Content for TS 23.540 Word version: 18.3.0
1…
4…
5…
5.1.3
5.1.4
5.1.5
5.1.6
5.1.7…
5.1.7.2.3…
5.1.7.3.2
5.1.7.3.3
5.1.7.3.4
5.1.7.3.5
5.1.7.4
5.1.8…
5.2…
6…
5.1.7 GPSI-to-Subscription-Network resolution procedure
5.1.7.1 General
5.1.7.2 GPSI-to-Subscription-Network resolution triggered by the SMS-GMSC
5.1.7.2.1 General
5.1.7.2.2 GPSI-to-Subscription-Network resolution triggered by the SMS-GMSC for Direct routing
...
...
5.1.7 GPSI-to-Subscription-Network resolution procedure p. 21
5.1.7.1 General p. 21
MT SMS delivery procedure requires routing based on the GPSI of the SMS recipient for interactions between the SMS-GMSC and the UDM, e.g., to retrieve the SMS routing information (e.g., the SMSF address) or report delivery status. In case that the SMS recipient belongs to a PLMN different from the PLMN of the SMS sender, the signaling takes place across PLMN borders.
When using service-based interface between the SMS-GMSC and the UDM, if the GPSI is the only known SMS recipient's identifier, the SMS-GMSC needs to determine the target PLMN to be able to interact with the UDM in the home PLMN of the SMS recipient. The SMS-GMSC can determine the target PLMN using one of the following mechanisms:
- GPSI-to-Subscription-Network resolution triggered by the NF consumer, described in clause 5.1.7.2.
- GPSI-to-Subscription-Network resolution using NRF, described in clause 5.1.7.4.
- GPSI-to-Subscription-Network resolution delegated by SCP, described in clause 5.1.7.3
5.1.7.2 GPSI-to-Subscription-Network resolution triggered by the SMS-GMSC p. 22
5.1.7.2.1 General p. 22
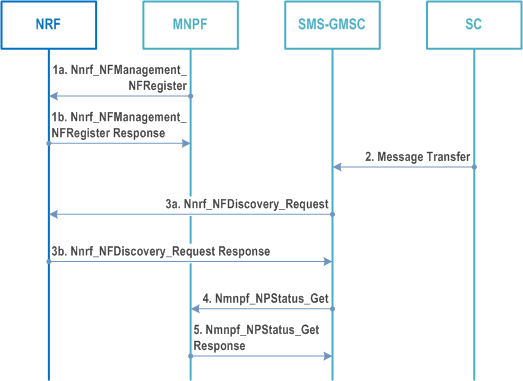
Step 1a-1b.
After step 5, the Mobile Terminated short message transfer procedures defined in clause 5.1 is performed from step 2a. The SMS-GMSC uses the target PLMN ID to discover the UDM NF profile via NRF for sending the routing information query to the UDM. If the target PLMN ID is not own network, the local NRF forwards the discovery request to the NRF of the target PLMN.
The MNPF registers in the NRF with a new NF Type (e.g. MNPF).
Step 2.
MT SMS interaction between SC and SMS-GMSC follow the current procedure as defined in TS 23.040.
Step 3a-3b.
The SMS-GMSC should query the NRF to find the MNPF instance that manages the PLMN ID of the recipients GPSI's subscription network. The MNPF may belong to the same PLMN with SMS-GMSC or belong to the number range holder network which is different with the PLMN of SMS-GMSC. In latter case, the local NRF forwards the discovery request to the NRF of the number range holder PLMN.
Step 4.
SMS-GMSC invokes Nmnpf_NPStatus_Get (GPSI) to the MNPF to get the target PLMN ID of the GPSI.
Step 5.
MNPF checks the portability status of the recipient GPSI and responds back with the target PLMN ID.
5.1.7.2.2 GPSI-to-Subscription-Network resolution triggered by the SMS-GMSC for Direct routing p. 23
When MNP is implemented in a country or number portability domain with direct routing mechanism, the originating network first does the number portability query to identify the recipient GPSI's subscription PLMN before routing any messages based on GPSI.
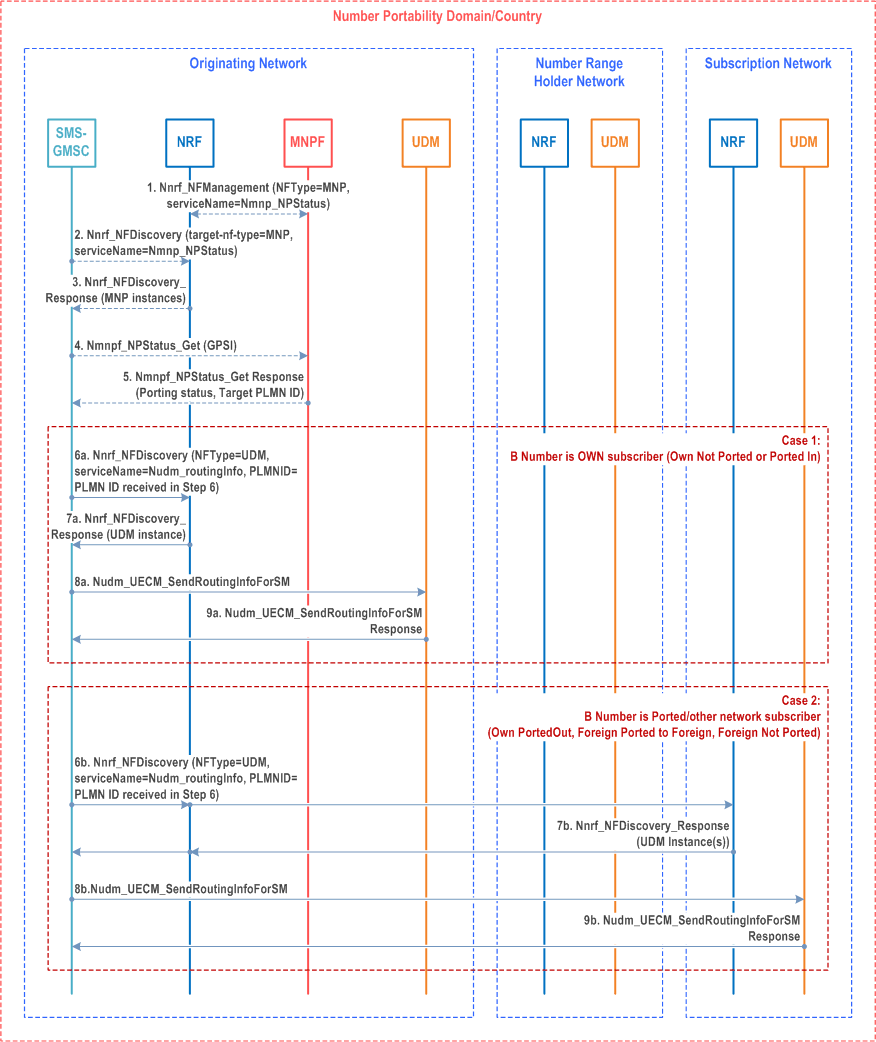
Step 1.
If the MNPF is deployed, the MNPF registers in the NRF with a new NF Type (e.g. MNPF).
Step 2-3.
The SMS-GMSC should query the NRF to find the MNPF instance that manages the PLMN ID of the recipients GPSI's subscription network.
Step 4.
SMS-GMSC invokes Nmnpf_NPStatus_Get (GPSI) to the MNPF to get the target PLMN ID of the GPSI.
Step 5.
MNPF checks the portability status of the recipient GPSI and responds back with the target PLMN ID.
Step 6-7.
SMS-GMSC shall query the NRF to find the UDM instance serving the target PLMN based on target PLMN ID received in step 6. For step 7b-8b, if the target PLMN ID is not the originating network, the local NRF forwards the discovery request to the NRF of the target PLMN.
Step 8-9.
SMS-GMSC invokes Nudm_UECM_SendRoutingInfoForSM (GPSI) to the UDM of the target PLMN to get the serving node instance for UE. The UDM shall check the registration/reachability flags to determine the potential target nodes and responds to the SMS-GMSC by sending Nudm_UECM_SendRoutingInfoForSM response, in this procedure the SMSF instance Id is included in the response message.