Content for TS 23.236 Word version: 18.0.0
7 Specific Examples
7.1 Building blocks for signalling flows
7.1.1 RAN node selecting CN node in A interface mode
7.1.2 RAN node selecting CN node in Gb interface mode
7.1.3 RAN node selecting CN node in Iu interface mode
7.1.4 New CN node selecting old CN node
7.1.5 Old CN node selecting new CN node
7.1.6 SGSN selecting MSC
7.2 Signalling flow for Attach (Iu interface mode)
...
...
7 Specific Examples p. 21
This clause describes specific examples of Iu Flex. First, building blocks of Iu Flex are described in clause 7.1. These building blocks are then used in signalling flows starting from clause 7.2.
The changes to the signalling flows are indicated in italic.
7.1 Building blocks for signalling flows p. 21
7.1.1 RAN node selecting CN node in A interface mode p. 21
Void
7.1.2 RAN node selecting CN node in Gb interface mode p. 21
Void
7.1.3 RAN node selecting CN node in Iu interface mode p. 21
Void
7.1.4 New CN node selecting old CN node p. 21
This building block describes how a new CN node selects the old CN node which was previously serving the MS. The new CN node has been allocated to serve the MS, and it may have to communicate with the old CN node e.g. in order to get IMSI of the MS or to get MM and PDP contexts of the MS.
7.1.5 Old CN node selecting new CN node p. 22
This building block describes how the old CN node selects a new CN node which starts to serve the MS. The old CN node has to select a new CN node e.g. when performing handover.
7.1.6 SGSN selecting MSC p. 22
Void
7.2 Signalling flow for Attach (Iu interface mode) p. 22
At attach, the RNC selects an SGSN to serve the MS. The attach procedure is shown in the Figure below.
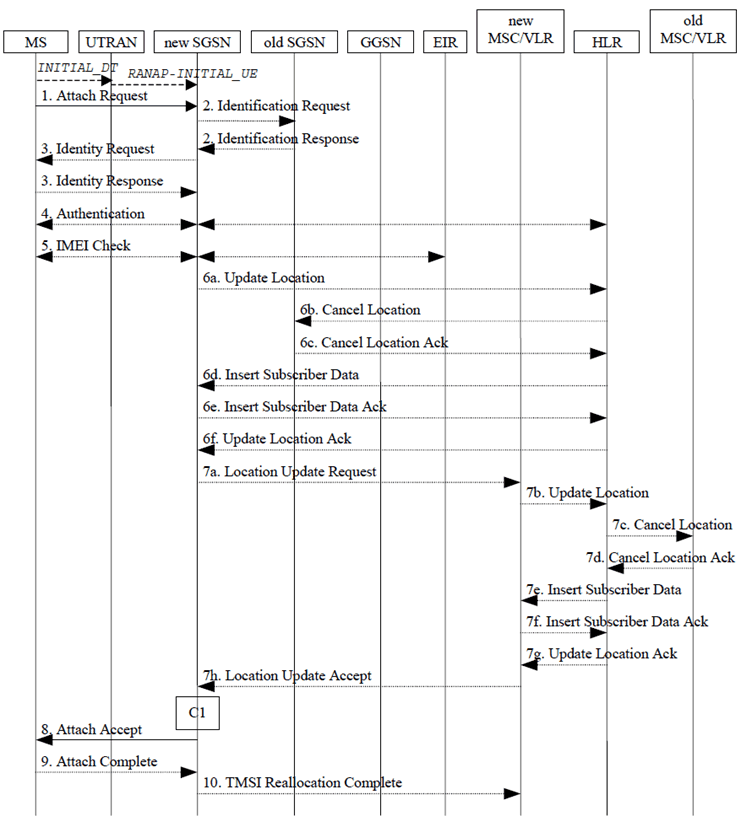
Step 1.
The Attach Request (old P-TMSI, old RAI, old P-TMSI Signature) is carried in the Initial Direct Transfer message (RRC) from the MS to the RNC. The RNC selects an SGSN to serve the MS as described in clause 7.1.3 and relays the Attach Request to the SGSN in the Initial UE message (RANAP).
Step 2.
If the MS identifies itself with P-TMSI and the SGSN has changed since detach, the new SGSN sends an Identification Request (P-TMSI, old RAI, old P-TMSI Signature) to the old SGSN to request the IMSI. The new SGSN selects the old SGSN as described in clause 7.1.4. The old SGSN responds with Identification Response (IMSI, Authentication Triplets (for GPRS) or Authentication Vectors (for UMTS)). If the MS is not known in the old SGSN, the old SGSN responds with an appropriate error cause. The old SGSN also validates the old P-TMSI Signature and responds with an appropriate error cause if it does not match the value stored in the old SGSN.
Step 3.
If the MS is unknown in both the old and new SGSN, the SGSN sends an Identity Request (Identity Type = IMSI) to the MS. The MS responds with Identity Response (IMSI).
Step 4.
The authentication functions are defined in the clause "Security Function" of TS 23.060. If no MM context for the MS exists anywhere in the network, then authentication is mandatory. Ciphering procedures are described in clause "Security Function" of TS 23.060. If P-TMSI allocation is going to be done and the network supports ciphering, the network shall set the ciphering mode.
Step 5.
The equipment checking functions are defined in the clause "Identity Check Procedures" of TS 23.060. Equipment checking is optional.
Step 6.
If the SGSN number has changed since the GPRS detach, or if it is the very first attach, then the SGSN informs the HLR:
Step 7.
- The SGSN sends an Update Location (SGSN Number, SGSN Address, IMSI) to the HLR.
- The HLR sends Cancel Location (IMSI, Cancellation Type) to the old SGSN with Cancellation Type set to Update Procedure.
- The old SGSN acknowledges with Cancel Location Ack (IMSI). If there are any ongoing procedures for that MS, the old SGSN shall wait until these procedures are finished before removing the MM and PDP contexts.
- The HLR sends Insert Subscriber Data (IMSI, GPRS Subscription Data) to the new SGSN.
- The new SGSN validates the MS's presence in the (new) RA. If due to regional subscription restrictions the MS is not allowed to attach in the RA, the SGSN rejects the Attach Request with an appropriate cause, and may return an Insert Subscriber Data Ack (IMSI, SGSN Area Restricted) message to the HLR. If subscription checking fails for other reasons, the SGSN rejects the Attach Request with an appropriate cause and returns an Insert Subscriber Data Ack (IMSI, Cause) message to the HLR. If all checks are successful then the SGSN constructs an MM context for the MS and returns an Insert Subscriber Data Ack (IMSI) message to the HLR.
- The HLR acknowledges the Update Location message by sending an Update Location Ack to the SGSN after the cancelling of old MM context and insertion of new MM context are finished. If the Update Location is rejected by the HLR, the SGSN rejects the Attach Request from the MS with an appropriate cause.
If Attach Type in step 1 indicated GPRS Attach while already IMSI attached, or combined GPRS / IMSI attached, then the VLR shall be updated if the Gs interface is installed. The VLR number is determined as described in clause 7.1.6. The SGSN starts the location update procedure towards the new MSC/VLR upon receipt of the first Insert Subscriber Data message from the HLR in step 6d). This operation marks the MS as GPRS-attached in the VLR.
Step 8.
- The SGSN sends a Location Update Request (new LAI, IMSI, SGSN Number, Location Update Type) message to the VLR. Location Update Type shall indicate IMSI attach if Attach Type indicated combined GPRS / IMSI attach. Otherwise, Location Update Type shall indicate normal location update. The VLR creates an association with the SGSN by storing SGSN Number.
- If the LA update is inter-MSC, the new VLR sends Update Location (IMSI, new VLR) to the HLR.
- If the LA update is inter-MSC, the HLR sends a Cancel Location (IMSI) to the old VLR.
- The old VLR acknowledges with Cancel Location Ack (IMSI).
- If the LA update is inter-MSC, the HLR sends Insert Subscriber Data (IMSI, GSM subscriber data) to the new VLR.
- The VLR acknowledges with Insert Subscriber Data Ack (IMSI).
- After finishing the inter-MSC location update procedures, the HLR responds with Update Location Ack (IMSI) to the new VLR.
- The VLR responds with Location Update Accept (VLR TMSI) to the SGSN. An Iu Flex aware VLR includes one of its (CS-)NRIs as part of VLR TMSI. The SGSN creates an association with the VLR by storing VLR number.
The SGSN selects Radio Priority SMS, and sends an Attach Accept (P-TMSI, VLR TMSI, P-TMSI Signature, Radio Priority SMS) message to the MS. P-TMSI is included if the SGSN allocates a new P-TMSI. An Iu Flex aware SGSN includes one of its (PS-)NRIs as part of P-TMSI.
Step 9.
If P-TMSI or VLR TMSI was changed, the MS acknowledges the received TMSI(s) by returning an Attach Complete message to the SGSN.
Step 10.
If VLR TMSI was changed, the SGSN confirms the VLR TMSI re-allocation by sending a TMSI Reallocation Complete message to the VLR.