Content for TS 23.207 Word version: 18.0.0
D Resource reservation and end-to-end RSVP p. 32
D.1 Resource reservation with end-to-end RSVP p. 32
For this case, RSVP is added to the GPRS bearer establishment procedures specified in TS 23.060, with no Service-based local policy.
The following figure is applicable to the Mobile Originating (MO) side.
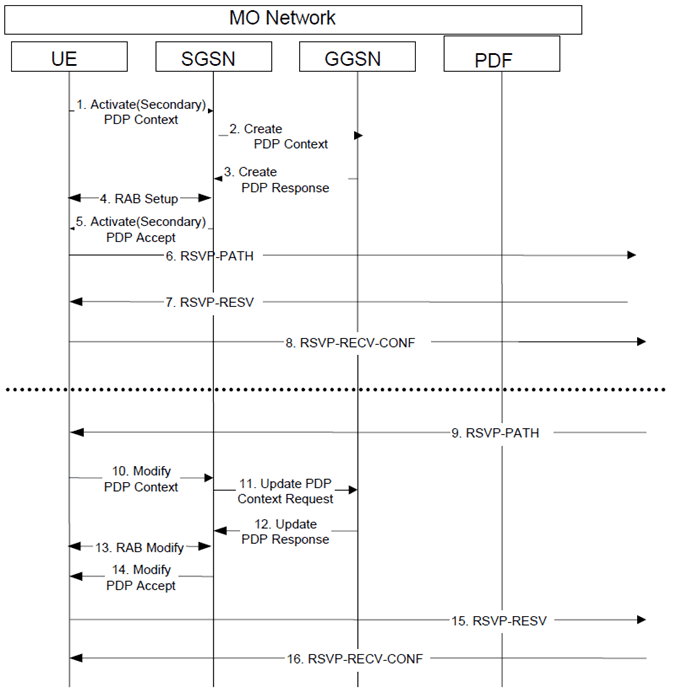
Step 1.
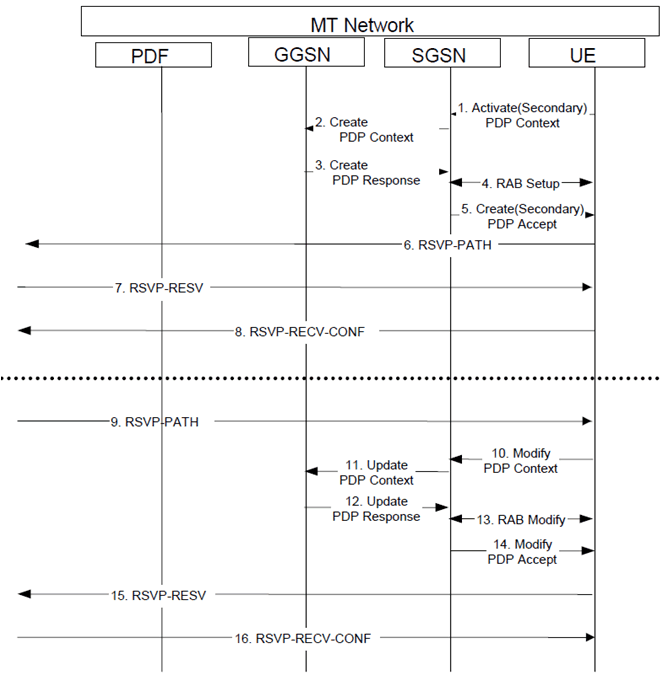
The following figure is applicable to the Mobile Terminating (MT) side. As the flow is the mirror of the Mobile Originating (MO) side, the step-by-step description is omitted.
The UE sends an Activate (Secondary) PDP Context message to the SGSN with the UMTS QoS parameters.
Step 2.
The SGSN sends the corresponding Create PDP Context message to the GGSN.
Step 3.
The GGSN authorizes the PDP context activation request according to the local operator's IP bearer resource based policy, the local operator's admission control function and the GPRS roaming agreements and sends a Create PDP Context Response message back to the SGSN.
Step 4.
RAB setup is done by the RAB Assignment procedure.
Step 5.
The SGSN sends an Activate (Secondary) PDP Context Accept message to UE.
Step 6.
UE sends an RSVP PATH message to the next hop, through the GGSN. The GGSN does not process the RSVP PATH message. Alternatively, the GGSN may process the RSVP PATH message and forward it to the next hop.
Step 7.
The UE receives the RSVP RESV message in the downlink direction, through the GGSN. The GGSN does not process the RSVP RESV message. Alternatively, the GGSN may process the RSVP RESV message and forward it to the UE.
Step 8.
The UE sends a RSVP RESV-CONF message to the next hop. The use of the RESV-CONF message is optional.
Step 9.
The UE receives a RSVP PATH message in the downlink direction, through the GGSN. The GGSN does not process the RSVP PATH message. Alternatively, the GGSN may process the incoming RSVP PATH message and forward it to the UE.
Step 10.
The UE may send a Modify PDP Context message to the SGSN with the necessary modification to UMTS QoS parameters according to the received RSVP PATH message.
Step 11.
The SGSN sends the corresponding Update PDP Context Request message to the GGSN.
Step 12.
The GGSN authorizes the PDP context modification according to the local operator's IP bearer resource based policy, the local operator's admission control function and the GPRS roaming agreements and sends an Update PDP Context Response message back to the SGSN.
Step 13.
The radio access bearer modification may be performed by the RAB Assignment procedure.
Step 14.
The SGSN sends a Modify PDP Context Accept message to UE.
Step 15.
UE sends the RSVP RESV message to the next hop, through the GGSN. The GGSN does not process the RSVP RESV message. Alternatively, the GGSN may process the RSVP RESV message and forward it to the next hop.
Step 16.
The UE receives the RSVP RESV-CONF message in the downlink direction. The use of the RESV-CONF message is optional.