Content for TR 23.700-89 Word version: 18.0.0
6.4 Solution 4: Enforcing RFSP index authorized by PCF in EPC without N26 interface
6.4.1 Description
6.4.2 Procedures
6.4.3 Impacts on services, entities and interfaces
...
...
6.4 Solution 4: Enforcing RFSP index authorized by PCF in EPC without N26 interface p. 15
6.4.1 Description p. 15
The solution addresses KI#1 is intended for the following interworking scenario (but could be applied to interworking scenario with N26 deployment):
ParameterProvision_Update service operation. The AMF also includes new parameter of validity time, indicating the time by which the RFSP index in use will take effect when the UE moves to EPS. If interfaces for user data interworking, coexistence and migration are deployed is deployed, then the UDM provisions new " RFSP index in use" and the validity time to the HSS using new service operation Nhss_ParameterProvision_Update .
When the UE moves from 5GS to EPS, if the HSS has received the "RFSP index in use" and validity time is not due, the HSS provides both " RFSP index in use" (together with validity time) and "Subscribed RFSP" values to the MME. The MME sets the "RFSP index in use" as the RFSP index to use to the eNB, to avoid any possible ping-pong issue of the UE moving between the 4G and 5G.
The MME continues to use the "RFSP index in use" over the "Subscribed RFSP" until the validity time is due. When the validity time is due, the MME re-evaluates the RFSP index as specified in clause 4.3.6 of TS 23.401.
If the UE moves further to another MME, the source/old MME provides "RFSP index in use" as in existing procedure and includes additionally the validity time if its indicated time is not due. When the validity time for the received RFSP in Useis due, the new MME re-evaluates RFSP index as specified in clause 4.3.6 of TS 23.401 and provides the updated RFSP index to the eNB.
If the MME does not support the new parameters for "RFSP index in use" and related validity time, the HSS modifies sends to MME the Subscribed RFSP index set to the value of RFSP index in use. When the validity time is due, the HSS modifies the Subscribed RFSP index back to the originally subscribed value and sends it to MME.
- 5GS to EPS Mobility without N26 interface. The PCF, in 5GC, may adjust the RFSP index to request RAN to direct the UE from 5G to 4G according to dynamic network situations, for example:
- Based on various analytics and prediction result from NWDAF (e.g. network congestion in 5G), the PCF may request to move some of the "5G prioritized" UEs to 4G access.
- According to a request from AF, the PCF may request RAN to move the requested UE(s) from 5G to 4G.
6.4.2 Procedures p. 16
The detailed procedure is described in Figure 6.4.2-1.
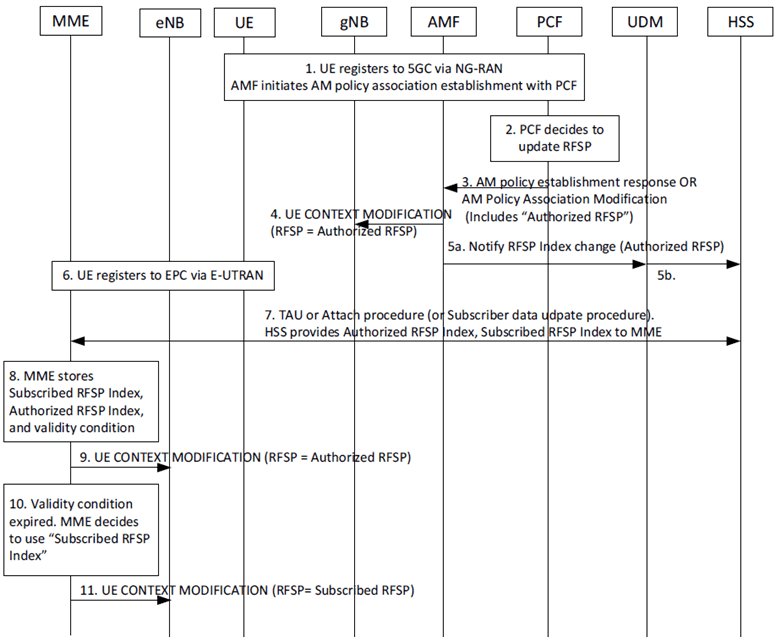
Figure 6.4.2-1: Procedure to Enforcing RFSP index authorized by PCF in EPC without N26 interface
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
Step 1.
Case-1:
The UE registers to 5GC via NG-RAN. AMF establishes AM Policy association with PCF as in clause 4.16.1.2 of TS 23.502.
Step 2.
The PCF decides to adjust the RFSP index to direct the UE from 5G to 4G. The PCF decision could be based on various inputs. For example:
Step 3.
- Based on various analytics and prediction result from NWDAF (e.g. network congestion in 5G).
- According to the request from AF.
The PCF provides the new "Authorized RFSP" for the UE by initiating AM Policy Modification procedure as in clause 4.16.2.2 of TS 23.502. The PCF provides additional validity time as the PCF determines that the change of authorized RFSP index value indicates a change from prioritizing 5G access to prioritizing 4G access for the UE.
Step 4.
The AMF set the Authorized RFSP as the RFSP index in use which is provided to the gNB in Subscriber Profile ID for RAT/Frequency priority IE in a UE CONEXT MODIFICATION procedure as in clause 8.3.4 of TS 38.413.
Step 5.
If N26 does not apply, and the AMF, then the AMF provisions "RFSP index in use" (set to the "Authorized RFSP" received from PCF) (which is applicable when UE is in EPS) and validity time to the UDM using existing Nudm_ParameterProvision_Update service operation. If the UDM and HSS are deployed separately then the UDM further provisions the "RFSP index in use" to the HSS using new service operation Nhss_ParameterProvision_Update . In a combined UDM+HSS deployment this step (step 5b in Figure 6.4.2-1) is not needed or handled in implementation specific way. In Nudm_ParameterProvision_Update service operation, the AMF includes additionally a validity time indicating that the "RFSP index in use" will take effect in EPS until the indicated time is due. The validity time will be included in Nhss_ParameterProvision_Update as well.
Step 6.
The UE is guided to 4G access,
If MME is upgraded and supports new parameters "RFSP index in use" and "validity time", steps 7-8 are performed
Step 7.
Case-2:
The UE performs TAU or Attach procedure, during which the HSS provides "RFSP index in use" together with the validity time to the MME serving the UE, along with the "Subscribed RFSP".
Step 8.
The MME stores the "Subscribed RFSP index", the "RFSP index in use" and a validity time for the "RFSP index in use" in the UE context in MME. During inter MME handover, the source MME also provides the validity condition to the target MME.
Continue at step 9.
If MME is not upgraded thus does not supports new parameters "RFSP index in use" and "validity time", steps 7a-8a are performed
Step 7a.
Case-2:
The UE performs TAU or Attach procedure, the HSS sends the subscribed RFSP index set to the value of RFSP index in use.
Step 8a.
MME chooses RFSP index as specified in clause 4.3.6 of TS 23.401 assuming that MME always chooses subscribed RFSP index.
Step 9.
The MME provides the "RFSP index" in Subscriber Profile ID for RAT/Frequency priority IE to the eNB in UE CONTEXT MODIFICATION procedure as in clause 8.3.4 of TS 36.413.
Case-1: If MME is upgraded and supports new parameters "RFSP index in use" and "validity time", step 10 is performed:
Step 10.
When the validity time is due, the MME may re-evaluate the RFSP index as specified in clause 4.3.6 of TS 23.401. When the validity time is due, the "RFSP index in use" is locally removed from the UDM/HSS.
Continue at step 11.
If MME is not upgraded thus does not supports new parameters "RFSP index in use" and "validity time", steps 10a-10b are performed:
Step 10a.
When the validity time is due, the HSS restore the subscribed RFSP index and provides the restored subscribed RFSP index to MME.
Step 10b.
The MME re-evaluates the RFSP index in use as specified in clause 4.3.6 of TS 23.401.
11. The MME provides the updated RFSP in use in Subscriber Profile ID for RAT/Frequency priority IE to the eNB in UE CONTEXT MODIFICATION procedure as in clause 8.3.4 of TS 36.413.
6.4.3 Impacts on services, entities and interfaces p. 18
This solution may have the following impacts to existing entities and interfaces:
AMF:
-
AMF invokes existing Nudm_
ParameterProvision_ service operation to UDM but with new parameter "RFSP index in use" (applicable only when UE is in EPS) and validity time by which the RFSP index in use is valid.Update
-
When UDM and HSS are deployed separately, the UDM invokes new service operation Nudm_
ParameterProvision_ with "RFSP index in use" and validity time.Update
- Provides the "RFSP index in use", validity time along with "Subscribed RFSP" for a UE to the MME in Update Location or as a Standalone Insert Subscriber Data operation.
- The "RFSP index in use" and its validity time are stored in the UDR.
- Determine whether MME supports the new feature requiring "RFSP index in use" and validity time.
- MME stores the "RFSP index in use" along with its validity conditions in the UE context in MME. As long as the validity condition is satisfied the MME uses "RFSP index in use" over "Subscribed RFSP". The MME provides the "RFSP index in use" as today and additionally includes its validity conditions to target MME during inter MME mobility. When the validity condition is expired, the MME re-evaluates the RFSP index as specified in clause 4.3.6 of TS 23.401.