Content for TR 22.801 Word version: 12.0.0
0 Introduction
1 Scope
2 References
3 Definitions and abbreviations
3.1 Definitions
3.2 Abbreviations
4 Background
4.1 Mobile data applications and their adverse system impacts
...
...
0 Introduction p. 4
Some mobile data applications might result in adverse impact to the mobile network, e.g. due to frequent idle-active mode changing, frequent start or stop of services, small data transmission, frequent live update, transmission of data burst. Hence, the network (both RAN and CN) may experience a flood of signalling and data traffic.
This study aims to investigate the service scenario/use cases of different mobile data applications. Their impact to the current system is generalized. Potential service and operational requirements are indentified for possible enhancements to the system.
1 Scope p. 5
To make the network better suited for mobile data applications, the aim/scope of this study is to:
- Capture real world data / analysis.
- Identify services scenarios / use cases for mobile data applications.
- Identify potential problems / issues caused by different mobile data applications.
- Identify potential service and operational requirements for possible enhancements to the system.
2 References p. 5
The following documents contain provisions which, through reference in this text, constitute provisions of the present document.
- References are either specific (identified by date of publication, edition number, version number, etc.) or non-specific.
- For a specific reference, subsequent revisions do not apply.
- For a non-specific reference, the latest version applies. In the case of a reference to a 3GPP document (including a GSM document), a non-specific reference implicitly refers to the latest version of that document in the same Release as the present document.
[1]
TR 21.905: "Vocabulary for 3GPP Specifications".
[2]
"Apple App Store Tops 300,000 Apps," internet source: http://www.pcmag.com/article2/0 ,2817,2373169,00.asp
[3]
"Crossing the 100,000 Applications Mark," internet source: http://blog.androlib.com/
[4]
"Smartphones and a 3G Network,": Signals Research Group.
[5]
"Diversity in Smartphone Usage,": H. Falaki, R. Mahajan, S. Kandula, D. Lymberopoulos, R. Govindan, and D. Estrin, MobiSys'10, June 2010.
[6]
"A First Look at Traffic on Smartphones,": H. Falaki, D. Lymberopoulos, R. Mahajan, S. Kandula, and D. Estrin, IMC November 2010.
[7]
"An Analysis of the Skype Peer-to-Peer Internet Telephony Protocol,": S. Baset and H. Schulzrinne, IEEE Infocom 2006.
[8]
"Find*Me," internet source: https://market.android.com/details?id=com.gpsshare.ads
[9]
[10]
[11]
[12]
[13]
C. Na, J. K. Chen, and T. S. Rappaport, "Measured Traffic Statistics and Throughput of IEEE 802.11b Public WLAN Hotspots with Three Different Applications,": IEEE Transactions On Wireless Communications, Nov. 2006.
[14]
F. Wamser, R. Pries, D. Staehle, K. Heck, and P. Tran-Gia, "Traffic characterization of a residential wireless Internet access,": Special Issue of the Telecommunication Systems (TS) Journal, 48: 1-2, 2010.
[15]
[16]
[17]
[18]
TS 26.346: "Multimedia Broadcast/Multicast Service (MBMS); Protocols and codecs".
[19]
[20]
[21]
[22]
X. Geng and A.B. Whinston, "Defeating Distributed Denial of Service Attacks,": IEEE Journal of IT Professional, Volume 2, Issue 4, Jul. 2000.
3 Definitions and abbreviations p. 6
3.1 Definitions p. 6
For the purposes of the present document, the terms and definitions given in TR 21.905 and the following apply. A term defined in the present document takes precedence over the definition of the same term, if any, in TR 21.905.
None
3.2 Abbreviations p. 6
For the purposes of the present document, the abbreviations given in TR 21.905 and the following apply. An abbreviation defined in the present document takes precedence over the definition of the same abbreviation, if any, in TR 21.905.
AoS
Always Online Service
Apps
Applications
CN
Core Network
DDoS
Distributed Denial of Service
EPC
Evolved Packet Core
IM
Instant Messaging
MODAI
Non-MTC Mobile Data Application Impacts
SNS
Social Network Services
SP
Service Provider
4 Background p. 6
4.1 Mobile data applications and their adverse system impacts p. 6
Today, there exist hundreds of thousands of mobile data applications for mobile devices [2] and [3]. Many of these applications utilize the mobile broadband connections to provide various types of communications to the users. While some of these applications focus on more "traditional" use cases such as web browsing or email reading, other emerging applications such as social networking applications help the users to "stay connected" with their friends on the go. Below is a short list of different categories of mobile data applications:
- Web browsing
- Weather/News updates
- VoIP (Skype, etc.)
- Social Networking (Facebook)
- Geo services (Google places/location-targeted ads)
- Online games
- Messaging (SMS and instant messaging)
- etc.
- One application can potentially cause multiple problems to the network.
- Different applications can contribute to the same problem to the network, thereby aggravating the problems observed in the EPC and RAN.
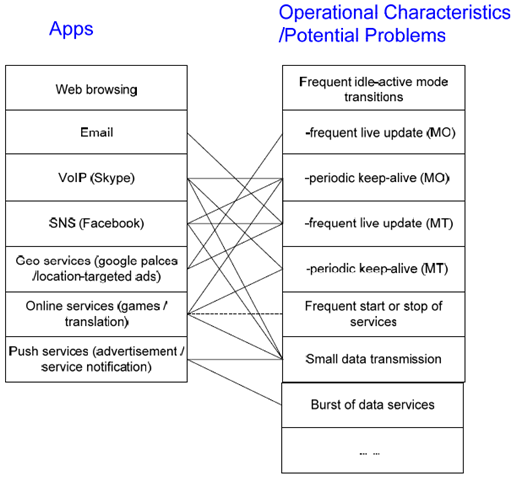
Figure 1: Many-to-many mapping between the mobile data applications and potential adverse system effects
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)