Content for TS 23.204 Word version: 18.0.0
6.4 Transport-level interworking: Successful encapsulated Short Message termination procedure from SMS-GMSC
6.4a Transport-level interworking: Short Message termination procedure without MSISDN from IMS network
...
...
6.4 Transport-level interworking: Successful encapsulated Short Message termination procedure from SMS-GMSC p. 21
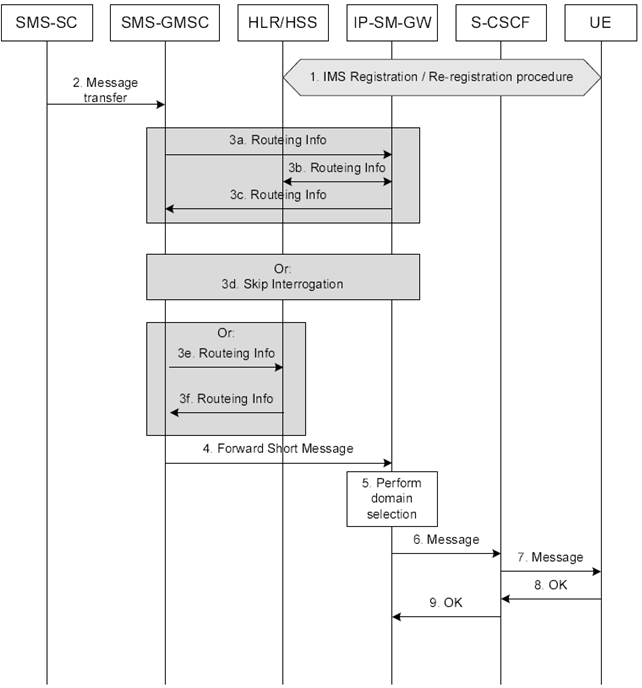
Figure 6.4: Successful encapsulated Short Message termination procedure
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
Step 1.
The UE registers to the S-CSCF according to the IMS registration procedure.
Step 2.
The SMS-SC forwards the Short Message (SMS DELIVER) to the SMS-GMSC.
Step 3.
Steps 3a to 3c are performed if SMS GMSC interrogates the HSS with MSISDN. For MT-SMS without MSISDN as defined in clause 6.0a, step 3d is performed if an IP-SM-GW address is available and need not be retrieved, and steps 3e to 3f are performed if an IP-SM-GW address needs to be retrieved.
Step 3a.
The SMS GMSC interrogates the HSS (using MSISDN) to retrieve routeing information. Based on the pre-configured IP-SM-GW address for the user, the HSS forwards the request to the corresponding IP-SM-GW.
Step 3b.
The HLR/HSS returns the addresses of the current MSC, SGSN, MME or SMSF to the IP SM GW for delivery of the Short Message in CS/PS domain. The HLR/HSS also returns the IMSI, for the IP SM GW to correlate the receipt of Short Message from the MT Correlation ID within the IMSI field of the Forward Short Message.
Step 3c.
The IP SM GW creates a MT Correlation ID as per TS 23.040 which associates the Send Routeing Info for SM with the subsequent Forward Short Message messages(s), and stores this along with the IMSI of the receiving subscriber. The IP-SM-GW returns only one address, which is of itself, along with the MT Correlation ID as routeing information to the SMS-GMSC.
Step 3d.
Interrogation is skipped in the context of T4 device triggering if an up to date IP-SM-GW address is already available at the SMS-SC/SMS-GMSC.
Step 3e.
The SMS GMSC interrogates the HSS (using IMSI) to retrieve routeing information.
Step 3f.
HLR/HSS returns the addresses of IP-SM-GW, MSC (MME), SGSN and/or SMSF. If IMS is to be used for MT-SMS then continue with step 4.
Step 4.
If steps 3a to 3c have been taken, SMS-GMSC delivers the Short Message (SMS DELIVER) to IP-SM-GW (AS) including the MT Correlation ID received from the IP SM GW, in the same manner that it delivers the Short Message to an MSC, SGSN, MME or SMSF. Otherwise, SMS-GMSC delivers the Short Message (SMS DELIVER) to IP-SM-GW (AS) including the IMSI.
Step 5.
The IP SM GW performs service authorization based on the stored subscriber data described in the clause 6.1. The IP SM GW shall check whether the subscriber is authorised to use the short message service (e.g. Operator Determined Barring settings), similar to the authorization performed by MSC/SGSN/MME/SMSF in case the Short Message is delivered via CS or PS domain. In addition, the IP SM GW shall also check whether the subscriber is authorised to use the encapsulated Short Message delivery via IMS. If the result of service authorization is negative, the IP SM GW shall not forward the message, and shall return the appropriate error information to the SMS-SC in a failure report. Domain selection function is not performed for MT-SMS without MSISDN (i.e. when IMSI is received in step 4) and IMS is used for delivery. Otherwise (i.e. when a MT Correlation ID is received in step 4), the IP-SM-GW performs domain selection function to determine the preferred domain for delivering the message according to operator policy and user preferences. The logic for selecting preferred route for message delivery is a matter of implementation.
Step 6.
If the preferred domain is IMS, the IP-SM-GW (AS) uses the TEL-URI associated with the IMSI of the message received for the target UE to send the Short Message (SMS DELIVER, SC Address) encapsulated in the appropriate SIP method towards the S-CSCF. If TEL URI is not available, SIP URI is used.
Step 7.
S-CSCF forwards the encapsulated Short Message (SMS-DELIVER, SC Address) to the UE.
Step 8.
The UE acknowledges the SIP request.
Step 9.
The S-CSCF forwards the acknowledgement of the SIP request to the IP-SM-GW (AS).
6.4a Transport-level interworking: Short Message termination procedure without MSISDN from IMS network |R12| p. 23
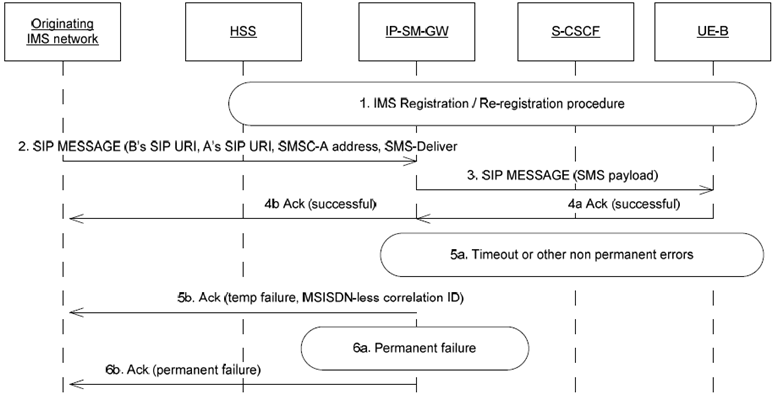
Step 1.
The UE-B registers to the S-CSCF according to the IMS registration procedure.
Step 2.
The originating IMS network which received the SM from the UE-A forwards the Short Message (SMS-DELIVER) to the terminating IMS network. It reaches the IP-SM-GW responsible for UE-B. For brevity, the intermediate IMS nodes interactions prior to reaching IP-SM-GW are not shown.
Step 3.
If local policy allows MSISDN-less SMS operation, IP-SM-GW tries to deliver the SM to UE-B.
Step 4a-4b.
SM is successfully delivered to UE-B. A success Delivery report is sent to the originating IMS network.
Step 5a.
If IP-SM-GW tried to deliver the SM but encountered some error (e.g. UE is memory full, UE not reachable, etc) then:
Step 5b.
IP-SM-GW returns a MSISDN-less Correlation ID to originating IMS network along with an indication of temporary failure.
Step 6a-6b.
if the IP-SM-GW refuses the MSISDN-less SMS operation due to local policy or other permanent errors (e.g. protocol error), IP-SM-GW returns a permanent error indication to the originating IMS network.