TS 22.135
Multicall —
Stage 1
V18.0.1 (PDF)
2024/03 21 p.
V17.0.0
2022/03 21 p.
V16.0.0
2020/06 21 p.
V15.0.0
2018/06 20 p.
V14.0.0
2017/03 21 p.
V13.0.0
2015/12 21 p.
V12.0.0
2014/10 21 p.
V11.0.0
2012/09 21 p.
V10.0.0
2011/04 21 p.
V9.0.0
2009/12 21 p.
V8.0.0
2009/01 21 p.
V7.0.0
2007/06 21 p.
V6.0.0
2004/12 21 p.
V5.0.0
2002/07 21 p.
V4.2.0
2002/12 21 p.
V3.4.0
2000/10 19 p.
- Rapporteur:
- Miss Miettinen, Natalia
NOKIA UK R&D Ltd
Content for TS 22.135 Word version: 18.0.1
1 Scope
2 References
3 Definitions, symbols and abbreviations
4 Description
5 Functional requirements
6 Exceptional procedures or unsuccessful outcome
7 Interaction with other services
8 Interaction with other network features and services
A Busy definition
B Cross Phase Compatibility
$ Change history
1 Scope p. 6
The present document presents describes Multicall supplementary service.
The general aspects, including definitions and recommended provision, of the description of the 3GPP Supplementary Services are given in TS 22.004.
2 References p. 6
The following documents contain provisions which, through reference in this text, constitute provisions of the present document.
- References are either specific (identified by date of publication, edition number, version number, etc.) or non specific.
- For a specific reference, subsequent revisions do not apply.
- For a non-specific reference, the latest version applies. In the case of a reference to a 3GPP document (including a GSM document), a non-specific reference implicitly refers to the latest version of that document in the same Release as the present document.
[1]
TS 22.001: "Principles of circuit telecommunication services supported by a Public Land Mobile Network (PLMN)".
[2]
TS 22.004: "General on Supplementary Services".
[3]
TS 22.024: "Description of Charge Advice Information (CAI)".
[4]
TS 22.030: "Man Machine Interface (MMI) of the Mobile Station (MS)".
[5]
TS 22.100: "UMTS Phase 1 Release 99".
[6]
TS 22.129: "Handover Requirement between UTRAN and GERAN or other Radio Systems".
[7]
TS 22.097: "Multiple Subscriber Profile (MSP) ".
3 Definitions, symbols and abbreviations p. 6
3.1 Definitions p. 6
CS Call:
Circuit switched call. A call routed through CS domain. CS call can be for example a speech call, fax call or data call. One call shall only use one bearer at the time
Multiparty:
Supplementary Service for speech conference service
Ncs MO:
maximum number of simultaneous mobile originating CS calls. The value of The Value of Ncs_MOis 7. If Ncs_MO has been reached, no more MO calls can be set-up
Ncs_MT:
Maximum number of simultaneous mobile terminating CS calls. The value of Ncs_MT is 7. If Ncs_MT has been reached, additional MT call attempts shall fail without any indication to the called subscriber
Nbr:
Maximum number of simultaneous CS bearers. The value of Nbr is the smallest value within the Nbr_User, Nbr_UE, and Nbr_SN
Nbr_User:
Maximum number of simultaneous CS bearers allowed, as defined by the user within the limits given by Nbr_SB
Nbr_SB:
Maximum number of simultaneous CS bearers allowed, defined by the service provider in the Multicall subscription
Nbr_UE:
Maximum number of simultaneous CS bearers supported by the UE
Nbr_SN:
Maximum number of simultaneous CS bearers supported by the serving network
4 Description p. 7
4.1 Description of multicall p. 7
The Multicall supplementary service enables a mobile subscriber to have several simultaneous CS calls, each call using its own dedicated bearer.
Only one CS bearer can used for speech at any one times.
A speech call is one of TS11 (Telephony), TS12 (Emergency Calls), and TS61 (Alternate speech/fax). If the bearer capability information is not available, e.g. the call is originated/transited by a PSTN, the basic service cannot be deduced and the network shall, for multicall purposes, handle the call as telephony.
A held call shall be regarded as using the bearer used while the call was active.
It shall be possible for each CS call to use a dedicated bearer of independent traffic and performance characteristics. It shall be possible to release each active CS call independently of any other CS call.
4.2 Applicability to telecommunication services p. 7
The applicability of this Supplementary Service is defined in TS 22.004.
5 Functional requirements p. 7
5.1 Provision p. 7
Multicall is provided by prior arrangement with the service provider.
Multicall shall be provisioned for all Basic Services (BS) subscribed to and to which it is applicable, i.e. not to any subset of these BS.
When the Multicall supplementary service is provisioned the maximum number of simultaneous CS beares available to the subscriber (Nbr_SB) shall be defined as part of the subscription. The value for Nbr_SB shall in the range from 2 up to 7.
5.2 Withdrawal p. 7
It shall be possible to withdraw the Multicall supplementary service subscription on request of the subscriber or for administrative reasons.
5.3 Registration p. 8
The user shall be able to modify the maximum number of CS bearers available (Nbr_User) within the limitations set by the service provider. (Nbr_SB).
If the subscriber attempts to register a value for Nbr_User that is higher than the value of Nbr_SB, the request shall be rejected and the subscriber shall be informed on the unsuccessful outcome on the request.
5.4 Erasure p. 8
Data related to the Multicall supplementary service shall be erased by the service provider as a result of withdrawal.
5.5 Activation p. 8
The Multicall supplementary service shall be activated by the service provider as a result of provision.
5.6 Deactivation p. 8
The Multicall supplementary service shall be deactivated by the service provider as a result of withdrawal.
5.7 Invocation p. 8
The Multicall supplementary service shall be invoked by the system when at least one call is in progress and another call with a dedicated bearer is to be set up. The Multicall service applies to mobile originating and mobile terminating calls.
5.8 Interrogation p. 8
The user shall be able to interrogate the network for the values of Nbr_User, Nbr_SB and Nbr_SN.
5.9 Call related procedures p. 8
5.9.1 Terminating CS call p. 8
The indication of a terminating CS call to the mobile terminal will be done by the Multicall supplementary service until either the maximum number of bearer (Nbr) or the maximum number of CS mobile terminating calls (Ncs_MT) has been reached.
If the maximum number of terminating calls (Ncs_MT) has been reached, and additional terminating call shall be reject without any indication to the subscriber.
If the maximum number of bearers (Nbr) has been reached an additional terminating call will be only indicated to the user if the user has the Call Waiting supplementary service active, see clause 7.3.2 for interactions with Call Waiting.
If Nbr and Ncs_MT havenot been reached, a terminating call is indicated to the user and she may react in the following way:
-
Accept the terminating call:
- The user/user applications shall have the possibility to allocate a new bearer for the terminating call.
- If the user has the Call Hold SS active, the user shall have the possibility to reuse/share an already established bearer (e.g. release existing calls or put an speech on hold and accept the terminating call).
-
Rejecting the terminating call:
- If the user rejects the terminating call the call shall be released in a normal way.
-
Ignore the incoming call:
- If the user ignores the indication of the terminating call (i.e. neither accepts nor rejects it ), the normal call handling shall apply, e.g. after the Alerting Timer expires the call will be released.
5.9.2 Originating CS call p. 9
If neither Nbr nor Ncs_MO have not been reached and the user wants to establish a new originating CS call she may act in the following way:
- allocate a new bearer for the originating call;
- reuse/share an already established bearer (e.g. to put an speech on hold and set-up a new call).
5.10 Charging requirements p. 9
Each of the calls using a dedicated bearer shall be charged individually.
Allocation of a dedicated bearer shall be visible in the charging data.
6 Exceptional procedures or unsuccessful outcome p. 9
6.1 Exceptional operation or unsuccessful outcome p. 9
The number of simultaneous CS bearers supported by the system may vary in different regions. For instance, after handover the number of simultaneous bearers available to the served subscriber may be lower than the number of already established bearers. Such events shall trigger changes to individual calls in any multicall scenario.
The handover requirements for multicall are specified in TS 22.129.
6.2 Registration p. 9
If the system cannot accept a registration request, the served mobile subscriber shall receive a notification that Multicall registration was not successful. Possible causes are:
- service not subscribed to;
- Nbr_User > Nbr_SB;
- insufficient information.
6.3 Erasure p. 9
No exceptional operation identified.
6.4 Activation p. 10
No exceptional operation identified.
6.5 Deactivation p. 10
No exceptional operation identified.
6.6 Invocation p. 10
If the served subscriber attempts to set up a new call with a dedicated bearer while the maximum number of bearers available to the subscriber (Nbr) has been reached, the call attempt shall be rejected by normal procedures, indicating that no more bearers are available.
6.7 Interrogation p. 10
When a mobile subscriber who is not provided with the Multicall supplementary service interrogates the service data of the Multicall supplementary service, she shall be notified that she is not subscribed to the service.
6.8 Roaming in non-supporting networks p. 10
Roaming into networks not supporting the Multicall supplementary service shall be possible. The served subscriber will not have any access to the Multicall supplementary service and the system should behave accordingly.
When the served subscriber performs any procedure related to Multicall service as described in the clauses above while roaming in a non-supporting network, she shall be notified that the service is not available.
7 Interaction with other services p. 10
7.1 Line Identification p. 10
7.1.1 Calling Line Identification Presentation (CLIP) p. 10
No impact, i.e. CLIP shall be provided with all calls.
7.1.2 Calling Line Identification Restriction (CLIR) p. 10
No impact, i.e. CLIR shall be provided with all calls.
7.1.3 Connected Line Identification Presentation (COLP) p. 10
No impact, i.e. COLP shall be provided with all calls.
7.1.4 Connected Line Identification Restriction (COLR) p. 10
No impact, i.e. COLR shall be provided with all calls.
7.2 Call Forwarding p. 11
7.2.1 Call Forwarding Unconditional (CFU) p. 11
No impact.
7.2.2 Call Forwarding on Busy (CFB) p. 11
No impact.
7.2.3 Call Forwarding on No Reply (CFNRy) p. 11
No impact.
7.2.4 Call Forwarding on Not Reachable (CFNRc) p. 11
No impact.
7.3 Call Completion p. 11
7.3.1 Call Hold (CH) p. 11
No impact, i.e. it shall be possible to put an established speech call on hold.
Irrespective of whether the maximum number of CS bearers (Nbr) is reached or not, and a terminating call is indicated to the user, she shall be able to accept the terminating call by applying the Call Hold service to an active speech call. By that she makes the bearer of the held call available to the new call.
7.3.2 Call Waiting (CW) p. 11
When the subscriber has at least one ongoing call and a new terminating call is speech; then Call Waiting shall be invoked if:
- there is an active speech call and Call Waiting is active and operative for speech or;
- there is a held speech call, with no active call on the same bearer, and Call Waiting is active and operative for speech or;
- there is a held speech call, with an active non-speech call on the same bearer, and Call Waiting is active and operative for that non-speech basic service or;
- there are no speech calls (including a call on hold), the maximum number of bearers (Nbr) has been reached and Call Waiting is active and operative for at least one of the basic services currently in use.
7.4 Multi Party (MPTY) p. 12
No Impact.
The number of MPTY member may be limited by Ncs_MO, Ncs_MT and Ncs.
7.5 Closed User Group (CUG) p. 12
No impact.
7.6 Advice of Charge (AoC) p. 12
The subscriber shall receive the AoC indication individually for each CS call.
For the AoCC service, the ACM (Accumulated Call Meter as defined in TS 22.024) shall reckon the sum of the charge generated by all simultaneous CS calls.
7.7 Call Barring p. 12
No impact.
7.7.1 Barring of all outgoing calls p. 12
No impact.
7.7.2 Barring of outgoing international calls p. 12
No impact.
7.7.3 Barring of outgoing international calls except those directed to the HPLMN country p. 12
No impact.
7.7.4 Barring of all incoming calls p. 12
No impact.
7.7.5 Barring of incoming calls when roaming p. 12
No impact.
7.8 Explicit Call Transfer (ECT) p. 12
No impact.
7.9 Completion of Call to Busy Subscriber (CCBS) p. 13
The definition of the IDLE state of subscriber A and destination B is not modified, i.e. a subscriber is considered to be IDLE when all the bearers (calls) for her have been released.
A subscriber to whom CCBS can be invoked shall be regarded as NDUB under the specific NDUB condition for Multicall (See Annex A).
7.10 Multiple Subscriber Profile (MSP) p. 13
No impact. The Multicall supplementary service shall be provisioned on a per subscriber basis. Nbr_SN, Nbr_SB, and Nbr_user shall apply over all profiles.
7.11 Calling Name Presentation (CNAP) p. 13
No impact.
7.12 User-to-User Signalling (UUS) p. 13
No Impact
7.13 enhanced Multi-Level Precedence and Pre-emption service (eMLPP) p. 13
No impact.
7.14 Call Deflection (CD) p. 13
No impact.
8 Interaction with other network features and services p. 13
8.1 CAMEL p. 13
No impact.
8.2 IST p. 13
No impact.
8.3 ODB p. 13
No impact.
8.4 Emergency Calls p. 13
The network shall handle emergency call at first priority. When a user originates an emergency call, the network shall behave as follows:
- The network, which supports Multicall, shall accept the emergency call within the serving network capability regardless of Multicall subscription limitation to the user.
- The MS shall ensure that an emergency call setup request is acceptable to a serving network which does not support multicall, if necessary by releasing one or more existing call.
A (Normative) Busy definition p. 15
NDUB (Network Determined User Busy) occurs when:
- The maximum number of mobile terminating calls (Ncs_MT) has been reached (NOTE 1).
- The maximum number of bearers (Nbr) has been reached and the maximum number of waiting calls has been reached (NOTE 2, NOTE3).
B Cross Phase Compatibility p. 16
This section details the cross phase compatibility requirements relating to the service requirements in this document.
B.1 Compatibility With Existing Standards p. 16
Where the service and operational requirements in this document relate to core network functionality, compatibility is required.
Multicall mechanisms are not applicable for GERAN.
B.2 Compatibility With Future Releases p. 16
It is envisaged that 3GPP standards will evolve in future releleases, for example with the addition of new service requirements. The standards which define the technical implementation should be developed in such a way that it is practical to add the requirements in this section in a backward compatible manner.
Following chapters include requirements that are foreseen for future release.
B.2.1 Multicall configuration p. 16
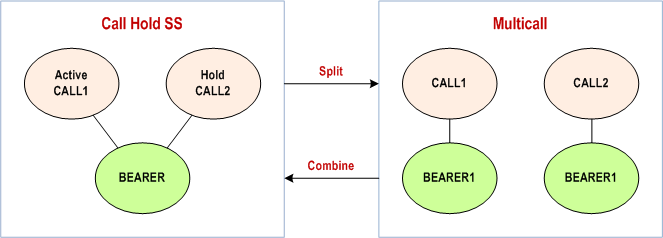
When having one active CS call and one held call on the same bearer. It shall be possible to create a new CS bearer and to move one of the calls to the new bearer, resulting both calls being active within the limits set by the operator/user and within the capability of the terminal. See Figure 2: Split of bearer.
When having two calls (multicall) on the separate bearers. It shall be possible to join both calls to one of the two bearers, put the one of the calls to hold and to release unused CS bearer. It shall be possible to select which call to put on hold. See Figure 2: Combination of bearers. (Note: there is no clear end-user service requirement for this feature at time being).
B.2.2 Several simultaneous speech calls / bearers p. 17
A Key requirements for multicall is to allow several simultaneous CS calls with dedicated bearers. The most important usage scenario is to allow several CS data bearers to be bind at application level resulting to higher than 64kbits/s data rates. Another important feature is to allow simultaneous speech and data calls.
It's been proposed that the multicall feature could be introduced in a phased manner; meaning that in the first phase, i.e. 3GPP release 99 does only support one active speech call at a time. However, Call control should not prohibit a complete set of multiple speech bearer services in future releases and UTRAN shall be designed in a flexible way to support multiple speech bearers. The specific NDUB definition for speech call shall be removed when multiple speech call is supported. At this release , Supplementary Services Call Waiting, Multiparty and Call Hold are used to offer simultaneous speech calls to user.
Ncs may be extended in further releases.
If multiple simultaneous speech calls are supported in the future then the Call Hold service may be used to reconfigure the number of bearers supporting speech calls if required during handover. e.g. in the case of handover to GERAN where only one speech call can be active at a time. This requirement is dependent on the user subscribing to Call Hold.
B.2.3 CCBS p. 17
At this release CCBS no enhancements for CCBS is required.
In the future releases the definition of IDLE state of subscriber A and destination B should be modified in away that the IDLE state is reach even if there are active CS calls but the maximum limit of CS calls is not reached.