Content for TS 23.292 Word version: 17.0.0
1…
4…
5…
7…
7.2…
7.3…
7.3.2.2…
7.3.2.2.4…
7.4…
7.4.2.2…
7.4.2.2.3…
7.4.2.2.7…
7.5…
7.6…
7.6.1.2.2.6…
7.6.1.2.3…
7.6.1.2.3.5…
7.6.1.2.3.6…
7.6.2…
7.6.2.7
7.6.2.8…
7.6.2.11…
7.6.3…
7.7…
7.7.2…
7.9…
7.9.2…
7.9.2.4
7.9.2.5
8…
A…
G…
H…
H.5…
H.5.3…
7.5 Service continuity
7.5.1 Service continuity for ICS UE
7.5.1.1 Service continuity while maintaining the use of CS access for the media
7.5.1.2 Service continuity when transferring the media of IMS sessions between PS and CS access
7.5a Addition of Gm service control to existing call
...
...
7.5 Service continuity p. 59
7.5.1 Service continuity for ICS UE p. 59
7.5.1.1 Service continuity while maintaining the use of CS access for the media p. 59
7.5.1.1.1 IMS sessions established using Gm reference point p. 59
7.5.1.1.1.1 Overview p. 59
When the CS bearer is used for the media of the IMS session, the Gm reference point may be used for communication of service control signalling, contingent upon the VPLMN support of the Gm reference point. A change of access network due to handover (e.g. as described in TS 23.009 and TS 25.413), may result in an inability to use the PS access for the Gm reference point while the use of CS access for the media of the IMS session is still possible; under such circumstance, the service continuity is maintained by switching the signalling transport over to the CS access, e.g. by switching the use of Gm with the I1 reference point or to not using Gm or I1.
7.5.1.1.1.2 Use of Gm reference point possible after handover p. 59
Standard Handover procedures, that are specific to different access networks (e.g. as described in TS 23.009 and TS 25.413), are used for handover of the Service Control Signalling Path and the CS Bearer Control Signalling Path along with the associated circuit bearer to the target access network.
The use of Gm reference point for Service Control Signalling Path is maintained upon handover.
7.5.1.1.1.3 Use of Gm reference point not possible after Handover p. 59
Standard CS handover procedures, that are specific to different access networks (e.g. as described in TS 23.009 and TS 25.413), are used to relocate the CS Bearer Control Signalling Path and the associated circuit bearer to the target access network. Upon completion of the handover of the CS Bearer Control Signalling Path and the associated circuit bearer to the target access, the UE sends a handover notification message to the SCC AS to indicate use of I1 for the Service Control Signalling Path if the I1 reference point is available in the target access network or to fallback to not using Gm or I1.
After handover, the I1 reference point is used for service control signalling in networks supporting the I1 reference point; the non ICS UE procedures apply in networks not supporting the I1 reference point.
7.5.1.1.1.3a Use of Service Control Signalling Path not possible after Handover p. 59
If the SCC AS detects that the ICS UE is not reachable over the Service Control Signalling Path and if the UE or the network does not support the MSC Server assisted mid-call feature as specified in TS 23.237, the SCC AS shall:
- clear any held sessions related to the user and update the remote leg if necessary; and
- clear any active session that is a conference initiated by the user and hosted in the IMS.
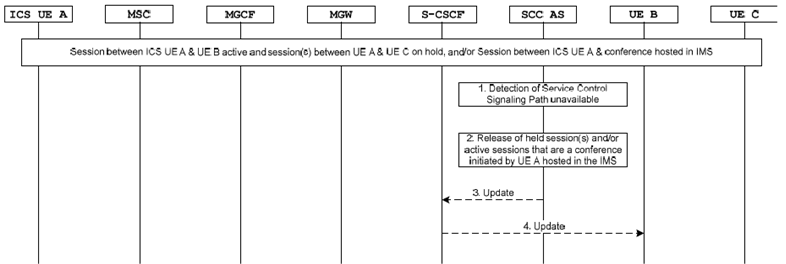
Figure 7.5.1.1.1.3a-1: release of held sessions at SCC AS when Service Control Signalling Path unavailable
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
Step 1.
The SCC AS detects that the ICS UE is not reachable over Service Control Signalling Path.
Step 2.
The SCC AS releases the held session between UE A and UE C and/or the active session that is a conference initiated by UE A and hosted in the IMS.
Step 3.
The SCC AS sends the UPDATE to the S-CSCF.
Step 4.
The S-CSCF forwards the UPDATE to the UE B to update the remote leg.
See TS 23.237 IMS Service Continuity.
7.5.1.2 Service continuity when transferring the media of IMS sessions between PS and CS access p. 60
See TS 23.237 IMS Service Continuity.
7.5a Addition of Gm service control to existing call |R9| p. 60
7.5a.1 Overview p. 60
A call can be established by an ICS UE that supports Gm, but without using the Gm reference point (for example, as a result of CSFB, or when in non-DTM GERAN coverage). If Gm is available after call establishment, or becomes available (for example, as a result of a change of access network due to handover), no mid-call services are applicable to the call, and the call is anchored in the SCC AS as described in clause 7.3.2.1 or 7.4.2.1, the UE may augment the ongoing CS call in order to be able to use Gm for service control signalling.
If the UE does augment the ongoing CS call with Gm service control signalling then the UE shall use Gm when establishing additional calls, or for any mid-call signalling. The UE shall continue to use Gm procedures until the existing calls end.
If the UE does not augment the ongoing CS call with Gm service control signalling then the UE shall use CS procedures when establishing additional calls, or for any mid-call signalling. The UE shall continue to use CS procedures until the existing calls end.
7.5a.2 Augmentation call flow p. 60
If configured to do so the ICS UE may invoke IMS signalling to add Gm service control to the ongoing session.
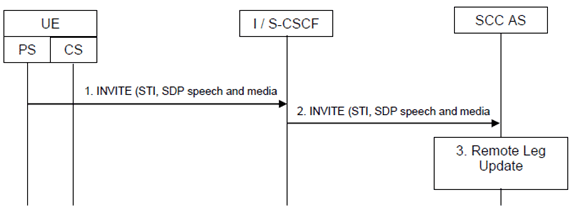
Step 1.
When the UE determines a need to augment a CS call with Gm, the UE initiates registration with IMS via the new PS access (if not already registered). It initiates the augmentation by sending an INVITE to establish the service control signalling via the PS access. The INVITE includes the SDP for speech or speech and video and non-real-time media flow(s) and the static (provisioned) STI, as defined in TS 23.237.
Step 2.
Standard procedures are used at S-CSCF for routing of the INVITE to the SCC AS.
Step 3.
The SCC AS identifies the session to be augmented using the STI. If the INVITE request contains additional PS media the SCC AS also performs the Remote Leg Update to update the combined session towards the Remote Leg.