Content for TR 22.851 Word version: 19.1.0
5 Use Cases
5.1 Use Case on Network Sharing without Direct Connections between the Shared Access and the Core Networks of the Participating Operators
5.1.1 Description
5.1.2 Pre-conditions
5.1.3 Service Flows
5.1.4 Post-conditions
5.1.5 Existing Features partly or fully covering Use Case Functionality
5.1.6 Potential New Requirements needed to support the Use Case
...
...
5 Use Cases p. 7
5.1 Use Case on Network Sharing without Direct Connections between the Shared Access and the Core Networks of the Participating Operators p. 7
5.1.1 Description p. 7
As stated in TS 22.261 the increased density of access nodes needed to meet future performance objectives pose considerable challenges in deployment and acquiring spectrum and antenna locations. RAN sharing is seen as a technical solution to these issues.
Sharing access networks and network infrastructure has become more important part of 3GPP systems.
When two or more operators have respectively deployed or plan to deploy 5G access networks and core networks, a MOCN configuration can be considered for network sharing between these operators, i.e., a Multi-Operator Core Network (MOCN) in which multiple CN nodes are connected to the same radio access and the CN nodes are operated by different operators.
One of the challenges for the partners' network operators is the maintenance generated by the interconnection (e.g., number of network interfaces) between the shared RAN and two or more core networks, especially for a large number of shared base stations.
For these reasons, it is suggested investigating other types of network sharing scenarios, where a 5G RAN is shared among multiple operators without necessarily assuming a direct connection between shared access and the core networks of the participating operators.
5.1.2 Pre-conditions p. 8
Two (or more) operators provide coverage with their respective radio access networks in different parts of a country but together cover the entire country.
There is an agreement between all the operators to work together and to build a shared network, but utilizing the different operator's allocated spectrum appropriately in different parts of the coverage area (for example, Low Traffic Areas, LTA and High Traffic Areas, HTA).
The hosting operator 1, as illustrated below, can share its NG-RAN with the participating operators with or without direct connections between the shared access and the core networks of the participating operators.
The following preconditions apply,
- OP1 owns the NG-RAN to be shared with three other operators; OP2, OP3, and OP4.
- NG-RAN is shared with certain conditions, e.g., within a specific 5G frequency band or within specific area.
- NG-RAN does not have direct connections between the shared access and the core networks of the participating operators OP2 and OP3.
- OP4 has a MOCN arrangement with OP1.
- In this example UE 1 is subscribed to OP1, UE 2 is subscribed to OP 2, UE 3 is subscribed to OP3, and UE 4 is subscribed to OP4.
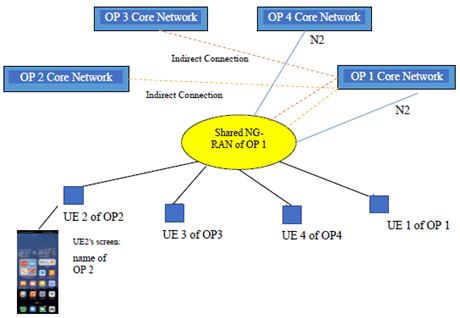
Figure 5.1.2-1: Different options both direct and indirect connections between the shared access and the core networks of the participating operators
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
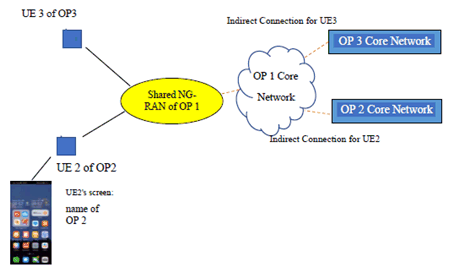
Figure 5.1.2-2: Indirect Network Sharing scenario involving core network of hosting operator between the shared access and the core networks of the participating operators
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
5.1.3 Service Flows p. 10
- UE1 can successfully attach to NG-RAN, and the display of the network operator name is the name of OP1.
- UE2 can successfully attach to NG-RAN, and the display of the network operator name is the name of OP2.
- UE3 can successfully attach to NG-RAN, and the display of the network operator name is the name of OP3.
- UE4 can successfully attach to NG-RAN, and the display of the network operator name is the name of OP4.
- The service provider of UE 1 is OP1.
- The service provider of UE 2 is OP2.
- The service provider of UE 3 is OP3.
- The service provider of UE 4 is OP4.
5.1.4 Post-conditions p. 10
The hosting network will be able to provide accessing to all participating operators' users.
5.1.5 Existing Features partly or fully covering Use Case Functionality p. 10
Network sharing has been studied in previous releases, where related normative stage 1 requirements are introduced in TS 22.101 and TS 22.261.
3GPP TS 22.101 introduces general requirements of network sharing, stated as follows:
Network sharing shall be transparent to the user.
The specifications shall support both the sharing of:
The provisioning of services and service capabilities is described in TS 22.101.
- radio access network only;
- radio access network and core network entities connected to radio access network.
The provision of services and service capabilities that is possible to offer in a network shall not be restricted by the existence of the network sharing It shall be possible for a core network operator to differentiate its service offering from other core network operators within the shared network.
It shall be possible to control the access to service capabilities offered by a shared network according to the core network operator the user is subscribed to.
The selection of 3GPP access network is described in clause 6.19 of TS 22.261:
The UE uses the list of PLMN/RAT combinations for PLMN selection, if available, typically during roaming situations. In non-roaming situations, the UE and subscription combination typically matches the HPLMN/EHPLMN capabilities and policies, from a SST (slice/service type) perspective. That is, a 5G UE accessing its HPLMN/EHPLMN should be able to access SSTs according to UE capabilities and the related subscription. […]
The 5G system shall support selection among any available PLMN/RAT combinations, identified through their respective PLMN identifier and Radio Access Technology identifier, in a prioritised order. The priority order may, subject to operator policies, be provisioned in an Operator Controlled PLMN Selector lists with associated RAT identifiers, stored in the 5G UE.
The 5G system shall support, subject to operator policies, a User Controlled PLMN Selector list stored in the 5G UE, allowing the UE user to specify preferred PLMNs with associated RAT identifier in priority order.
5.1.6 Potential New Requirements needed to support the Use Case p. 11
[PR 5.1.6-001]
The 5G system shall be able to support network sharing with indirect connection between the Shared NG-RAN and one or more Participating NG-RAN Operators' core networks.
[PR 5.1.6-002]
The 5G system shall be able to support means for Participating Operators to provide their operator's name to a registered UE, for display to the user.