Content for TS 23.402 Word version: 18.3.0
0…
4…
4.2…
4.2.2
4.2.3
4.3…
4.4…
4.5…
4.5.7…
4.6…
4.7…
4.7.2…
4.8…
4.8.2a…
4.9…
5…
5.2…
5.4…
5.5
5.6…
5.7…
5.8…
6…
6.2…
6.3
6.4…
6.4.3…
6.5…
6.6…
6.7…
6.8…
6.10…
6.13…
6.15…
7…
7.2…
7.3
7.4…
7.5…
7.6…
7.8…
7.10…
8…
8.2.1.2
8.2.1.3…
8.2.2
8.2.3…
8.2.6…
8.3…
8.4…
8.5…
9…
9.3…
9.4…
10…
13…
16…
16.1.2…
16.1.6…
16.2…
16.2.1a…
16.3…
16.4…
16.7…
16.8…
16.10…
17…
A…
C…
E…
6.5 Detach and PDN Disconnection for S2c in Trusted Non-3GPP IP Access
6.5.1 General
6.5.2 UE-initiated PDN disconnection Procedure
6.5.3 HSS / AAA-initiated Detach Procedure
6.5.4 PDN-GW-initiated PDN Disconnection Procedure
...
...
6.5 Detach and PDN Disconnection for S2c in Trusted Non-3GPP IP Access p. 135
6.5.1 General p. 135
This clause is related to the cases where at least one DSMIPv6 PDN disconnection procedure is performed. In case of detach the DSMIPv6 PDN disconnection is executed for all the existing PDNs connections, while in the case of disconnecting a single PDN connection the DSMIPv6 PDN disconnection is executed only for the individual PDN connection.
The DSMIPv6 PDN disconnection procedure is on a per PDN basis and allows:
- the UE to inform the network that it requests to release a S2c based PDN connection, and
- the network to inform the UE that a S2c based PDN connection is disconnected.
- Explicit PDN disconnection: The network or the UE explicitly requests PDN disconnection and signal with each other.
- Implicit PDN disconnection: The network disconnects the UE from a PDN, without notifying the UE. This is typically the case when the network presumes that it is not able to communicate with the UE, e.g. due to radio conditions.
- UE-Initiated PDN disconnection Procedure;
- AAA/HSS-initiated Detach Procedure;
- PDN-GW-initiated PDN disconnection Procedure.
6.5.2 UE-initiated PDN disconnection Procedure p. 136
The PDN disconnection procedure when initiated by the UE is illustrated in Figure 6.5.2-1. In case of detaching the UE from EPS, the procedure defined in this clause must be repeated for each PDN.
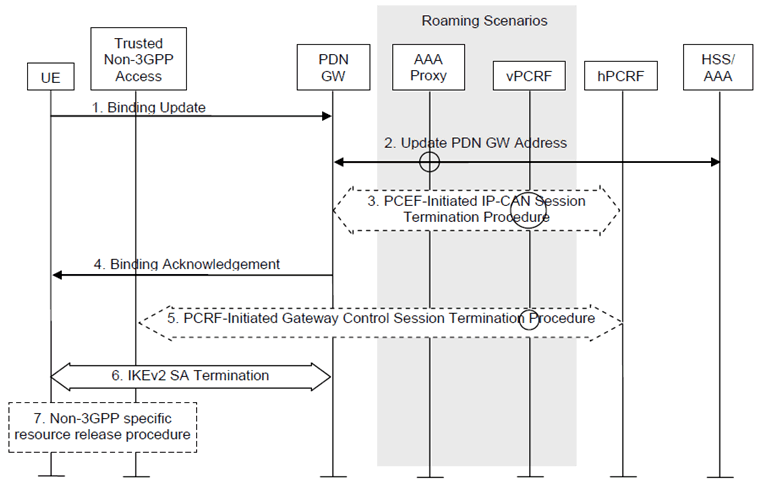
Figure 6.5.2-1: UE-initiated DSMIPv6 PDN disconnection procedure in Trusted Non-3GPP Access Network
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
Non-roaming (Figure 4.2.2-2), home routed roaming (Figure 4.2.3-3) and Local Breakout (Figure 4.2.3-4) cases are supported by this procedure. The AAA proxy and vPCRF are only used in the case of home routed roaming and Local Breakout. In non-roaming scenarios, the AAA proxy and vPCRF are not involved.
The optional interaction steps between the gateways and the PCRF in the procedures only occur if dynamic policy provisioning is deployed. Otherwise policy may be statically configured with the gateway.
Step 1.
If the UE wants to terminate a S2c session for a given PDN, it shall send a de-registration Binding Update (HoA, Lifetime=0) as specified in RFC 5555.
Step 2.
The PDN-GW informs the 3GPP AAA Server of the PDN disconnection. If the PDN-GW is in the VPLMN, signalling may be routed via a 3GPP AAA Proxy in the VPLMN. If the UE no longer has any context in the 3GPP AAA Server, the 3GPP AAA Server notifies the HSS as described in clause 12.1.2.
Step 3.
If there is an active PCC session for the UE, the PDN-GW shall execute a PCEF-Initiated IP-CAN session Termination Procedure with the PCRF as specified in TS 23.203.
Step 4.
The PDN-GW shall send a Binding Acknowledgement as specified in RFC 5555
Step 5.
The PCRF shall remove all active QoS rules which refer to the Home Address. The PCRF executes a PCRF-Initiated Gateway Control Session Termination Procedure with the Trusted Non-3GPP IP Access as specified in TS 23.203. The Trusted Non-3GPP IP Access will no longer perform any QoS policy or gateway control function associated with the terminated session.
This step describes the case where there are no QoS rules remaining for that UE at the trusted non-3GPP access and thus the GW control session termination is executed. In case there are still active QoS rules for the UE, the GW control session termination procedure is replaced by a QoS rule provision procedure.
Step 6.
The UE terminates the IKEv2 security association for the given PDN as defined in RFC 5996
Step 7.
After IKEv2 SA termination, non-3GPP specific resource release procedure may be executed.
6.5.3 HSS / AAA-initiated Detach Procedure p. 137
The Detach procedure when initiated by the HSS/AAA is illustrated in Figure 6.5.3-1. The Detach procedure defined in this clause must be repeated for each PDN.
If the HSS/AAA-initiated detach procedure has been initiated to delete the UE from the Evolved Packet Core, the HSS/AAA server shall initiate the detach procedure for each of the access systems to which the UE is registered.
In the explicit detach procedure steps 2, 3 and 7 of Figure 6.5.3-1, are performed as illustrated. In the implicit detach, steps 2, 3 and 7 of Figure 6.5.3-1, are omitted.
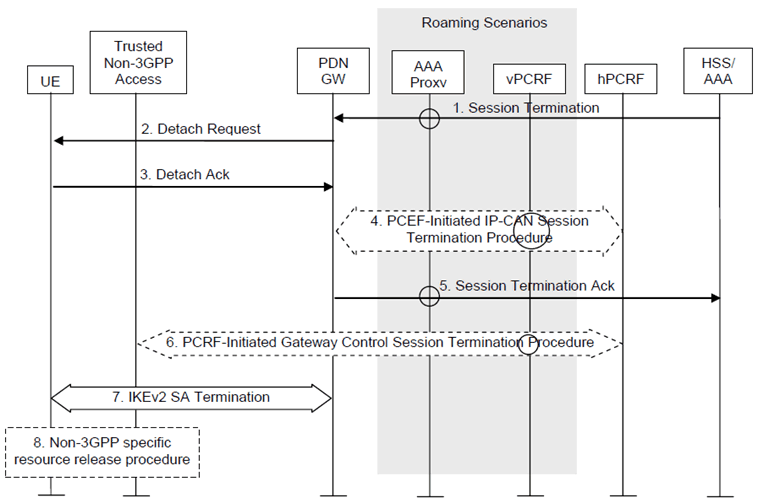
Figure 6.5.3-1: AAA/HSS-initiated S2c detach procedure in Trusted Non-3GPP Access Network
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
Non-roaming (Figure 4.2.2-1), home routed roaming (Figure 4.2.3-2) and Local Breakout (Figure 4.2.3-4) cases are supported by this procedure. The 3GPP AAA proxy and vPCRF are only used in the case of home routed roaming and Local Breakout. In non-roaming scenarios, the 3GPP AAA proxy and vPCRF are not involved.
If dynamic policy provisioning is not deployed, the optional steps 4 and 6 do not occur. Instead, the PDN-GW may employ static configured policies.
Step 1.
If the HSS/AAA wants to request the immediate termination of a S2c session for a given UE and a given PDN, it shall send a Session Termination message to the PDN-GW. In the roaming case signalling may be routed via a 3GPP AAA Proxy in the VPLMN.
Step 2.
The PDN-GW shall send a detach request message.
Step 3.
The UE shall acknowledge the detach request.
Step 4.
If there is an active PCC session for the UE, the PDN-GW shall execute a PCEF-Initiated IP-CAN Session Termination Procedure with the PCRF as specified in TS 23.203.
Step 5.
The PDN-GW shall acknowledge the termination of the S2c session to the AAA. If the detach procedure was initiated from the 3GPP AAA Server and if the UE no longer has any context in the 3GPP AAA Server, the 3GPP AAA Server communicates the HSS as described in clause 12.1.2. If the detach procedure was initiated by HSS, the 3GPP AAA Server replies to the HSS as described in clause 12.1.3.
Step 6.
The PCRF shall remove any active QoS Policy rule which is referred to the Home Address. The PCRF executes a PCRF-Initiated Gateway Control Session Termination Procedure with the Trusted Non-3GPP IP Access as specified in TS 23.203. The Trusted Non-3GPP IP Access will no longer perform any QoS policy or gateway control function associated with the terminated session.
This step describes the case where there are no QoS rules remaining for that UE at the trusted non-3GPP access and thus the GW control session termination is executed. In case there are still active QoS rules for the UE, the GW control session termination procedure is replaced by a QoS rule provision procedure.
Step 7.
The PDN-GW or the UE terminates the IKEv2 security association for the given PDN as defined in RFC 5996.
Step 8.
After IKEv2 SA termination, non-3GPP specific resource release procedure may be executed.
6.5.4 PDN-GW-initiated PDN Disconnection Procedure p. 138
The PDN Disconnection procedure when initiated by the PDN-GW is illustrated in Figure 6.5.4-1.
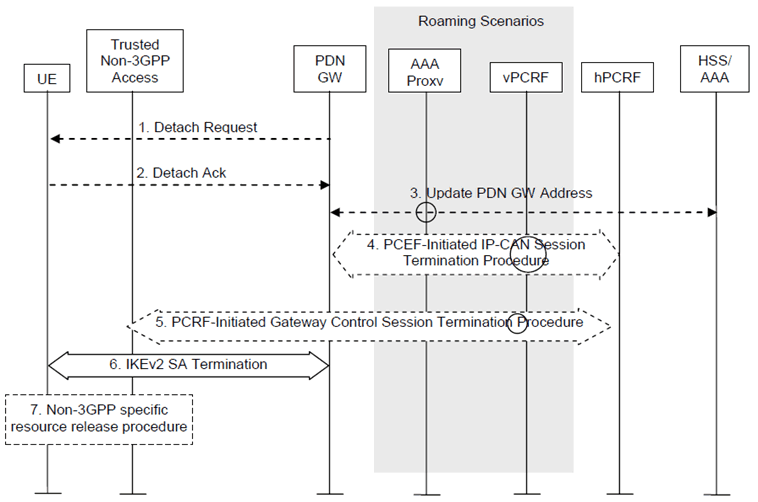
Figure 6.5.4-1: PDN-GW- initiated PDN Disconnection S2c procedure in Trusted Non-3GPP Access Network
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
Non-roaming (Figure 4.2.2-1), home routed roaming (Figure 4.2.3-2) and Local Breakout (Figure 4.2.3-4) cases are supported by this procedure. The 3GPP AAA proxy and vPCRF are only used in the case of home routed roaming and Local Breakout. In non-roaming scenarios, the 3GPP AAA proxy and vPCRF are not involved.
If dynamic policy provisioning is not deployed, the optional step 3 does not occur. Instead, the PDN-GW may employ static configured policies.
If the PDN-GW-initiated PDN Disconnection Procedure is triggered by the UE binding lifetime expiration (Implicit PDN disconnection procedure), steps 1 and 2 may be omitted.
Step 1.
In the explicit detach procedure the PDN-GW shall send a detach request message.
Step 2.
In the explicit detach procedure, the UE shall acknowledge the detach request.
Step 3.
The PDN-GW informs the 3GPP AAA Server of the PDN disconnection. If the PDN-GW is in the VPLMN, signalling may be routed via a 3GPP AAA Proxy in the VPLMN. If the UE no longer has any context in the 3GPP AAA Server, the 3GPP AAA Server notifies the HSS as described in clause 12.1.2.
Step 4.
If there is an active PCC session for the UE, the PDN-GW shall execute a PCEF-Initiated IP-CAN Session Termination Procedure with the PCRF as specified in TS 23.203.
Step 5.
The PCRF shall remove all active QoS rules which refer to the Home Address. The PCRF executes a Gateway Control and QoS Rules Provision procedure or, if this is the last PDN Connection for the UE, a PCRF-Initiated Gateway Control Session Termination Procedure with the Trusted Non-3GPP IP Access as specified in TS 23.203. The Trusted Non-3GPP IP Access will no longer perform any QoS policy or gateway control function associated with the terminated PDN Connection.
Step 6.
The PDN-GW or the UE may terminate the IKEv2 security association for the given PDN as defined in RFC 5996.
Step 7.
After IKEv2 SA termination, non-3GPP specific resource release procedure may be executed.