Content for TS 23.292 Word version: 17.0.0
1…
4…
5…
7…
7.2…
7.3…
7.3.2.2…
7.3.2.2.4…
7.4…
7.4.2.2…
7.4.2.2.3…
7.4.2.2.7…
7.5…
7.6…
7.6.1.2.2.6…
7.6.1.2.3…
7.6.1.2.3.5…
7.6.1.2.3.6…
7.6.2…
7.6.2.7
7.6.2.8…
7.6.2.11…
7.6.3…
7.7…
7.7.2…
7.9…
7.9.2…
7.9.2.4
7.9.2.5
8…
A…
G…
H…
H.5…
H.5.3…
7.4 Terminations
7.4.1 Terminating sessions that use PS media
7.4.2 Terminating sessions that use CS media
7.4.2.1 Non ICS UE terminating sessions that use CS media
7.4.2.1.1 Overview
7.4.2.1.2 Termination using I2 reference point
7.4.2.1.3 Termination to non ICS UE not registered in IMS
...
...
7.4 Terminations p. 42
7.4.1 Terminating sessions that use PS media p. 42
7.4.1.1 Full duplex speech via PS p. 42
When the ICS UE has access to a PS network that supports the full duplex speech component of an IMS service, terminating IMS procedures (as described in clause 5.7 of TS 23.228) shall be used to terminate the session to the ICS UE. The S-CSCF shall insert the SCC AS in the IMS session path using terminating initial filter criteria. The SCC AS shall be the last AS inserted into the session path.
7.4.1.2 Void
7.4.1.3 Void
7.4.2 Terminating sessions that use CS media p. 42
7.4.2.1 Non ICS UE terminating sessions that use CS media p. 42
7.4.2.1.1 Overview p. 42
All ICS User incoming sessions are directed to IMS for delivery to the ICS User.
Non ICS UEs which have been successfully registered in IMS by the MSC Server will have a registration binding at the S-CSCF containing the MSC Server as the contact address.
The SCC AS shall be inserted in the IMS session path using the terminating iFC. The SCC AS performs T-ADS for selection of an access and returns information to assist with S-CSCF selection of a registered contact address. When the T-ADS function selects the MSC Server enhanced for ICS, the SCC AS directs the IMS terminating session towards the contact address of the MSC Server.
On receipt of the session initiation message, the MSC Server enhanced for ICS shall perform the necessary interworking between the I2 reference point and CS signalling (e.g. as described in TS 24.008). The MSC Server shall also control a CS-MGW using the Mc reference point to perform the necessary interworking between RTP bearers on the Mb reference point and CS access bearers and adds the User Location Information (e.g. CGI or SAI) and/or UE Time Zone Information to the response to the session initiation.
The SCC AS may select to breakout an incoming session to the CS domain in following cases:
- A non ICS UE is not registered in IMS but can be attached to the CS network at an MSC Server. In this case, terminating iFC forwards the call to the SCC AS.
- A non ICS UE is registered in IMS, the access network does not support the media type (as defined in clause 22.4 of TS 22.101), but the UE still can be attached to the CS network at an MSC Server. In this case, terminating iFC forwards the call to the SCC AS.
- S-CSCF releases the current terminating session setup toward SCC AS/T-ADS as defined in TS 24.229; and
- T-ADS redirects the session to the new MSC.
- S-CSCF releases the current terminating session setup toward SCC AS/T-ADS as defined in TS 24.229;
- Based on operator policy, T-ADS may start a timer. The timer is stopped when new registration is received for the UE;
- If the T-ADS stopped the timer itself, T-ADS redirects the session to the new MSC;
- If the timer expires, T-ADS may invoke other procedure to redeliver the call (e.g. routing the call to the CS domain).
7.4.2.1.2 Termination using I2 reference point p. 44
Figure 7.4.2.1.2-1 describes how IMS terminations are performed via CS access for non ICS UE registered in IMS. This call flow also applies for an ICS UE attached to an MSC Server enhanced for ICS where the incoming session is delivered to the ICS UE using standard CS terminating procedures, as specified in clause 7.4.2.2.5.
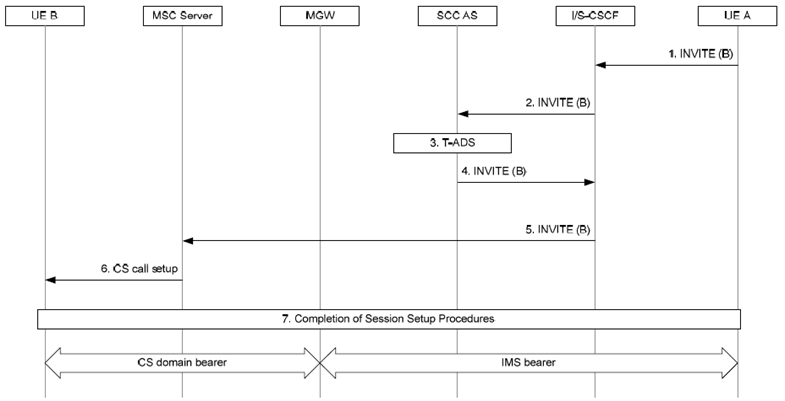
Figure 7.4.2.1.2-1: IMS Termination via CS Access for non ICS UE registered in IMS
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
Step 1.
An incoming INVITE is received at the S-CSCF of the B-party via the I-CSCF.
Step 2.
The S-CSCF performs standard service control execution procedures. Filter criteria direct the S-CSCF to send the INVITE to the SCC AS.
Step 3.
The SCC AS performs terminating access domain selection. The SCC AS chooses the CS access network and the MSC Server contact address, amongst the registered contact addresses for the UE B, for the setup of the media.
Step 4.
The SCC AS establishes a new session by sending an INVITE to the UE B via the S-CSCF.
Step 5.
The S-CSCF forwards the INVITE to the MSC Server based on the contact address stored during registration, using standard IMS procedures.
Step 6.
The MSC Server sends a Setup message to the UE B.
Step 7.
Completion of the session and bearer control setup procedures. For video call, to complete the session and bearer setup, the specific handling as described in clause 7.4.2.1.1 applies. The MSC Server adds the User Location Information (e.g. CGI or SAI) and/or UE Time Zone Information of the terminating user to the session initiation response message.
7.4.2.1.3 Termination to non ICS UE not registered in IMS p. 44
Figure 7.4.2.1.3-1 describes how IMS terminations are performed via CS access for non ICS UE not registered in IMS. This call flow also applies for an ICS UE attached to an MSC Server where the incoming session is delivered to the ICS UE using standard CS terminating procedures, as specified in clause 7.4.2.2.5.
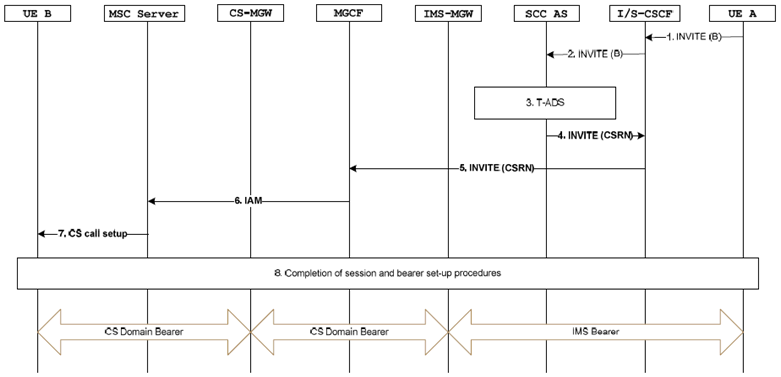
Figure 7.4.2.1.3-1: IMS Termination via CS Access for non ICS UE not registered in IMS
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
Step 1.
An incoming INVITE is received at the S-CSCF of the B-party.
Step 2.
The S-CSCF performs standard unregistered service control execution procedures. The terminating iFC direct the INVITE to the SCC AS for terminating access domain selection.
Step 3.
The T-ADS function chooses breakout to the CS domain. A CSRN is fetched for routing to the CS domain. If the SCC AS interacts with the HSS to fetch the CSRN, it may also indicate to the HSS the support of MTRR as specified in TS 23.018.
Step 4.
The SCC AS establishes a new session by sending an INVITE containing the CSRN and ICS indicator towards the S-CSCF.
Step 5.
The S-CSCF then performs CS breakout according to existing IMS procedures. The call is routed to the CS domain via the BGCF/MGCF.
Step 6.
The MGCF sends an IAM to the MSC Server.
Step 7.
The MSC Server performs paging procedures and sends the CS call setup message to the UE B. If the UE does not respond to the paging request as meanwhile it has performed registration with a new MSC Server, the network may either use the MTRF or MTRR feature as specified in TS 23.018 in order to re-direct the call towards the new MSC Server. If MTRR is used the SCC AS emulates GMSC behavior and may request to to re-restart call handling from step 3 onwards.
Step 8.
Completion of the session and bearer control setup procedures. To complete the session and bearer setup for a video call the specific handling as described in clause 7.4.2.1.1 applies. The MGCF may map cause codes received over the CS leg differently compared to normal CS breakout. If the SCC AS has User Location Information (e.g. CGI or SAI) and/or UE Time Zone Information available (e.g. from step 3, or by interacting with the HSS at this time), it adds it to the SIP response.