reference model p. 11
Figure 4.2.2-1a and Figure 4.2.2-1b show the high level view of the reference architectures with MBMS for LTE-Uu based V2X communication. V2X Application Server may apply either MB2 or xMB reference points when managing MBMS service related information via BM‑SC, MB2 reference point as defined in TS 23.468 provides functionality related to group communication and xMB reference point as defined in TS 26.348 provides functionality overall for any content and also supports security framework between content provider and BM‑SC.
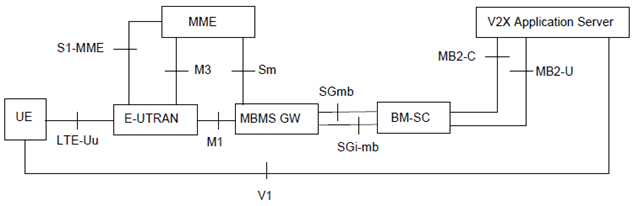
Figure 4.2.2-1a: Reference architecture for MBMS for LTE-Uu based V2X communication via MB2
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
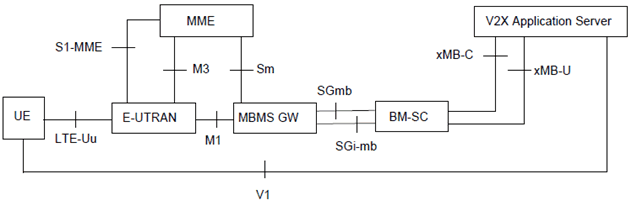
Figure 4.2.2-1b: Reference architecture for MBMS for LTE-Uu based V2X communication via xMB
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
4.2.3 Reference points p. 12
V1:
The reference point between the V2X application in the UE and in the V2X Application Server. This reference point is out of scope of this specification.
V2:
The reference point between the V2X Application Server and the V2X Control Function in the operator's network. The V2X Application Server may connect to V2X Control Functions belonging to multiple PLMNs.
V3:
The reference point between the UE and the V2X Control Function in UE's home PLMN. It is based on the service authorization and provisioning part of the PC3 reference point defined in clause 5.2 of TS 23.303. It is applicable to both PC5 and LTE-Uu based V2X communication and optionally MBMS and LTE-Uu based V2X communication.
V4:
The reference point between the HSS and the V2X Control Function in the operator's network.
V5:
The reference point between the V2X applications in the UEs. This reference point is not specified in this release of the specification.
V6:
The reference point between the V2X Control Function in the HPLMN and the V2X Control Function in the VPLMN.
PC5:
The reference point between the UEs used for user plane for ProSe Direct Communication for V2X Service.
S6a:
In addition to the relevant functions defined in TS 23.401 for S6a, in case of V2X Service S6a is used to download V2X Service related subscription information to MME during E-UTRAN attach procedure or to inform MME subscription information in the HSS has changed.
S1-MME:
In addition to the relevant functions defined in TS 23.401 for S1-MME, in case of V2X Service it is also used to convey the V2X Service authorization from MME to eNodeB.
xMB:
The reference point between the V2X Application Server (e.g. Content Provider) and the BM‑SC, and defined in TS 26.348.
MB2:
The reference point between the V2X Application Server and the BM‑SC, and defined in TS 23.468.
SGmb/SGi-mb/M1/M3:
The SGmb/SGi-mb/M1/M3 reference points are internal to the MBMS system and are defined in TS 23.246.
LTE-Uu:
The reference point between the UE and the E-UTRAN.
4.3 Functional entities p. 13
4.3.1 V2X Control Function p. 13
4.3.1.1 General p. 13
The V2X Control Function is the logical function that is used for network related actions required for V2X. In this version of the specification it is assumed that there is only one logical V2X Control Function in each PLMN that supports V2X Services.
V2X Control Function is used to provision the UE with necessary parameters in order to use V2X communication. It is used to provision the UEs with PLMN specific parameters that allow the UE to use V2X in this specific PLMN. V2X Control Function is also used to provision the UE with parameters that are needed when the UE is "not served by E-UTRAN".
V2X Control Function may also be used to obtain V2X USDs for UEs to receive MBMS based V2X traffic, through V2 reference point from the V2X Application Server.
V2X Control Function may also obtain the parameters required for V2X communications over PC5 reference point, from the V2X Application Server via V2 reference point.
4.3.1.2 V2X Control Function discovery p. 13
The V2X Control Function of HPLMN is discovered through interaction with the Domain Name Service function. The FQDN of a V2X Control Function in the Home PLMN may either be pre-configured in the UE, provisioned by the network or self-constructed by the UE, e.g., derived from the PLMN ID of the HPLMN. The IP address of a V2X Control Function in the Home PLMN may also be provisioned to the UE.
4.3.2 UE p. 13
The UE may support the following functions:
- Exchange of V2X control information between UE and the V2X Control Function over the V3 reference point.
- Procedures for V2X communication over PC5 reference point and/or LTE-Uu reference point.
- Configuration of parameters for V2X communication (e.g., destination Layer-2 IDs, radio resource parameters, V2X Application Server address information, mapping between service types and V2X frequencies). These parameters can be pre-configured in the UE, or, if in coverage, provisioned by signalling over the V3 reference point from the V2X Control Function in the HPLMN.
- Provided with V2X USDs for receiving MBMS based V2X traffic via existing MBMS service announcement mechanisms, or provisioned from V2X Control Function, or provisioned from the V2X Application Server via V1 reference point.
- Provisioned with V2X Server USDs for receiving V2X Application Server information via MBMS.
4.3.3 V2X Application Server p. 14
The V2X Application Server (V2X AS) may support the following capabilities:
- Receiving uplink data from the UE over unicast.
- Delivering data to the UE(s) in a target area using Unicast Delivery and/or MBMS Delivery.
- Mapping from geographic location information to appropriate target MBMS SAI(s) for the broadcast.
- Mapping from geographic location information to appropriate target 3GPP ECGI(s) for the broadcast.
- Mapping from UE provided ECGI to appropriate target MBMS SAI(s) for the broadcast.
- Providing the appropriate ECGI(s) and/or MBMS SAI(s) to BM‑SC.
- Pre-configured with Local MBMS (L.MBMS) information (e.g. IP multicast address, multicast source (SSM), C-TEID).
- Pre-configured with L.MBMS's IP address and port number for the user-plane.
- Sending L.MBMS information to the BM‑SC.
- Requests BM‑SC for allocation/de-allocation of a set of TMGIs.
- Requests BM‑SC for activating/deactivating/modifying the MBMS bearer.
- Providing the V2X USDs for UE to receive MBMS based V2X traffic to V2X Control Function.
- Providing the parameters for V2X communications over PC5 reference point to V2X Control Function.
- Providing the parameters for V2X communications over PC5 reference point to UE.
4.3.4 MME p. 14
In addition to the functions defined in TS 23.401 and TS 23.246, in case of V2X the MME performs the following functions:
- Obtains subscription information related to V2X as part of the subscription data.
- Provides indication to the E-UTRAN about the UE authorization status on V2X use.
4.3.5 BM-SC p. 14
In addition to the functions defined in TS 23.246 and TS 23.468, in case of V2X the BM‑SC performs the following functions:
- Receives L.MBMS information from V2X Application Server.
- Sends L.MBMS information to the MBMS-GW.
4.3.6 MBMS-GW p. 14
In addition to the functions defined in TS 23.246, in case of V2X the MBMS-GW performs the following functions:
- If receiving L.MBMS information from the BM‑SC, skipping the allocation procedure for IP multicast distribution, e.g., allocating an IP multicast address.