Content for TR 33.854 Word version: 17.1.0
6.15 Solution #15: UAV and UAV-C Pairing Authorization and Security Aspects
6.15.1 Solution overview
6.15.2 Solution details
6.15.3 Solution evaluation
...
...
6.15 Solution #15: UAV and UAV-C Pairing Authorization and Security Aspects p. 53
6.15.1 Solution overview p. 53
This solution address key issues #2 and #7. Further, the solution takes into account the following SA2 clause 4.2 of TR 23.754 Architectural Assumptions.
- For networked UAV controllers and non-networked UAV controllers, pairing between the UAV and the UAV controller for the use of UAV3 or UAV5 may be at least authorized, or even authenticated. The pairing authorization/authentication, when performed, is authorized by the USS/UTM, not by the 3GPP system. The 3GPP system enables such authorization process. The result of such authorization/authentication are made known to the MNO in order to enable the USS/UTM to enable the connectivity between the UAV and the UAV controller.
6.15.2 Solution details p. 53
The authorization of UAV and UAV-C pairing can be performed by the USS/UTM (after a successful primary authentication and during/after a successful UAS authentication) when a UAV initiates a PDU session establishment or when the UAV modifies the existing PDU session to set up C2 connection with the UAV-C for enabling the UAS service as shown in Figure 6.15.2-1. At this step, it is considered that UAV and UAV-C has already performed successful UAS registration with the USS/UTM (and has UAS authorization and security information provided by the USS/UTM). The UAV includes Pairing authorization request information containing UAV-C ID, Auth Token, UAS ID, Security context ID in addition to its CAA-level UAV ID in the PDU session establishment request message (or in PDU session modification request) to SMF along with the UAV operation request and SMF can send the UAV operation Request along with the received Pairing authorization request information to the UFES and the UFES forwards the same to the USS/UTM. UAV operation Request procedure can be based on agreements from SA2 TR 23.754. The USS/UTM on receiving the Pairing authorization request information along with UAV operation request can perform the UAV and UAV-C pairing authorization and session security set up. Pairing authorization can also be referred C2 Association authorization. The solution considers that, the UAV-C information (i.e., a UAV-C ID) with which the UAV can form an UAS can be available in the USS and it can also be prepositioned to the UAV along with the CAA-level UAV ID provisioning (out of 3GPP scope) as a precondition.
UAV and UAV-C pairing authorization and session security set up procedure is described as follows.
As a precondition, the UAV and UAV-C is registered to the 3GPP network and both UAV and UAV-C has successfully performed UAS Authentication and authorization with the USS/UTM and established a PDU Session with the USS/UTM. Alternatively, the UAV-C may be connected to the USS/UTM over internet.
Step 1.
The UAV sends to the AMF, a PDU Session establishment Request with Pairing Authorization Request Information. Pairing Authorization Request Information includes UAV ID, Target UAV-C ID, UAS ID, UAV Authorization Token (the one received during successful UAA from USS/UTM), UAS Security Context Identifier (the one received during the successful UAA from USS/UTM to uniquely identify the UAS security context information established between UAV and USS/UTM).
Step 2.
The AMF on receiving the PDU Session establishment Request with Pairing Authorization Request Information, checks if the UAV-ID is authorized to request pairing authorization based on the locally stored UAS authentication and authorization results, authorization information (Token) and UAV-C ID (if available). If both the received Pairing authorization request information and locally stored information matches, the AMF considers the check as successful and perform step 3. If the AMF does not find any UAS authentication results or if the authentication result or authorization information locally stored does not match with the received authorization information, then the AMF triggers UAA as in Solution#7.
Step 3.
The AMF sends Nsmf_PDUSession_CreateSMContext Request to the SMF with the received Pairing Authorization Request Information which includes UAV ID, Target UAV-C ID, UAS ID, UAV Authorization Token, UAS Security Context Identifier and 3GPP UAV ID (i.e., GPSI).
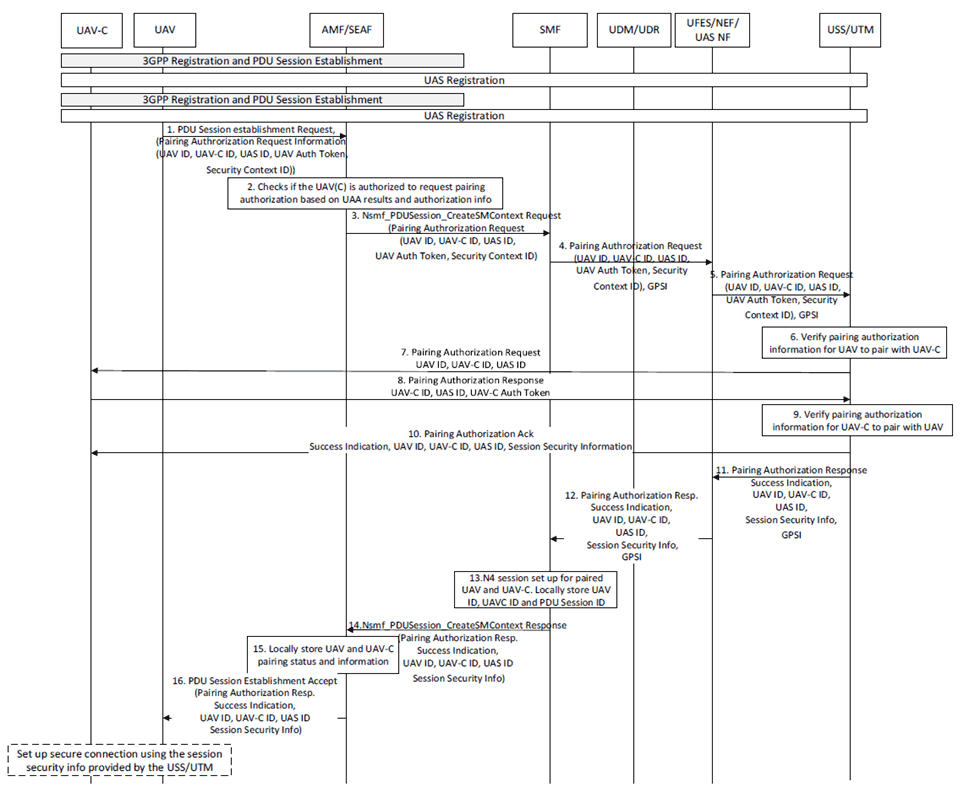
Step 4.
Optionally Step 7-10 can be skipped and only step 10 is performed if the UAV-C is connected to the USS/UTM over internet.
The SMF sends the received Pairing Authorization Request to the UFES (in a service operation message) with UAV ID, Target UAV-C ID, UAS ID, UAV Authorization Token, UAS Security Context Identifier along with GPSI and UAV IP address (based on TR 23.754).
Step 5.
The UFES sends the received Pairing Authorization Request to the USS/UTM (in a service operation message) with UAV ID, Target UAV-C ID, UAS ID, UAV Authorization Token, UAS Security Context Identifier along with GPSI and UAV IP address.
Step 6.
The USS/UTM verifies the information received in the Pairing Authorization Request with the locally stored information and if the verification is successful, the USS/UTM determines to authorize pairing for the UAV.
Step 7.
The UAV and UAV-C uses the received session security information to set up a secure connection between UAV and UAV-C for the C2 connection.
In case of modifying the existing PDU session during pairing authorization, the steps 1-3 and steps 14-16 will use PDU session modification related message (i.e., PDU session modification request/response message instead of PDU session initiation request/response and PDU session update SM context message instead of PDU session create SM context message accordingly.). The SMF performs the configuration of the PDU Session accordingly to enforce pairing based on the received UAV-C authorization Pairing Authorization Response.
Pairing Authorization Revocation:
The USS/UTM sends to the UAV-C identified with the UAV-C ID (via the 3GPP network or over internet) a Pairing Authorization Request, which includes UAV ID, UAV-C ID and UAS ID.
Step 8.
The UAV-C in response sends to USS/UTM, a Pairing Authorization Response message which includes UAV-C ID, UAS ID, UAV-C IP address, and UAV-C Authorization Token.
Step 9.
The USS/UTM verifies the information such as UAV-C ID, UAS ID, and UAV-C Authorization Token received in the Pairing Authorization Response message by checking with the locally stored information. If the received authorization information match with the locally stored information, the USS/UTM considers the UAV-C pairing authorization as successful.
Step 10.
The USS/UTM sends a Pairing Authorization Acknowledgement/Notification message to the UAV-C, which contains Pairing Success Indication, UAV ID, UAV-C ID, UAS ID, and Session Security Information (i.e., to set up session security), UAV IP address.
Step 11.
Further the USS/UTM sends a Pairing Authorization Response/Accept message to the UFES in response to receiving step 5. The Pairing Authorization Response contains Pairing Success indication, UAV ID, UAV-C ID, UAS ID, Session Security Information, GPSI, and UAV-C IP address.
Step 12.
The UFES sends the received Pairing Authorization Response to the SMF, which contains Pairing Success indication, UAV ID, UAV-C ID, UAS ID, Session Security Information, GPSI and UAV-C IP address.
Step 13.
The SMF locally stores the information received in the Pairing Authorization Response as part of pairing authorization status information. Further performs N4 session set up for the authorized pair of UAV and UAV-C.
Step 14.
The SMF sends Nsmf_PDUSession_CreateSMContext Response to the AMF with the received Pairing Authorization Response Information which includes Success Indication, UAV ID, UAV-C ID, UAS ID, and Session Security Information.
Step 15.
The AMF optionally stores the UAV ID and UAV-C ID along with the pairing authorization status and UAS ID.
Step 16.
The AMF sends a PDU Session Establishment Accept message to the UAV over the N1 interface and the PDU Session Establishment Accept message includes the received Authorization Response Information which includes Success Indication, UAV ID, UAV-C ID, UAS ID, and Session Security Information.
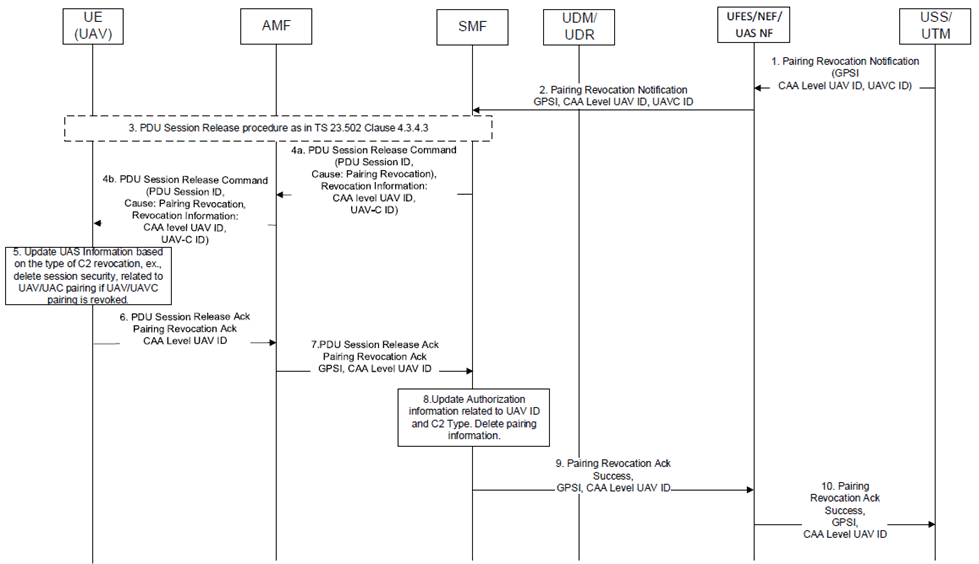
UAV and UAV-C pairing revocation is shown in Figure 6.15.2-2 and the steps involved in the pairing revocation is described as follows.
Step 1.
Pairing Revocation related to UAV-Controller (UAV-C) Change:
The USS/UTM when it determines to revoke UAV/UAV-C pairing (also known as C2 pairing or C2 association), the USS/UTM sends a Pairing Revocation Notification to the UFES with the GPSI, CAA Level UAV ID and UAV-C ID.
Step 2.
The UFES uses the Nudm_UECM_Get Request/Response service operation to fetch the serving SMF information corresponding to the GPSI. Further, the UFES sends the received Pairing Revocation Notification message to the serving SMF, which contains GPSI, CAA Level UAV ID, and UAV-C ID.
Step 3.
The SMF on receiving the Pairing Revocation Notification, checks if there is any active PDU Session corresponding to the indicated CAA level UAV ID with a UAV-C ID. If there is any active PDU Session, the SMF performs PDU Session release procedure for the associated PDU Session IDs using the existing procedure in clause 4.3.4.3 of TS 23.502 with the following adaptations.
Step 4a.
The SMF sends a PDU Session Release command to the AMF including the PDU Session ID along with a suitable cause value and a pairing revocation information containing CAA level UAV ID and UAV-C ID based on the received pairing revocation notification.
Step 4b.
The AMF forwards the PDU Session Release command to the UAV which includes PDU Session ID, with a suitable cause value, and a pairing revocation information containing CAA level UAV ID and UAV-C ID.
Step 5.
The UAV on receiving the PDU Session Release command with a pairing revocation information will delete the locally stored pairing authorization information (token, lifetime, identifiers or any related information) and associated security information for the UAV and UAV-C pairing indicated in the revocation information.
Step 6.
The UAV sends a PDU Session Release acknowledgement message to the AMF by including the Pairing Revocation Ack indication and CAA Level UAV ID.
Step 7.
The AMF deletes locally stored pairing information (such as pairing authorization information and paired UAV and UAV-C IDs if available) for the UAV corresponding to its CAA Level UAV ID. Further the AMF sends a PDU Session Release Acknowledgement message to the SMF with the GPSI, received Pairing Revocation Ack indication and CAA Level UAV ID.
Step 8.
The SMF on receiving the Pairing Revocation Ack indication deletes locally stored pairing information (such as pairing authorization information and paired UAV and UAV-C IDs) if available for the UAV corresponding to its CAA Level UAV ID.
Step 9.
Further, the SMF sends a Pairing Revocation Acknowledgement to the UFES with the received GPSI, Success Indication, and CAA Level UAV ID.
Step 10.
The UFES forwards the received Pairing Revocation Acknowledgement to the USS/UTM with the received Success Indication, GPSI and CAA Level UAV ID.
Step 1.
Applicability to EPS:
The UAV/UAV-C (i.e., C2) Pairing authorization and Revocation procedure described in this section can be applicable to EPS, with the adaptation of using MME, SMF+PGW-C, UPF+PGW-U and HSS+UDM respectively. 3GPP NF/UFES can act as a UAS NF or UAS control function in the 3GPP network which can be a standalone network function, or a service offered by the SCEF in the EPS. The message name used in EPS procedure can be aligned with SA2 where required during the normative work. The UAV and UAV-C pairing authorization when connected to EPS is described as follows.
The UAV is communicating with UAV-C1 after a successful pairing authorization.
Step 2.
The USS/UTM determines to change the UAV-C for a UAV (the determination aspects at USS/UTM are out of 3GPP scope) and sends to SMF via UFES a UAV Operation update message with 3GPP UAV ID, new authorization data (i.e., CAA level UAV ID, new UAV-C2 info (example., ID and IP address), session security information and new UAS ID if any), pairing authorization indication and Cause indicating UAV-C Change.
Step 3.
The SMF initiates PDU session modification procedure (via the serving AMF with the UAV) by sending to AMF, N1 SM container with PDU session Modification command along with the received Pairing authorization indication, new authorization data and a suitable cause value based on the received UAV-C change indication.
Step 4.
The AMF forwards the PDU session modification command message to the UAV along with the received Pairing authorization indication, new authorization data and a suitable cause value based on UAV-C change indication.
Step 5.
The UAV updates the pairing information based on the received new authorization data and sends a PDU Session Modification Command Ack to AMF. The AMF can update the locally stored pairing information if any (such as paired UAV and UAV-C information, authorization status based on new authorization data received) and forwards the received PDU Session Modification Command Ack to SMF. The SMF can also update the locally stored pairing information if any and updates N4 session of the UPF(s) that are involved by the PDU Session Modification for the new authorized pair of UAV and new UAV-C2 (based on UAV and UAV-C information received from USS/UTM).
Step 6.
The UAV communicates with the UAV-C2.
Step 1.
The UAV and UAV-C can use the received session security information to set up a secure connection between UAV and UAV-C for the C2 connection.
The UAV and UAV-C pairing revocation can be applicable to EPS as described below.
The USS/UTM when it determines to revoke UAV/UAV-C pairing (also known as C2 pairing or C2 association), the USS/UTM sends a Pairing Revocation Notification to the UFES with the 3GPP UAV ID (i.e., an external identifier), CAA Level UAV ID and UAV-C ID. The UFES sends the received Pairing Revocation Notification message to the SMF+PGW-C and a PDN connection disconnection and bearer deactivation can be initiated based on TR 23.754 and TS 23.401 accordingly. The Delete Session/bearer Request can be sent by SMF+PGW-C to MME via S-GW with a suitable cause value and a pairing revocation information containing CAA level UAV ID and UAV-C ID based on the received pairing revocation notification. During bearer deactivation, the MME can send to the UAV, a suitable cause value and a pairing revocation information containing CAA level UAV ID and UAV-C ID. The UAV on receiving the pairing revocation information will delete the locally stored pairing authorization information and security information for the UAV and UAV-C pairing and releases all resources corresponding to the PDN connection. The UAV sends in response, a pairing revocation acknowledgement and CAA level UAV ID to the MME. The MME sends a PDN connection Release Acknowledgement (example., in a delete bearer response) to SMF+PGW-C via SGW with the external ID, Pairing Revocation Ack indication and CAA Level UAV ID. The SMF+PGW-C on receiving the Pairing Revocation Ack indication deletes locally stored pairing information (such as pairing authorization information and paired UAV and UAV-C IDs). Further, the SMF+PGW-C sends a Pairing Revocation Acknowledgement to the UFES with the received 3GPP UAV ID, Success Indication, and CAA Level UAV ID. The UFES forwards the received Pairing Revocation Acknowledgement to the USS/UTM with the received Success Indication, 3GPP UAV ID and CAA Level UAV ID. In case of UAV change, an authorization indication, new authorization data with cause as UAV change can be notified by the USS/UTM to the UFES. The PDN connection modification can be triggered by the SMF+PGW-C and the UAV can be notified with an authorization indication, new authorization data with cause as UAV change to allow the UAV to update the pairing authorization information during the PDN connection modification. The UAV updates the pairing information based on the received new authorization data and sends an acknowledgement back to MME. The MME forwards the received acknowledgement to SMF+PGW-C. The SMF+PGW-C can also update the locally stored pairing information if any (such as paired UAV and UAV-C information, authorization status based on new authorization data received) and updates session that are involved by the PDN connection Modification for the new authorized pair of UAV and new UAV-C2 (based on UAV and UAV-C information received from USS/UTM).
The UAV sends to MME, a PDN connection Request with Pairing Authorization Request Information. Pairing Authorization Request Information includes UAV ID, Target UAV-C ID, UAS ID, UAV Authorization Token (the one received during successful UAA from USS/UTM), UAS Security Context Identifier (the one received during the successful UAA from USS/UTM to uniquely identify the UAS security context information established between UAV and USS/UTM).
Step 2.
The MME on receiving the PDN connectivity Request with Pairing Authorization Request Information, checks if the UAV-ID is authorized to request pairing authorization based on the locally stored UAS authentication and authorization results, authorization information (Token) and UAV-C ID (if available). If both the received Pairing authorization request information and locally stored information matches, the MME considers the check as successful and perform step 3. If the MME does not find any UAS authentication results or if the authentication result or authorization information locally stored does not match with the received authorization information, then the AMF triggers UAA as in Solution#7.
Step 3.
The MME sends Create Session Request to the SMF+PGW-C via S-GW with the received Pairing Authorization Request Information which includes UAV ID, Target UAV-C ID, UAS ID, UAV Authorization Token, UAS Security Context Identifier and 3GPP UAV ID (i.e., an external identifier).
Step 4.
The SMF+PGW-C sends the received Pairing Authorization Request to the UFES which contains UAV ID, Target UAV-C ID, UAS ID, UAV Authorization Token, UAS Security Context Identifier along with 3GPP UAV ID and UAV IP address (based on TR 23.754).
Step 5.
The UFES sends the received Pairing Authorization Request to the USS/UTM.
Step 6-10.
Steps 6-10 can be performed as described for 5GS.
Step 11.
Further the USS/UTM sends a Pairing Authorization Response/Accept message to the UFES in response to receiving step 5. The Pairing Authorization Response contains Pairing Success indication, UAV ID, UAV-C ID, UAS ID, Session Security Information, 3GPP UAV ID, and UAV-C IP address.
Step 12.
The UFES sends the received Pairing Authorization Response to the SMF+PGW-C.
Step 13.
The SMF+PGW-C locally stores the information received in the Pairing Authorization Response as part of pairing authorization status information. Further performs N4 session set up for the authorized pair of UAV and UAV-C.
Step 14.
The SMF+PGW-C sends Create Session Response to the MME via S-GW, with the received Pairing Authorization Response Information which includes Success Indication, UAV ID, UAV-C ID, UAS ID, and Session Security Information.
Step 15.
The MME optionally stores the UAV ID and UAV-C ID along with the pairing authorization status and UAS ID.
Step 16.
The MME sends a PDN Connection Accept message to the UAV over the NAS and the PDN Connection Accept message includes the received Authorization Response Information which includes Success Indication, UAV ID, UAV-C ID, UAS ID, and Session Security Information.
6.15.3 Solution evaluation p. 58
AMF in 5GS and SMF+PGW-C in EPS: On receiving a pairing authorization request information, need to verify if the UAV-ID is authorized to request pairing authorization based on the locally stored UAS authentication and authorization results, authorization information (i.e., Auth Token) and UAV-C ID (if available). If there are no UAS authentication results available or if does not match, then triggers UAA before performing pairing authorization.
After a successful pairing authorization, receives (from USS/UTM via UFES) and forwards the Authorization Response Information with Success Indication, UAV ID, UAV-C ID, UAS ID, and Session Security Information to the UAV, to allow session security set up between the paired UAV and UAVC. Also stores the UAV ID and UAV-C ID along with the pairing authorization status and UAS ID to enable handling of paired connections later (example. during pairing revocation and UAVC change).
UE: On a PDU session establishment related to C2, sends Pairing Authorization Request Information which includes UAS ID, UAV Auth Token, and UAS Security Context Identifier.
On a PDU session or PDN connection release related to a pairing revocation requested by the USS/UTM (via UFES), the UAV is notified (via AMF/MME accordingly) with a Pairing Revocation Indication and pairing revocation information to enable UAV to delete any pairing authorization information locally stored.
On a PDU session/PDN connection modification related to a UAVC change requested by the USS/UTM (via UFES), the UAV is notified (via AMF and MME accordingly) with a UAVC Change and new authorization information to enable UAV to update any pairing authorization information locally stored.6.16.