Content for TS 23.436 Word version: 18.2.0
5 Application architecture for ADAES
5.1 General
5.2 Functional architecture
5.2.1 General
5.2.2 On-network Functional Architecture
5.2.3 Off-network Functional Architecture
5.3 ADAE internal architecture
...
...
5 Application architecture for ADAES p. 11
5.1 General p. 11
This clause provides the functional architecture for ADAE. This includes the on-network and off-network functional models which are provided in detail in clause 5.2.
In addition, the ADAE internal architecture is described in 5.3, which aligns with the 3GPP data analytics framework (specified in TS 23.288) and introduces new logical entities within ADAE framework, such as the A-DCCF and A-ADRF.
5.2 Functional architecture p. 11
5.2.1 General p. 11
The functional architecture for the application data analytics enablement is based on the generic functional model specified in clause 6.2 of TS 23.434. It is organized into functional entities to describe a functional architecture which addresses the support for application data analytics enablement aspects for vertical applications.
5.2.2 On-network Functional Architecture p. 11
For the on-network functional architecture, both service-based representation and reference point representation are provided.
Figure 5.2.2-1 depicts the application data analytics enablement architecture in the non-roaming case, using the reference point representation showing how various entities interact with each other.
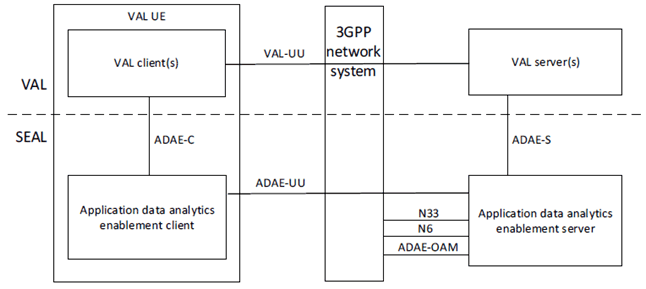
Figure 5.2.2-1: Architecture for application data analytics enablement - reference points representation
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
The application data analytics enablement client communicates with the application data analytics enablement server over the ADAE-UU reference point. The application data analytics enablement client provides the support for application data analytics enablement functions to the VAL client(s) over ADAE-C reference point. The VAL server(s) communicates with the application data analytics enablement server over the ADAE-S reference point. The application data analytics enablement server, acting as AF, may communicate with the 5G Core Network functions (over N33 reference point to NEF and N6 reference point to UPF) and OAM (over ADAE-OAM interface).
Figure 5.2.2-2 exhibits the service-based interfaces for providing and consuming application data analytics enablement services. The application data analytics enablement server could provide service to VAL server and ADAE client through interface SAdae.
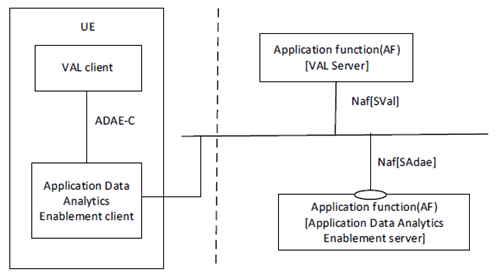
Figure 5.2.2-2: Architecture for application data analytics enablement - Service based representation
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
Figure 5.2.2-3 illustrates the service-based representation for utilization of the 5GS network services based on the 5GS SBA specified in TS 23.501.
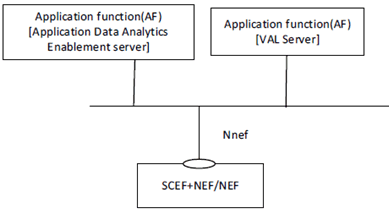
Figure 5.2.2-3: Architecture for application data analytics enablement utilizing the 5GS network services based on the 5GS SBA - Service based representation
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
Figure 5.2.2-4 illustrates the architecture for inter-service communication between ADAES server and other SEAL server.
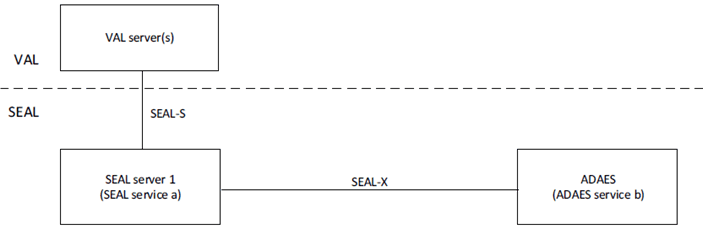
Figure 5.2.2-4: Inter-service communication between ADAES server and other SEAL server
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
The ADAE server interacts with another SEAL server for inter-service communication over SEAL-X reference point.
5.2.3 Off-network Functional Architecture p. 13
Figure 5.2.3-1 illustrates the generic off-network functional model for ADAE.
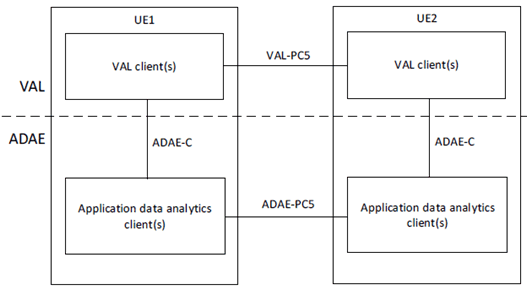
In the vertical application layer, the VAL client of UE1 communicates with VAL client of UE2 over VAL-PC5 reference point. An application data analytics enablement client of UE1 interacts with the corresponding application data analytics enablement client of UE2 over ADAE-PC5 reference points. The UE1, if connected to the network via Uu reference point, can also act as a UE-to-network relay, to enable UE2 to access the VAL server(s) over the VAL-UU reference point.
The service-based interface representation is specified in clause 15 of TS 23.434.
5.3 ADAE internal architecture p. 14
In ADAE framework, A-DCCF and A-ADRF can be defined as functionalities within the internal ADAE architecture and can offer the following functionalities:
- Application layer - Data Collection and Coordination Function (A-DCCF) coordinates the collection and distribution of data requested by the consumer (ADAE server). Data Collection Coordination is supported by a A-DCCF. ADAE server can send requests for data to the A-DCCF rather than directly to the Data Sources. A-DCCF may also perform data processing/abstraction and data preparation based on the VAL server requirements.
- Application layer - Analytics and Data Repository Function (A-ADRF) stores historical data and/or analytics, i.e., data and/or analytics related to past time period that has been obtained by the consumer (e.g. ADAE server). After the consumer obtains data and/or analytics, consumer may store historical data and/or analytics in an A-ADRF. Whether the consumer directly contacts the A-ADRF or goes via the A-DCCF is based on configuration.
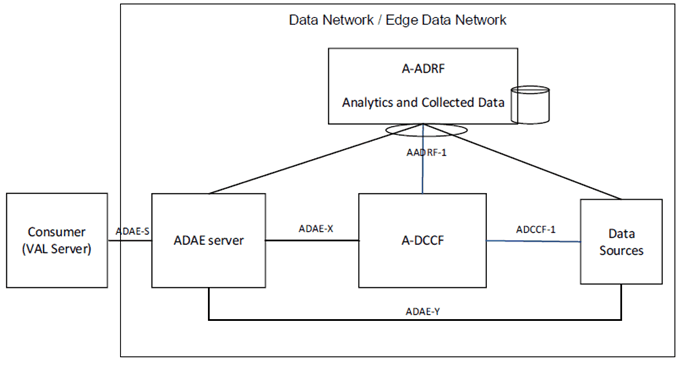
In this model, an A-DCCF is used to fetch data or put data into an application-level entity (e.g. A-ADRF, Data Source). Such A-DCCF coordinates the collection and distribution of data requested by ADAE server (over ADCCF-1, ADAE-X). ADAE server can also directly interact with the Data Sources via ADAE-Y.
Also, Application layer - Analytics and Data Repository Function (A-ADRF) can be used to store historical data and/or analytics, i.e., data and/or analytics related to past time period that has been obtained by the ADAE server (via AADRF-1) or other NFs/NWDAF. ADAE server can also fetch historical data from A-ADRF. Whether the ADAE server directly contacts the A-ADRF or goes via the A-DCCF is based on configuration.
Data Sources can be 5GS data sources (5GC, OAM) or enablement layer data sources (SEAL, EEL) or external data sources at the DN side (VAL server/ EAS) and VAL UEs. A-DCCF and A-ADRF can be used only for interacting with certain data sources (e.g., 5GC, OAM) based on configuration, and can be hidden from the VAL layer.