Content for TS 23.632 Word version: 18.4.0
5.3.4 Support for PDU session continuity during intersystem mobility procedures p. 16
When the UE is connected to 5GS or 5GC-N3IWF, the PGW-C+SMF may store in UDM the PGW-C+SMF FQDN for S5/S8/S2b interface, within the UE context in SMF data, when the PWG-C+SMF registers in UDM. The AMF serving 3GPP access may also notify the UDM to store the association between DNN and PGW-C+SMF FQDN which supports EPS interworking as Intersystem continuity context.
During mobility from 5GC to EPC or EPC/ePDG, or mobility from 5GC-N3IWF to EPC, or mobility from EPC/ePDG to EPC, the HSS uses the Nudm_SDM_Get service operation to retrieve the PGW-C+SMF FQDN for S5/S8/S2b interface from UDM, and subscribes to be notified using Nudm_SDM_Subscribe when the Intersystem continuity context data or the UE context in SMF data are modified. The HSS retrieves both the UE context in SMF data and the Intersystem continuity context data from UDM. The HSS checks the Intersystem continuity context first. If no PGW-C+SMF FQDN associated with the APN exists in Intersystem continuity context, the HSS selects one of the PGW-C+SMF FQDN for the APN from the UE context in SMF data based on operator's policy.
During UE registration for the scenario when ePDG is connected to SMF+PGW-C and S6b in not used, the HSS subscribes to be notified from the UDM using Nudm_SDM_Subscribe when the UE context in SMF data is modified as new PDU sessions established in the ePDG are not updated in the HSS via the SWx interface.
Figure 5.3.4-1 shows the interaction between the HSS and the UDM in an interworking scenario when the UE attaches to the EPC or EPC/ePDG.
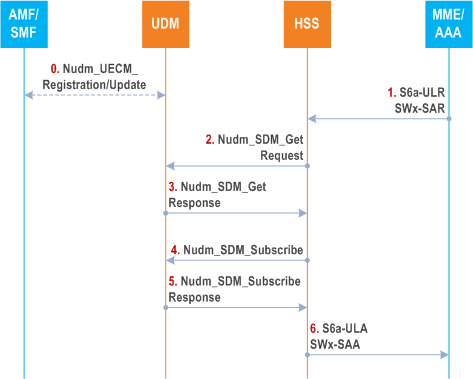
Step 0.
Figure 5.3.4-2 shows the interaction between the HSS and the UDM when the HSS receives notification from the UDM when the data requested is modified.
While the UE is connected to the 5GC, the AMF and/or SMF may store in UDM the association between DNN and PGW-C+SMF FQDN which supports EPS interworking.
If the 5GS UDR is used, the UDM updates the 5GS-UDR with the DNN and PGW-C+SMF FQDN association.
Step 1.
The HSS receives an S6a ULR or SWx SAR request containing the IMSI of the subscriber.
The HSS reads the subscription information related to the IMSI. If the EPC-UDR is used, the HSS retrieves the subscription information from the EPS-UDR. The UE's subscription may include subscribed APNs that support interworking with 5GS.
Step 2.
If the subscription information related to the IMSI includes subscribed APNs that support interworking with 5GS, then the HSS uses the Nudm_SDM_Get service operation to fetch the UE context in SMF data and the Intersystem continuity context data for the user in AMF data, if any. The HSS includes the user's IMSI received in step 1 as the user's SUPI in this request.
Step 3.
The UDM responds to the HSS.
The HSS checks the Intersystem continuity context first. If no PGW-C+SMF FQDN associated with an DNN exists in Intersystem continuity context, the HSS selects one of the PGW-C+SMF FQDN for the APN from the UE context in SMF data based on operator's policy.
Step 4-5.
The HSS subscribes to be notified using Nudm_SDM_Subscribe service operation when the Intersystem continuity context data or the UE context in SMF data are modified.
Step 6.
The HSS responds to the MME with an S6a-ULA response or to the AAA with an SWx-SAA response including the PGW-C+SMF FQDN associated with subscribed APNs that support interworking with 5GS, if any. This step may happen at any time after step 3, not necessarily after steps 4-5.
If an S6a ULR is received, the HSS performs steps 3 and 4 of clause 5.3.2.
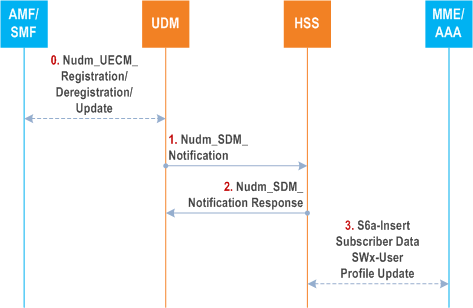
Step 0.
Figure 5.3.4-3 shows the interaction between the HSS and the UDM when the HSS unsubscribes from the UDM to be notified when the data requested is modified.
The AMF and/or SMF may add or remove or update the association between DNN and PGW-C+SMF FQDN stored in the UDM.
If the 5GS UDR is used, the UDM updates the 5GS-UDR with the DNN and PGW-C+SMF FQDN association.
Step 1.
If the UDM finds the UE context in SMF data or the Intersystem continuity context is changed, and the active subscription from the HSS exists for the UE to be notified on the change of the UE context in SMF data or the Intersystem continuity context, then the UDM uses the Nudm_SDM_Notification service operation to notify the HSS. Notifications may be limited to cases of PGW ID (FQDN and/or IP) being changed. As part of this notification the UDM informs the HSS whether the SMF indicated that the access to 5GC was via an ePDG.
Step 2.
The HSS responds to the UDM.
The HSS checks the change of the association between APN and PGW-C+SMF FQDN. If multiple PGW-C+SMF FQDN exists in the UE context in SMF data, the HSS selects one of the PGW-C+SMF FQDN for the APN based on operator's policy.
Step 3.
The HSS may further trigger PDN GW Identify Notification procedure, as defined in clause 12.1.4 and clause 12.1.5 in TS 23.402.
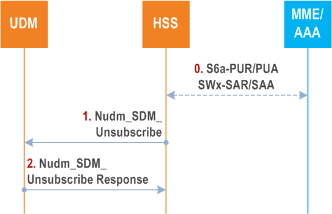
Step 0.
When the UE is connected to EPC, the MME stores in HSS the PGW-C+SMF FQDN for S5/S8 interface via S6a reference point. When the UE is connected to EPC via an ePDG, and the S6b reference point is deployed between the PGW-C+SMF and AAA, the AAA stores in HSS the PGW-C+SMF FQDN for S5/S8 interface via SWx reference point.
During mobility from EPC or EPC/ePDG to 5GC, or mobility from EPC to 5GC-N3IWF, the UDM uses the Nhss_
The HSS checks the conditions to unsubscribe the notification of the UE context in SMF data or the Intersystem continuity context from the UDM, when the UE's 3GPP access or Non-3GPP access registration in EPC is not valid. For example, when the MME performs purge UE procedure, or the AAA performs UE deregistration towards the HSS, or the registration of the user in EPC is cancelled due to mobility from EPC to 5GC.
Step 1.
The HSS unsubscribes to be notified using Nudm_SDM_Unsubscribe service operation towards the UDM.
Step 2.
The UDM responds to the HSS.
Step 0.
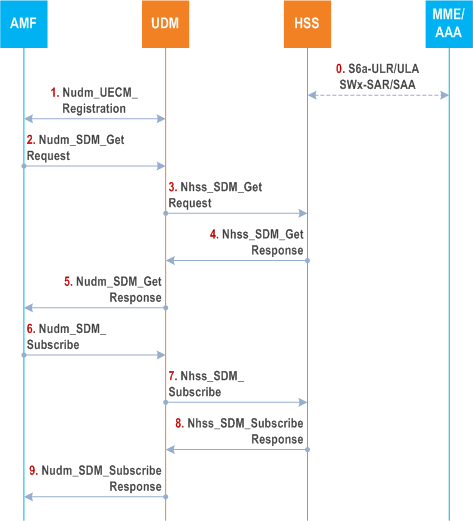
Figure 5.3.4-5 shows the interaction between the HSS and the UDM when the UDM receives notification from the HSS when the data requested is modified.
While the UE is connected to the EPC or EPC/ePDG, the MME or the AAA informs the HSS of the PGW-C+SMF address and associated APN.
Step 1.
UE moves to 5G coverage, the AMF registers with the UDM using Nudm_UECM_Registration for 3GPP access.
The UDM performs steps 3 and 4 in clause 5.3.3.
Step 2.
The AMF retrieves the Access and Mobility Subscription data, SMF Selection Subscription data and UE context in SMF data using Nudm_SDM_Get .
Step 3.
If the subscription information related to the SUPI includes subscribed DNNs that support interworking with EPS, then the UDM uses the Nhss_SDM_Get service operation to fetch the PGW-C+SMF information. The UDM includes the user's IMSI derived from SUPI.
Step 4.
The HSS responds to the UDM.
Step 5.
The UDM includes the PGW-C+SMF address associated with subscribed DNNs that support interworking with EPS, if any, as UE context in SMF data in Nudm_SDM_Get_Response .
Step 6.
After a successful response is received, the AMF subscribes to be notified when the data requested is modified using Nudm_SDM_Subscribe service operation.
Step 7.
If the UE context in SMF data is subscribed to be notified and the subscription information related to the SUPI includes subscribed DNNs that support interworking with EPS, the UDM subscribes towards the HSS (if not already subscribed, for the same UE) to be notified when the PGW-C+SMF information is modified using Nhss_SDM_Subscribe service operation.
Step 8.
The HSS responds to the UDM.
Step 9.
The UDM responds to the AMF.
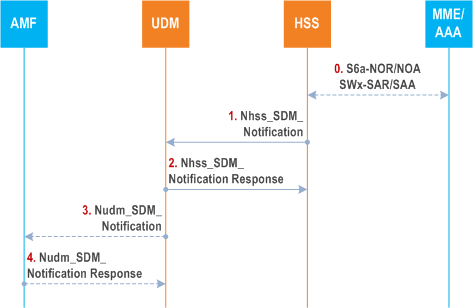
Step 0.
Figure 5.3.4-6 shows the interaction between the HSS and the UDM when the UDM unsubscribes from the HSS to be notified when the data requested is modified.
The MME or the AAA may add or update the association between APN and PGW-C+SMF FQDN stored in the HSS.
Step 1.
If the HSS finds the association between APN and PGW-C+SMF FQDN is changed, and the active subscription from the UDM exists for the UE to be notified on the change of the data requested, then the HSS uses the Nhss_SDM_Notification service operation to notify the UDM.
Step 2.
The UDM responds to the HSS.
Step 3 - 4.
If the UDM finds the association between DNN and PGW-C+SMF FQDN is changed, and the active subscription from the AMF exists for the UE to be notified on the change of the UE context in SMF data, then the UDM notifies the AMF using the Nudm_SDM_Notification service operation.
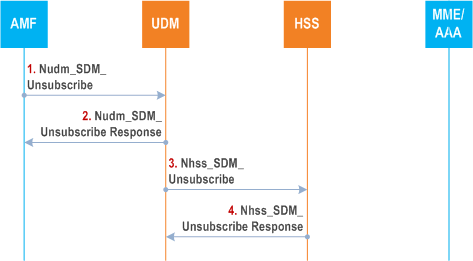
Step 1 - 2.
The AMF unsubscribes to be notified using Nudm_SDM_Unsubscribe service operation.
Step 3.
If the UE context in SMF data is unsubscribed, and no other AMF has subscribed to the same data (UE context in SMF) for the same UE, the UDM unsubscribes towards the HSS to be notified when the PGW-C+SMF information is modified using Nhss_SDM_Unsubscribe service operation.
Step 4.
The HSS responds to the UDM.