Content for TS 38.323 Word version: 18.0.0
A Ethernet Header Compression (EHC) protocol
A.1 EHC principle
A.2 EHC packet format and parameters
A.2.1 EHC packet format
A.2.1.1 EHC Full Header packet and EHC Compressed Header packet
A.2.1.2 EHC feedback packet
A.2.2 Parameters
A.2.2.1 F/C
A.2.2.2 CID
A (Normative) Ethernet Header Compression (EHC) protocol |R16| p. 44
A.1 EHC principle p. 44
The Ethernet header compression (EHC) protocol compresses Ethernet header as shown in Figure A.1-1 [15]. The fields that are compressed (i.e. removed from the Ethernet header) by the EHC protocol are: DESTINATION ADDRESS, SOURCE ADDRESS, 802.1Q TAG, and LENGTH/TYPE. The fields PREAMBLE, SFD, and FCS are not transmitted in 3GPP system, and thus not considered in EHC protocol. There may be more than one 802.1Q TAG fields in the Ethernet header, and all are compressed by the EHC protocol. The padding (PAD) is not compressed by the EHC protocol.
![Reproduction of 3GPP TS 38.323, Fig. A.1-1: Ethernet packet format [15]](../img/tinv-38-323-A.1-1.gif)
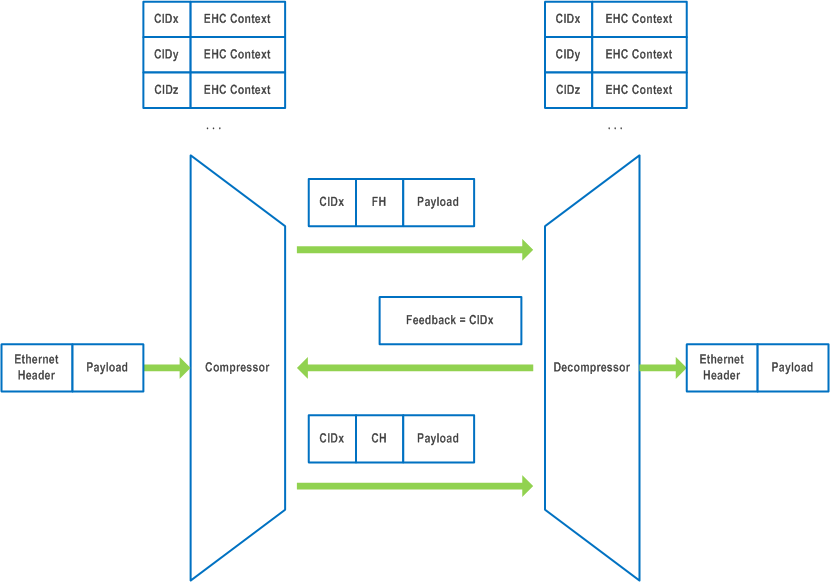
The EHC compressor and the EHC decompressor store original header field information as a "EHC context". Each EHC context is identified by a unique identifier, called Context ID (CID). The EHC context must be synchronized between the EHC compressor and the EHC decompressor; otherwise, the EHC decompressor erroneously decompresses the "Compressed Header (CH)" packets.
For an Ethernet packet stream, the EHC compressor establishes the EHC context and associates it with the CID. Then, the EHC compressor transmits the "Full Header (FH)" packet to the EHC decompressor including the associated CID. The EHC compressor keeps transmitting the FH packets until the EHC feedback is received from the EHC decompressor.
When the EHC decompressor receives the FH packet, the EHC decompressor establishes the EHC context identified by the CID, and transmits the EHC feedback to the EHC compressor to indicate that the EHC context associated with the CID is successfully established in the EHC decompressor.
After receiving the EHC feedback, the EHC compressor starts to transmit the CH packets to the EHC decompressor including the associated CID. The CH packet includes only the header fields not stored in the EHC context.
When the EHC decompressor receives the CH packet, the EHC decompressor restores original header fields based on the stored EHC context identified by the associated CID.
Figure A.1-2 represents a conceptual view of EHC operation.
A.2 EHC packet format and parameters p. 46
A.2.1 EHC packet format p. 46
A.2.1.1 EHC Full Header packet and EHC Compressed Header packet p. 46
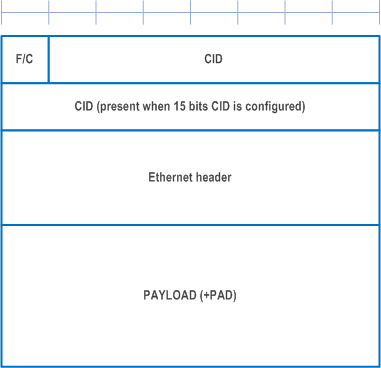
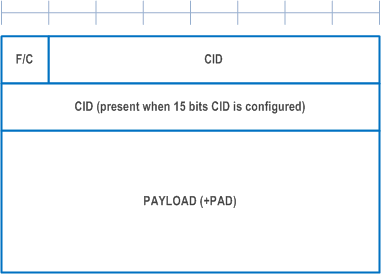
Figure A.2.1.1-1 and Figure A.2.1.1-2 show the formats of EHC FH packet and EHC CH packet, respectively.
A.2.1.2 EHC feedback packet p. 47
Figure A.2.1.2-1 shows the format of the EHC feedback packet.

A.2.2 Parameters p. 47
A.2.2.1 F/C p. 47
Length:
1 bit
This field indicates whether the corresponding EHC packet is a FH packet or a CH packet.
| Bit | Description |
|---|---|
| 0 | FH packet |
| 1 | CH packet |
A.2.2.2 CID p. 47
Length:
7, or 15 bits. The length of the CID is configured by upper layers (ehc-CID-Length in TS 38.331).
The CID = "all zeros" indicates that the corresponding Ethernet header is "uncompressed". The EHC decompressor does not establish the EHC context identified by the CID = "all zeros".