Content for TS 23.204 Word version: 18.0.0
6 Procedures
6.0 General
6.0a SMS without MSISDN in IMS
6.1 Registration procedure
6.2 De-registration procedure
6.3 Transport-level interworking: Successful encapsulated Short Message origination procedure with MSISDN
...
...
6 Procedures p. 15
6.0 General |R8| p. 15
The clause describes the procedures for the support of transport-level interworking between Short Message service and encapsulated Short Message via IP service, for the support of the service-level interworking for the Short Message service and Instant Messaging service as defined in OMA-TS-SIMPLE_IM-V1_0 [12], for the support of the service-level interworking for the Short Message service and Converged IP Messaging service as defined in OMA-TS-CPM_Conv_Fnct-V1_0 [17] and for the support of receiving MT-SMS to a UE without MSISDN. Clauses only applying to either transport-level interworking or service-level interworking are indicated as such.
6.0a SMS without MSISDN in IMS |R11| p. 15
6.0a.1 MO-SMS without MSISDN in IMS |R12| p. 15
For MO-SMS without MSISDN, the IP-SM-GW of the originating side fills the RP-OA field with a value that indicates UE is MSISDN-less to satisfy the protocol requirement. If the originating UE does not have MSISDN or the recipient UE is addressed with SIP-URI (i.e., recipient is not addressed with MSISDN) then IP-SM-GW first tries to deliver the SMS directly to the terminating IMS network. If the terminating IMS network does not accept SMS delivery without MSISDN and responds with a permanent error indication, then IP-SM-GW shall abort any further re-attempt and responds back to sender that SMS delivery has failed.
If the terminating IMS network indicates the SMS delivery failed due to temporary reasons (e.g, UE is not reachable) and the response has included the MSISDN-less correlation ID for the recipient then IP-SM-GW forwards both the SM and MSISDN-less correlation ID to the SMSC for storage and for subsequent retries.
6.0a.2 MT-SMS without MSISDN in IMS |R12| p. 15
For device triggering, the selection of IMS to deliver MT-SMS without MSISDN is defined in TS 23.682.
For SMS between IMS UEs without MSISDN, the delivery of MT-SMS to the recipient is based on the identity from the SIP MESSAGE received from the originating IMS network or retrieved using the MSISDN-less correlation ID from the Forward-Short-Message received from SMSC.
This clause describes the additional functionality required for the delivery of MT-SMS toward a UE in IMS without MSISDN.
During UE IMS registration procedure, the serving IP SM GW obtains IMSI of the UE from the S-CSCF and the serving IP-SM-GW address is indicated to HSS as defined in clause 6.1 and HSS stores this IP-SM-GW address. IP SM GW subscribes to event registration package to receive UE's IMPU (i.e. SIP URI). UE which does not have MSISDN will have at least one SIP-URI as IMPU. When IP-SM-GW receives SM from SMSC with IMSI as the recipient address (i.e. device triggering as defined in TS 23.682), IP SM GW shall try to deliver the MT-SMS via IMS without retrying to other domain.
When IP-SM-GW receives a SM from originating IMS network via SIP MESSAGE and IP-SM-GW failed to deliver the SM to the recipient and future retry is allowed and possible, then IP-SM-GW shall return a MSISDN-less correlation ID along with an indication of temporary error pointing to unsuccessful delivery attempt to the originating IMS network. This MSISDN-less Correlation ID includes sender's SIP URI, recipient's SIP URI, and HLR-Id which identifies receiver's HLR.
6.1 Registration procedure p. 16
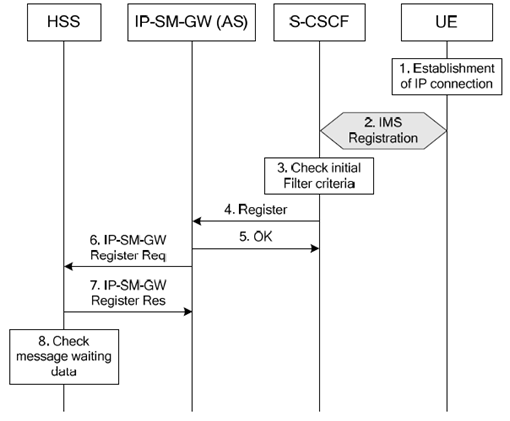
Step 1.
The UE establishes IP connection.
Step 2.
At any time after the establishment of the IP connection, the UE registers at the S-CSCF according to the IMS registration procedures.
Step 3.
S-CSCF checks the initial filter criteria retrieved from the HSS during the IMS registration procedure.
Step 4.
After successful IMS registration and based on the retrieved initial filter criteria, the S-CSCF informs the IP-SM-GW (AS) about the registration of the user. IMSI is informed to the IP SM GW (AS) when there is no MSISDN in the UE's IMS subscription profile.
Step 5.
The IP-SM-GW (AS) returns OK to the S-CSCF.
Step 6.
The IP-SM-GW (AS) sends IP-SM-GW Register Req to the HSS.
Step 7.
The HSS stores the received IP-SM-GW address if necessary or for MT-SMS without MSISDN (see clause 6.0a.2), uses it as an indication that the UE is available to be accessed via the IMS to trigger an Alert service centre message if the message waiting flag is set, and responses to the IP-SM-GW (AS) with IP SM GW Register Res. IP SM GW gets the IMPU (SIP URI) for SMS delivery without TEL-URI from registration event package.
Step 8.
After successful registration of the IP SM GW address at the HSS the HSS checks whether message waiting data are stored and alerts all SCs using procedures described in TS 23.040 (see also clause 6.5b).
6.2 De-registration procedure p. 17
6.2.1 UE initiated p. 17
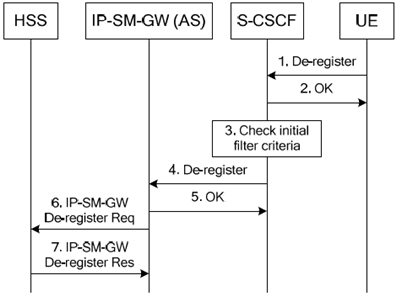
Step 1.
At any time after the registration procedure, the UE may initiate a de-registration procedure. The UE sends a De-Register request (Register request with Expires header having value 0) to the S-CSCF.
Step 2.
S-CSCF responds to the UE with OK.
Step 3.
S-CSCF checks the initial filter criteria retrieved from the HSS during the IMS registration procedure.
Step 4.
Based on initial filter criteria the S-CSCF informs the IP-SM-GW (AS) about the de-registration of the user.
Step 5.
The IP-SM-GW (AS) returns OK to the S-CSCF.
Step 6.
The IP-SM-GW (AS) de-registers the UE at the HSS sending a De-register Req.
Step 7.
The HSS de-registers the UE and responds to the IP-SM-GW (AS) with De-register Res.
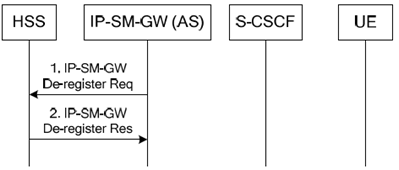
6.2.2 Network initiated p. 17
6.3 Transport-level interworking: Successful encapsulated Short Message origination procedure with MSISDN p. 18
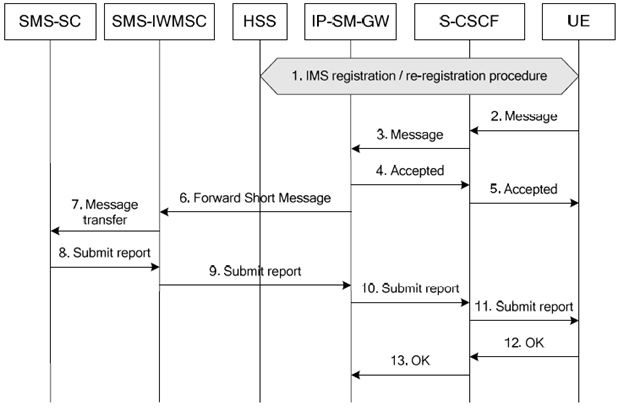
Figure 6.3: Successful encapsulated Short Message origination procedure
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
Step 1.
The UE registers to S-CSCF according the IMS registration procedure. Note that I-CSCF and P-CSCF are not shown in this figure.
Step 2.
UE submits the encapsulated Short Message (SMS-SUBMIT, SC Address) to the S-CSCF using an appropriate SIP method.
Step 3.
S-CSCF forwards the encapsulated Short Message (SMS- SUBMIT, SC Address) to IP-SM-GW (AS) based on stored iFC.
Step 4.
IP-SM-GW (AS) acknowledges the SIP message.
Step 5.
SIP message acknowledge is forwarded by S-CSCF to UE.
Step 6.
The IP-SM-GW performs service authorization based on the stored subscriber data as described in the clause 6.1. The IP SM GW shall check whether the subscriber is authorised to use the short message service (e.g. Operator Determined Barring settings), similar to the authorization performed by MSC/SGSN in case the Short Message is delivered via CS or PS domain. In addition, the IP-SM-GW shall also check whether the user is authorised to use the encapsulated Short Message delivery via IMS. If the result of service authorization is negative, the IP-SM-GW shall not forward the message, and shall return the appropriate error information to the UE in a failure report. Otherwise, the IP-SM-GW (AS) extracts the Short Message (SMS- SUBMIT) and forwards it towards the SMS-SC (SC Address) via the SMS-IWMSC using standard MAP or Diameter based (SGd/Gdd) signalling (as described in TS 23.040).
Step 7.
The SMS-IWMSC forwards the Short Message (SMS-SUBMIT) to the SMS-SC (see TS 23.040).
Step 8.
SMS-SC sends a Submit report (SMS-SUBMIT REPORT) to SMS-IWMSC (see TS 23.040).
Step 9.
SMS-IWMSC sends the Submit report to IP-SM-GW (AS) (see TS 23.040).
Step 10.
IP-SM-GW (AS) sends the Submit report to S-CSCF, encapsulated in an appropriate SIP request.
Step 11.
The S-CSCF sends the Submit report to the UE.
Step 12.
The UE acknowledges the SIP request.
Step 13.
The S-CSCF forwards the acknowledgement of the SIP request to IP-SM-GW (AS).