Content for TS 23.292 Word version: 17.0.0
1…
4…
5…
7…
7.2…
7.3…
7.3.2.2…
7.3.2.2.4…
7.4…
7.4.2.2…
7.4.2.2.3…
7.4.2.2.7…
7.5…
7.6…
7.6.1.2.2.6…
7.6.1.2.3…
7.6.1.2.3.5…
7.6.1.2.3.6…
7.6.2…
7.6.2.7
7.6.2.8…
7.6.2.11…
7.6.3…
7.7…
7.7.2…
7.9…
7.9.2…
7.9.2.4
7.9.2.5
8…
A…
G…
H…
H.5…
H.5.3…
7.6.3 Service consistency for non ICS UE when attached to an MSC Server not enhanced with ICS
7.6.3.1 Line ID Services (OIP, OIR, TIP, TIR)
7.6.3.2 Communication Diversion Services
7.6.3.3 Communication Barring
7.6.3.4 Communication Hold/Resume
7.6.3.5 Explicit Communication Transfer
7.6.3.6 Conferencing
7.6.3.7 User configuration of Supplementary Services
7.6.3.8 Customized Alerting Tone (CAT)
7.6.3.9 Communication Waiting
7.6.3.10 Communication Completion on Busy Subscriber/No Reply/Not Logged In
7.6.3.10.1 Communication Completion Terminated at Served User
7.6.3.10.2 Communication Completion Originated at Served User
...
...
7.6.3 Service consistency for non ICS UE when attached to an MSC Server not enhanced with ICS p. 95
7.6.3.1 Line ID Services (OIP, OIR, TIP, TIR) p. 95
The service control for the Line ID services may be provided by the CS domain if they are provisioned in the CS domain.
7.6.3.2 Communication Diversion Services p. 95
7.6.3.2.1 Communication Diversion services; CFU, CFNL p. 95
Standard IMS procedures apply toward IMS on behalf of the non-ICS UE.
7.6.3.2.2 Communication Diversion services; CFNR, CFB p. 95
IMS control of the CFNR and CFB services are provided toward IMS on behalf of the non-ICS UE.
7.6.3.2.2a Communication Diversion services; CFNRc |R11| p. 95
IMS control of the CFNRc service is provided on behalf of non-ICS UE. The MGCF may use the ICS indication as means to map cause codes received over the CS leg to appropriate IMS error code so that CFNRc can be triggered in the IMS domain.
7.6.3.2.3 Communication Diversion services; Communication Deflection p. 95
The service control for the Call Deflection service may be provided by the CS domain (if it is provisioned in the CS domain) or may be provided by IMS.
7.6.3.3 Communication Barring p. 96
Standard IMS procedures apply toward IMS on behalf of the non-ICS UE.
7.6.3.4 Communication Hold/Resume p. 96
The service control for the Call Hold and Retrieve services may be provided by the CS domain if they are provisioned in the CS domain.
7.6.3.5 Explicit Communication Transfer p. 96
The service control for the Explicit Call Transfer service may be provided by the CS domain if it is provisioned in the CS domain.
7.6.3.6 Conferencing p. 96
The service control for the Multiparty service may be provided by the CS domain if it is provisioned in the CS domain.
If the access transfer from PS to CS has been performed, the MSC Server not enhanced for ICS may subscribe to the conference related events in IMS. And if the UE has a subscription for the conference event package, the MSC server should send the conference related events to UE.
7.6.3.7 User configuration of Supplementary Services p. 96
7.6.3.7.1 UE not supporting multimedia telephony p. 96
When using procedures as defined in TS 24.010, and the MSC Server enhanced for ICS does not implement a communication service setting conversion function or the UE is using MSC Server not enhanced for ICS, the following apply:
- No activation or deactivation of supplementary services shall be allowed by the CS network.
- Interrogations of CFU and CNFL (clause 7.6.3.2.1), CFNR, CFNRc and CFB (clause 7.6.3.2.2) and Communication Barring (clause 7.6.3.3) shall not be allowed by the CS network.
7.6.3.7.2 UE supporting multimedia telephony p. 96
Refer to clause 7.6.1.3.
7.6.3.8 Customized Alerting Tone (CAT) |R10| p. 96
Standard IMS procedures apply toward IMS on behalf of the non-ICS UE.
7.6.3.9 Communication Waiting |R10| p. 96
A network provider may allow UE based CW by activating CW in the CS service profile as specified in TS 23.083.
7.6.3.10 Communication Completion on Busy Subscriber/No Reply/Not Logged In |R11| p. 97
7.6.3.10.1 Communication Completion Terminated at Served User p. 97
For IMS sessions established by UEs in the IMS network, where on the terminating side the MSC Server is not enhanced for ICS and the UE is in the CS domain the CC services can be provided by the IMS network.
Figure 7.6.3.10.1-1 describes a call flow via an MSC Server not enhanced for ICS. CCNR and CCNL follow the same principles.
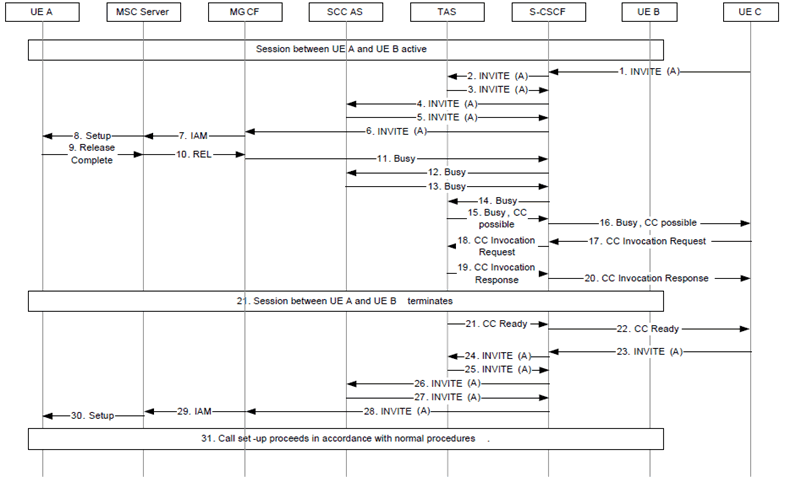
Figure 7.6.3.10.1-1: IMS Communication Completion to Busy Subscriber via MSC Server not enhanced for ICS
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
There is an ongoing session between UE A and UE B.
Step 1.
An incoming INVITE is received at the S-CSCF of UE A.
Step 2-6.
Via Initial Filter Criteria the INVITE is forwarded to the TAS and the SCC AS, before it is forwarded to the MGCF.
Step 7.
The MGCF sends an IAM message to the MSC Server to inform it of the incoming call.
Step 8.
The MSC Server sends a Setup message to UE A to inform about the incoming call. Depending on CW settings the MSC Server may send a REL response immediately.
Step 9.
UE A responds with a Release Complete message with cause #17 "user busy".
Step 10.
The MSC Server maps the Release Complete message to a REL message.
Step 11.
The MGCF maps the REL message to a SIP Busy message.
Step 12-14.
The SIP Busy message is forwarded via SCC AS and S-CSCF to the TAS.
Step 15.
The TAS adds a CC possible indicator to the Busy response.
Step 16.
The Busy response is forwarded towards UE C.
Step 17.
A CC Invocation Request is received at the S-CSCF of UE A.
Step 18.
The CC Invocation Request is forwarded to the TAS.
Step 19.
The TAS accepts the CC Invocation Request, sends a CC Invocation Response towards UE C and begins supervising UE A for becoming not busy.
Step 20.
The CC Invocation Response is forwarded by the S-CSCF towards UE C.
Step 21.
The Session between UE A and UE B terminates.
Step 22.
After an appropriate time to allow UE A to initiate a call, the TAS sends a CC Ready notification towards UE C.
Step 23.
The CC ready notification is forwarded by the S-CSCF towards UE C.
Step 24.
An INVITE Request resulting from the CC ready notification is received by the S-CSCF.
Step 25.
The INVITE Request is received by the TAS.
Step 26.
After appropriate checking that the INVITE request is resulting from the CC ready notification the TAS forwards the INVITE request to the S-CSCF.
Step 27-31.
The call set-up proceeds in accordance with normal procedures.
7.6.3.10.2 Communication Completion Originated at Served User p. 98
For IMS sessions established by UEs in the CS domain and the MSC Server is not enhanced for ICS the Communication Completion can be controlled by the IMS provided that the originating TAS performs a specific 3pcc procedure to initiate the CC call.
Figure 7.6.3.10.2-1 describes a call flow via an MSC Server not enhanced for ICS. CCNR and CCNL follow the same principles.
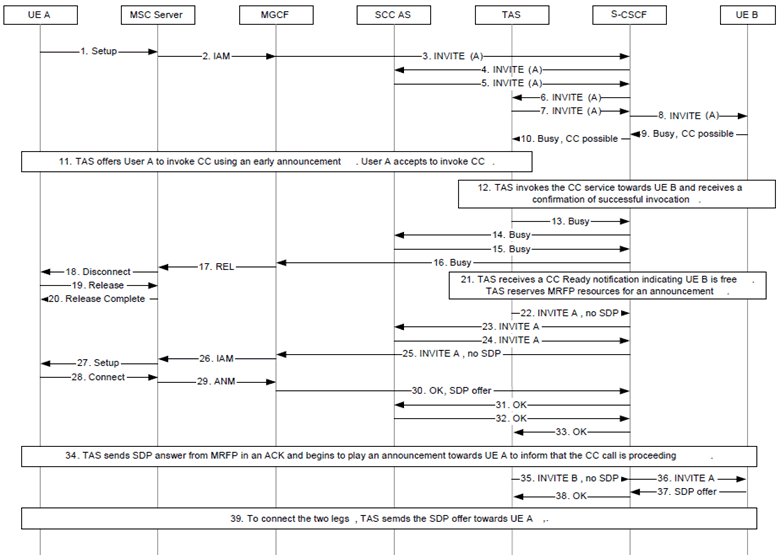
Figure 7.6.3.10.2-1: IMS Communication Completion via MSC Server not enhanced for ICS
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
There is an ongoing session between UE A and UE B.
Step 1-10.
UE A initiates a call towards UE B, which responds with Busy and a CC possible indication.
Step 11.
The TAS offers Communication Completion via announcement and in-band activation to user A who accepts.
Step 12.
The TAS invokes the CC service towards user B. The TAS is notified that the invocation is successful.
Step 13-20.
The Busy response without Communication Completion possible indication is sent towards UE-A. The call terminates following normal procedures.
Step 21.
TAS receives a CC ready notification indicating that UE B is free. The TAS can reserve announcement resources now or after step 33.
Step 22-27.
To start the recall procedure the TAS sends an INVITE without SDP towards UE A.
Step 28-33.
UE A answers the call, information is sent to the TAS. The MGCF includes an SDP offer in the OK message.
Step 35.
After completion of announcement, the INVITE without SDP is sent towards B. After receipt of Ringing response, a ring tone is played towards UE A.
Step 37.
UE B answers the call and includes an SDP offer.
Step 39.
The TAS uses this SDP offer to update the SDP towards UE A. UE A and UE B are now connected, and the announcement resources can be released.