TS 25.450
UTRAN – Iupc Interface –
General Aspects and Principles
V18.0.0 (PDF)
2024/03 14 p.
V17.0.0
2022/03 14 p.
V16.0.0
2020/06 14 p.
V15.0.0
2018/06 14 p.
V14.0.0
2017/03 14 p.
V13.0.0
2015/12 14 p.
V12.0.0
2014/09 14 p.
V11.0.0
2012/09 14 p.
V10.1.0
2011/06 14 p.
V9.0.1
2011/04 14 p.
V8.0.0
2009/01 14 p.
V7.2.0
2007/10 14 p.
V6.2.0
2005/10 13 p.
V5.2.0
2005/06 14 p.
- Rapporteur:
- Mr. Flore, Dino
Content for TS 25.450 Word version: 18.0.0
1 Scope p. 5
The present document is an introduction to the TSG RAN TS 25.45z series of UMTS Technical Specifications that define the Iupc Interface. The Iupc interface is a logical interface for the interconnection of Stand-Alone SMLC (SAS) and Radio Network Controller (RNC) components of the Universal Terrestrial Radio Access Network (UTRAN) for the UMTS system.
2 References p. 5
The following documents contain provisions which, through reference in this text, constitute provisions of the present document.
- References are either specific (identified by date of publication, edition number, version number, etc.) or non-specific.
- For a specific reference, subsequent revisions do not apply.
- For a non-specific reference, the latest version applies. In the case of a reference to a 3GPP document (including a GSM document), a non-specific reference implicitly refers to the latest version of that document in the same Release as the present document.
[1] Void
[2]
TS 25.451: "UTRAN Iupc Interface: Layer 1".
[3]
TS 25.452: "UTRAN Iupc Interface: Signalling Transport".
[4]
TS 25.453: "UTRAN Iupc Interface PCAP Signalling".
[5]
ITU-T Recommendation Q.711 (1996-07): "Functional description of the signalling connection control part".
[6]
ITU-T Recommendation Q.712 (1996-07): "Definition and function of signalling connection control part messages".
[7]
ITU-T Recommendation Q.713 (1996-07): "Signalling connection control part formats and codes".
[8]
ITU-T Recommendation Q.714 (1996-07): "Signalling connection control part procedures".
[9]
TS 23.003: "Numbering, Addressing and Identification".
[10] Void
[11]
TS 25.305: "Stage 2 functional specification of UE positioning in UTRAN"
3 Definitions and abbreviations p. 5
3.1 Definitions p. 5
For the purposes of the present document, the following terms and definitions apply:
Stand-Alone SMLC (SAS):
As defined in TS 25.305.
RNC Centric:
In this mode of operation (defined in TS 25.305), the RNC is responsible for position method selection and initiation of the selected positioning method. Once a position method is selected, the RNC may interact with the SAS to exchange data as well as for execution of the selected positioning method.
SAS Centric:
In this mode of operation (defined in TS 25.305), the SAS is responsible for position method selection and initiation of the selected positioning method. Once a position method is selected, the SAS may interact with the RNC to exchange data to enable it to execute the selected positioning method.
3.2 Abbreviations p. 6
For the purposes of the present document, the following abbreviations apply:
GANSS
Galileo and Additional Navigation Satellite Systems
GNSS
Global Navigation Satellite System
GPS
Global Positioning System
GT
Global Title
M3UA
SS7 MTP3 User Adaptation Layer
PCAP
Position Calculation Application Part
RNC
Radio Network Controller
SAS
Stand-Alone SMLC
SCCP
Signalling Connection Control Part
SMLC
Serving Mobile Location Centre
SPC
Signalling Point Code
SRNC
Serving Radio Network Controller
SS7
Signalling System No 7
SSN
Sub-System Number
UE
User Equipment
UMTS
Universal Mobile Telecommunication System
UTRAN
Universal Terrestrial Radio Access Network
3.3 Specification Notations p. 6
For the purposes of the present document, the following notations apply:
[FDD]
This tagging of a word indicates that the word preceding the tag "[FDD)]" applies only to FDD. This tagging of a heading indicates that the heading preceding the tag "[FDD]" and the section following the heading applies only to FDD.
[TDD]
This tagging of a word indicates that the word preceding the tag "[TDD]" applies only to TDD, including 7.68 Mcps TDD, 3.84Mcps TDD and 1.28Mcps TDD. This tagging of a heading indicates that the heading preceding the tag "[TDD]" and the section following the heading applies only to TDD, including 7.68 Mcps TDD, 3.84Mcps TDD and 1.28Mcps TDD.
[7.68Mcps TDD]
This tagging of a word indicates that the word preceding the tag "[7.68Mcps TDD]" applies only to 7.68Mcps TDD. This tagging of a heading indicates that the heading preceding the tag "[7.68Mcps TDD]" and the section following the heading applies only to 7.68Mcps TDD.
[3.84Mcps TDD]
This tagging of a word indicates that the word preceding the tag "[3.84Mcps TDD]" applies only to 3.84Mcps TDD. This tagging of a heading indicates that the heading preceding the tag "[3.84Mcps TDD]" and the section following the heading applies only to 3.84Mcps TDD.
[1.28Mcps TDD]
This tagging of a word indicates that the word preceding the tag "[1.28Mcps TDD]" applies only to 1.28Mcps TDD. This tagging of a heading indicates that the heading preceding the tag "[1.28Mcps TDD]" and the section following the heading applies only to 1.28Mcps TDD.
[FDD - …]
This tagging indicates that the enclosed text following the "[FDD - " applies only to FDD. Multiple sequential paragraphs applying only to FDD are enclosed separately to enable insertion of TDD specific (or common) paragraphs between the FDD specific paragraphs.
[TDD - …]
This tagging indicates that the enclosed text following the "[TDD - " applies only to TDD including 7.68 Mcps TDD, 3.84Mcps TDD and 1.28Mcps TDD. Multiple sequential paragraphs applying only to TDD are enclosed separately to enable insertion of FDD specific (or common) paragraphs between the TDD specific paragraphs.
[7.68Mcps TDD - …]
This tagging indicates that the enclosed text following the "[7.68Mcps TDD - " applies only to 7.68Mcps TDD. Multiple sequential paragraphs applying only to 7.68Mcps TDD are enclosed separately to enable insertion of FDD and TDD specific (or common) paragraphs between the 7.68Mcps TDD specific paragraphs.
[3.84Mcps TDD - …]
This tagging indicates that the enclosed text following the "[3.84Mcps TDD - " applies only to 3.84Mcps TDD. Multiple sequential paragraphs applying only to 3.84Mcps TDD are enclosed separately to enable insertion of FDD and TDD specific (or common) paragraphs between the 3.84Mcps TDD specific paragraphs.
[1.28Mcps TDD - …]
This tagging indicates that the enclosed text following the "[1.28Mcps TDD - " applies only to 1.28Mcps TDD. Multiple sequential paragraphs applying only to 1.28Mcps TDD are enclosed separately to enable insertion of FDD and TDD specific (or common) paragraphs between the 1.28Mcps TDD specific paragraphs.
Procedure
When referring to a procedure in the specification, the Procedure Name is written with the first letters in each word in upper case characters followed by the word "procedure", e.g. RNSAP Basic Mobility Procedures.
Message
When referring to a message in the specification, the MESSAGE NAME is written with all letters in upper case characters followed by the word "message", e.g. RADIO LINK SETUP REQUEST message.
Frame
When referring to a control or data frame in the specification, the CONTROL/DATA FRAME NAME is written with all letters in upper case characters followed by the words "control/data frame", e.g. DCH data frame.
4 General Aspects p. 7
4.1 Introduction p. 7
The logical interface between a RNC and a SAS within the UTRAN is referred to the Iupc interface.
4.2 Iupc Interface General Principles p. 7
The general principles for the specification of the Iupc interface are as follows:
- the Iupc interface should be open;
- complex functionality shall as far as possible be avoided over Iupc. Advanced optimisation solutions may be added in later versions of the standard;
- from a logical standpoint, the Iupc is a point-to-point signalling interface between an RNC and SAS within the UTRAN, even though there may not be a direct physical connection between these two nodes;
- one RNC may connect to one SAS. One SAS may provide services to one RNC;
- neither the physical structure nor any internal protocols of the RNC or SAS shall be visible over Iupc and are thus not limiting factors, e.g., when introducing future technology.
4.3 Iupc Interface Specification Objectives p. 8
The Iupc interface specifications shall facilitate the following:
- inter-connection of RNCs and SASs from different manufacturers;
- separation of Iupc interface Application functionality and Transport Network functionality to facilitate introduction of future technology.
4.4 Iupc Interface Capabilities p. 8
4.4.1 General p. 8
The Iupc interface connects a RNC and a SAS.
4.4.2 Position Calculation Services p. 8
The Iupc interface enables an SRNC and a SAS to exchange information that is related to the positioning of a single UE. These exchanges involve the transfer of UE Positioning measurement data or UE position estimate data.
4.4.3 Information Exchange Services p. 8
The Iupc interface enables an RNC to request specific GNSS (GPS or GANSS) related data from an SAS on demand, on modification, or at regular intervals.
4.4.4 SAS Centric Position Services |R7| p. 8
The Iupc interface enables an RNC and a SAS to exchange information that is related to the positioning of a single UE, using SAS Centric mode of operation.
4.5 Iupc Interface Characteristics p. 8
4.5.1 Uses of SCCP p. 8
4.5.1.1 General p. 8
The SCCP, ITU-T Rec. Q.711 [5], ITU-T Rec. Q.712 [6], ITU-T Rec. Q.713 [7] and ITU-T Rec. Q.714 [8], is used to transport messages between the RNC and SAS. One user function of the SCCP, called Positioning Calculation Application Part (PCAP), is defined TS 25.453.
Both connectionless and connection-oriented procedures are used to support PCAP. TS 25.453 explain whether connection oriented or connectionless services should be used for a layer 3 procedure.
4.5.1.2 SCCP Addressing p. 8
The inclusion of caller party address in SCCP message is mandatory. PCAP may use SSN, SPC and/or GT and any combination of them as addressing schemes for the SCCP. When GT addressing is utilised, the following settings shall be used:
- SSN Indicator = 1 (PCAP SSN as defined in TS 23.003).
- Global Title Indicator = 0100 (GT includes translation type, numbering plan, encoding scheme and nature of address indicator).
- Translation Type = 0000 0000 (not used).
- Numbering Plan = 0001 (E.163/4).
- Nature of Address Indicator = 000 0100 (International Significant Number).
- Encoding Scheme = 0001 or 0010 (BCD, odd or even).
- Routing indicator = 0 or 1 (route on GT or PC/SSN).
4.5.1.3 SCCP connection establishment p. 9
Information Exchange services
A new SCCP connection is established when the RNC initiates a class-1 elementary procedure for Information Exchange services and there is no signalling bearer existing for this purpose.
An SCCP connection is always established by the RNC.
SAS Centric Position services
A new SCCP connection is established when the RNC initiates a class-1 elementary procedure, with respect to each new positioning request, for SAS Centric Position services.
An SCCP connection is always established by the RNC.
Initiation
The RNC sends SCCP CONNECTION REQUEST message to the SAS. A PCAP message is included in the user data field of the SCCP CONNECTION REQUEST message.Termination
- successful outcome: The SCCP CONNECTION CONFIRM message, which may optionally contain a PCAP message in the user data field, is returned to the RNC.
- unsuccessful outcome: If the SCCP signalling connection establishment fails, an SCCP CONNECTION REFUSAL message will be sent back to the RNC. This message may contain a PCAP message.

Figure 1: Setting-up of RNC Initiated SCCP Signalling Connection with SAS
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
4.5.1.4 SCCP connection release p. 9
This procedure is always initiated by the RNC. An SCCP connection is released when the RNC realises that a given signalling connection is no longer required. This is accomplished by the RNC sending a SCCP RELEASED message.
4.5.1.5 General SCCP Abnormal Conditions p. 10
If a user-out-of-service information or signalling-point-inaccessible information is received by the RNC, no new attempt to establish SCCP connections towards the affected point code will be started until the corresponding user-in-service information or signalling-point-accessible information is received.
When a user-out-of-service information or signalling-point-inaccessible is received by the RNC, an optional timer may be started. When the timer expires, all the SCCP connections towards the affected point code will be released. When the user-in-service or signalling-point-accessible is received, the timer is stopped.
If for any reason an SCCP connection is released, the optional timer expires or a connection refusal is received while any of the SAS procedures are being performed or while a dedicated resource is still allocated, the procedures associated to that SCCP connection shall be terminated (at both the RNC side and the SAS side).
5 Functions of the Iupc Interface Protocols p. 10
5.1 List of Functions p. 10
The list of functions on the Iupc interface is the following:
- Management of GPS Related Data;
- Management of Position Calculation Functions;
- Management of SAS Centric Position Functions;
- Management of GANSS Related Data,
5.2 Management of GPS Related Data p. 10
An RNC may request GPS related data from an SAS in order to provide GPS assistance data to a single UE. Alternatively, an RNC may request GPS related data from an SAS in order to support the broadcast of GPS assistance data to multiple UEs in a particular area via system information messages. Each type of GPS related data may be requested on demand, on modification, or at regular intervals.
5.3 Management of Position Calculation Functions p. 10
To support a UE-assisted positioning attempt involving a single UE, an RNC provides an SAS with one or more sets of
- GPS or GANSS measurement data,
- ODTOA measurement data,
- Cell ID measurement data.
5.4 Management of SAS Centric Position Functions |R7| p. 10
In the SAS Centric mode of operation, the RNC may initiate a positioning event, the SAS may activate a positioning method requesting the RNC for relevant data, and on completion of the position determination process the SAS may return the final response to the RNC. In addition, during an ongoing positioning event, the RNC may send the SAS a modified set of positioning parameters, or the RNC may even instruct the SAS to abort the positioning process itself.
5.5 Management of GANSS Related Data |R7| p. 11
This management of the GANSS Related Data is the same as the management of the GPS Related Data described in section 5.2, except that it is applicable to Galileo and Additional Navigation Satellite Systems instead of GPS.
6 Other Iupc Interface Specifications p. 11
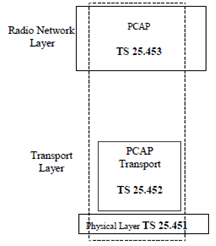
6.1 UTRAN Iupc Interface: Layer 1 (TSG RAN 25.451) p. 11
TS 25.451 specifies the standards allowed for implementation of Layer 1 (physical layer) on the Iupc interface.
6.2 UTRAN Iupc Interface: Signalling Transport (TSG RAN 25.452) p. 11
TS 25.452 specifies the signalling transport related to PCAP signalling to be used across the Iupc interface.
6.3 PCAP Specification (TSG RAN 25.453) p. 11
TS 25.453 specifies the standards for PCAP specification to be used over the Iupc interface.
6.4 Summary of UTRAN Iupc Interface Technical Specifications p. 11
The relationship between the technical specifications that define the UTRAN Iupc interface is shown in figure 2.