Content for TS 23.236 Word version: 18.0.0
7.4 Signalling flow for Routing Area Update (Iu interface mode) p. 27
The routing area update procedure is shown in the Figure below.
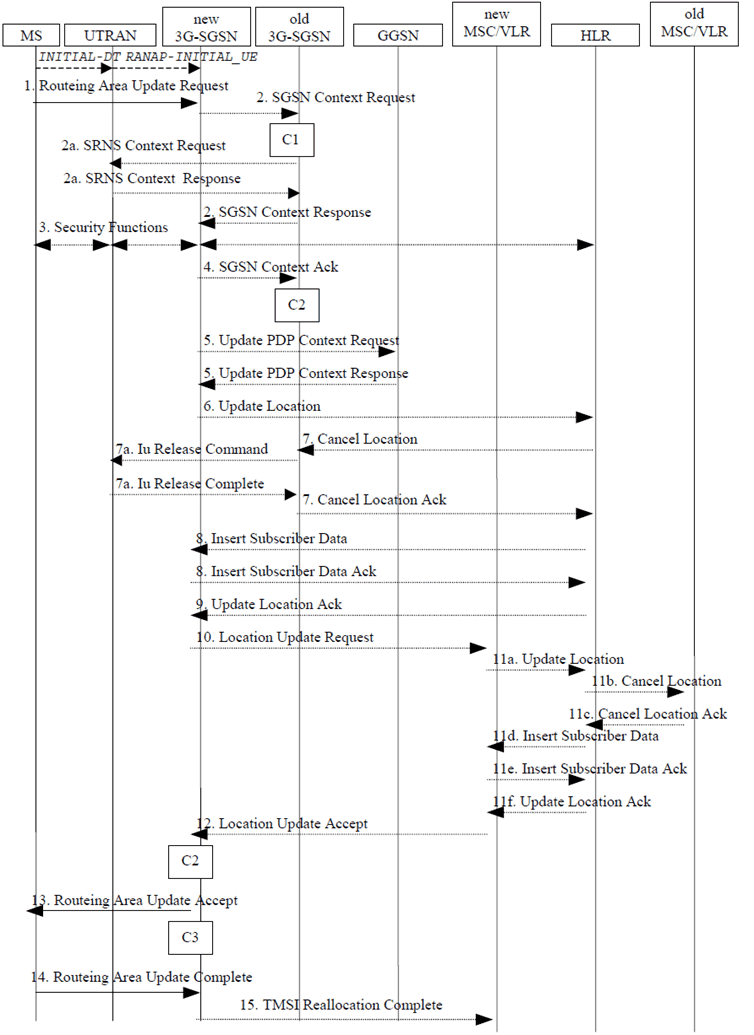
Figure 7: Signalling flow for Routing Area Update (Iu interface mode)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
Step 1.
The RRC connection is established, if not already done. The Routeing Area Update Request (old P-TMSI, old RAI, old P-TMSI Signature) is carried in the Initial Direct Transfer message (RRC) from the MS to the RNC. The RNC selects an SGSN to serve the MS as described in clause 7.1.3 and relays the Routeing Area Update Request to the SGSN in the Initial UE message (RANAP).
Step 2.
If the RA update is an Inter-SGSN Routeing area update and if the MS was in PMM IDLE state, the new SGSN sends an SGSN Context Request message (old P-TMSI, old RAI, old P-TMSI Signature) to the old SGSN to get the MM and PDP contexts for the MS. The new SGSN selects the old SGSN as described in clause 7.1.4. The old SGSN validates the old P-TMSI Signature and responds with an appropriate error cause if it does not match the value stored in the old SGSN. This should initiate the security functions in the new SGSN. If the security functions authenticate the MS correctly, the new SGSN shall send an SGSN Context Request (IMSI, old RAI, MS Validated) message to the old SGSN. MS Validated indicates that the new SGSN has authenticated the MS. If the old P-TMSI Signature was valid or if the new SGSN indicates that it has authenticated the MS, the old SGSN responds with SGSN Context Response (Cause, IMSI, MM Context, PDP contexts). If the MS is not known in the old SGSN, the old SGSN responds with an appropriate error cause. The old SGSN starts a timer. The new SGSN shall ignore the MS Network Capability contained in MM Context of SGSN Context Response only when it has previously received an MS Network Capability in the Routeing Area Request.
Step 3.
- If the MS is PMM CONNECTED in the old 3G SGSN, the old SGSN shall send an SRNS Context Request (IMSI) message to the old SRNS to retrieve the sequence numbers for the PDP context for inclusion in the SGSN Context Response message from the SRNS. Upon reception of this message, the SRNS buffers and stops sending downlink PDUs to the MS and returns an SRNS Context Response (IMSI, GTP SNDs, GTP SNUs, PDCP SNUs) message. The SRNS shall include for each PDP context the next in-sequence GTP sequence number to be sent to the MS and the GTP sequence number of the next uplink PDU to be tunnelled to the GGSN. For each active PDP context using acknowledged mode, the SRNS also includes the uplink PDCP sequence number (PDCP SNU). PDCP SNU shall be the next in-sequence PDCP sequence number expected from the MS (per each active radio bearer).
Security functions may be executed. These procedures are defined in clause "Security Function" of TS 23.060. If the security functions do not authenticate the MS correctly, the routeing area update shall be rejected, and the new SGSN shall send a reject indication to the old SGSN. The old SGSN shall continue as if the SGSN Context Request was never received.
Step 4.
If the RA update is an Inter-SGSN Routeing area update, the new SGSN sends an SGSN Context Acknowledge message to the old SGSN. The old SGSN marks in its context that the MSC/VLR association and the information in the GGSNs and the HLR are invalid. This triggers the MSC/VLR, the GGSNs, and the HLR to be updated if the MS initiates a routeing area update procedure back to the old SGSN before completing the ongoing routeing area update procedure.
Step 5.
If the RA update is an Inter-SGSN RA Update and if the MS was in PMM IDLE state, the new SGSN sends Update PDP Context Request (new SGSN Address, QoS Negotiated, Tunnel Endpoint Identifier) to the GGSNs concerned. The GGSNs update their PDP context fields and return an Update PDP Context Response (Tunnel Endpoint Identifier). Note: If the RA update is an Inter-SGSN routeing area update initiated by an MS in PMM CONNECTED state, the Update PDP Context Request message is sent as described in clause "Serving RNS Relocation Procedures" of TS 23.060.
Step 6.
If the RA update is an Inter-SGSN RA Update, the new SGSN informs the HLR of the change of SGSN by sending Update Location (SGSN Number, SGSN Address, IMSI) to the HLR.
Step 7.
If the RA update is an inter-SGSN RA Update, the HLR sends Cancel Location (IMSI, Cancellation Type) to the old SGSN with Cancellation Type set to Update Procedure. If the timer described in step 2 is not running, the old SGSN removes the MM context. Otherwise, the contexts are removed only when the timer expires. It also ensures that the MM context is kept in the old SGSN in case the MS initiates another inter SGSN routeing area update before completing the ongoing routeing area update to the new SGSN. The old SGSN acknowledges with Cancel Location Ack (IMSI).
Step 8.
- If the MS is PMM CONNECTED in the old 3G SGSN, the old 3G SGSN sends an Iu Release Command message to the old SRNC. The SRNC responds with an Iu Release Complete message.
If the RA update is an inter-SGSN RA Update, the HLR sends Insert Subscriber Data (IMSI, subscription data) to the new SGSN. The new SGSN validates the MS's presence in the (new) RA. If due to regional subscription restrictions the MS is not allowed to be attached in the RA, the SGSN rejects the Routeing Area Update Request with an appropriate cause, and may return an Insert Subscriber Data Ack (IMSI, SGSN Area Restricted) message to the HLR. If all checks are successful, the SGSN constructs an MM context for the MS and returns an Insert Subscriber Data Ack (IMSI) message to the HLR.
Step 9.
If the RA update is an Inter-SGSN RA Update, the HLR acknowledges the Update Location by sending Update Location Ack (IMSI) to the new SGSN.
Step 10.
If Update Type indicates combined RA / LA update with IMSI attach requested, or if the LA changed with the routeing area update, the association has to be established. The VLR number is determined as described in clause 7.1.6. The new SGSN sends a Location Update Request (new LAI, IMSI, SGSN Number, Location Update Type) to the VLR. Location Update Type shall indicate IMSI attach if Update Type in step 1 indicated combined RA / LA update with ISI attach requested. Otherwise, Location Update Type shall indicate normal location update. The SGSN starts the location update procedure towards the new MSC/VLR upon receipt of the first Insert Subscriber Data message from the HLR in step 8). The VLR creates or updates the association with the SGSN by storing SGSN Number.
Step 11.
If the subscriber data in the VLR is marked as not confirmed by the HLR, the new VLR informs the HLR. The HLR cancels the old VLR and inserts subscriber data in the new VLR (this signalling is not modified from existing GSM signalling and is included here for illustrative purposes):
Step 12.
- The new VLR sends an Update Location (new VLR) to the HLR.
- The HLR cancels the data in the old VLR by sending Cancel Location (IMSI) to the old VLR.
- The old VLR acknowledges with Cancel Location Ack (IMSI).
- The HLR sends Insert Subscriber Data (IMSI, GSM subscriber data) to the new VLR.
- The new VLR acknowledges with Insert Subscriber Data Ack (IMSI).
- The HLR responds with Update Location Ack (IMSI) to the new VLR.
The new VLR allocates a new TMSI and responds with Location Update Accept (VLR TMSI) to the SGSN. VLR TMSI is optional if the VLR has not changed. An Iu Flex aware VLR includes one of its (CS-)NRIs as part of VLR TMSI. The SGSN creates an association with the VLR by storing VLR number.
Step 13.
The new SGSN validates the MS's presence in the new RA. If due to roaming restrictions the MS is not allowed to be attached in the SGSN, or if subscription checking fails, the SGSN rejects the routeing area update with an appropriate cause. If all checks are successful, the new SGSN establishes MM context for the MS. The new SGSN responds to the MS with Routeing Area Update Accept (P-TMSI, VLR TMSI, P-TMSI Signature). An Iu Flex aware SGSN includes one of its (PS-)NRIs as part of P-TMSI.
Step 14.
The MS confirms the reallocation of the TMSIs by returning a Routeing Area Update Complete message to the SGSN.
Step 15.
The new SGSN sends a TMSI Reallocation Complete message to the new VLR if the MS confirms the VLR TMSI.