Content for TS 23.066 Word version: 18.0.0
C.3 Call Scenarios
C.3.1 Call to a Non-Ported Number or Number Ported into the Network
C.3.2 Call to a Ported Number - Originating Network = Subscription Network - Direct Routeing
...
...
C.3 Call Scenarios p. 66
The notation TT=SRI in diagrams in this clause assumes that SRI=CRMNP for ETSI and SRI = Translation Type 14 for ANSI. The use of other translation types is for further study. The message flows for the following scenarios are based on the use of an SCCP relay function in MNP-SRF(s). The message flows for the higher level relay function (e.g. TC relay) in MNP-SRF are not covered here, but the principle can be found in clause B.4.2. For further details of the signalling relay function, the reader is referred to [7].
C.3.1 Call to a Non-Ported Number or Number Ported into the Network p. 67
Figure C.3.1 shows the signalling involved for a call to a non-ported number or number ported into the network (see 3G TS 23.018).
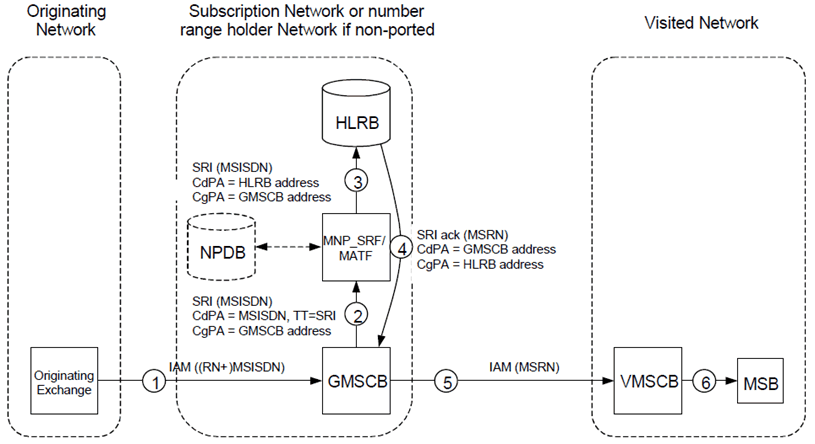
- From an Originating Exchange a call is set up to MSISDN. The call is routed to the subscription network being the number range holder network, if the number is non-ported.
- When GMSCB receives the ISUP IAM, it requests routeing information by submitting a MAP SRI to the MNP_SRF/MATF. The TT on SCCP may be set to 'SRI'.
- When the MNP_SRF/MATF receives the message, the MNP_SRF/MATF analyses the MSISDN in the CdPA and identifies the MSISDN as being non-ported. The MNP_SRF/MATF function then replaces the CdPA by an HLRB address. After modifying the CdPA, the message is routed to HLRB.
- When HLRB receives the SRI, it responds to the GMSCB by sending an SRI ack with an MSRN that identifies the MSB in the VMSCB.
- GMSCB uses the MSRN to route the call to VMSCB.
C.3.2 Call to a Ported Number - Originating Network = Subscription Network - Direct Routeing p. 68
Figure C.3.2 shows the signalling involved for a call to a ported number via direct routeing where the call is originated in the subscription network.
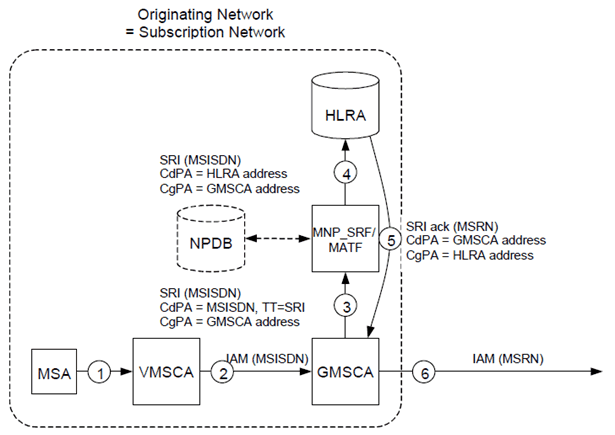
Figure C.3.2: Call to a ported number via direct routeing where the call is originated in the subscription network
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
- MSA originates a call to MSISDN.
- VMSCA routes the call to the network's GMSCA.
- When GMSCA receives the ISUP IAM, it requests routeing information by submitting a MAP SRI to the MNP_SRF/MATF. The TT on SCCP may be set to 'SRI'.
- When the MNP_SRF/MATF receives the message, it analyses the MSISDN in the CdPA and identifies the MSISDN as being ported into the network. The MNP_SRF/MATF function then replaces the CdPA by an HLRA address. After modifying the CdPA, the message is routed to HLRA.
- When HLRA receives the SRI, it responds to the GMSCA by sending an SRI ack with an MSRN that identifies the MSB in the VMSCB.
- GMSCA uses the MSRN to route the call to VMSCB.