Content for TR 22.855 Word version: 18.0.1
1 Scope p. 8
The present document provides Stage 1 potential 5G service requirements for ranging based services. In the context of the present document, Ranging-based services are to be understood as the applications utilizing the distance between two UEs and/or the direction of one UE from the other one.
The aspects addressed in the present document include:
- Identify Use cases and potential requirements of ranging-based services directly between two or more UEs, e.g. accuracy of distance and direction, maximum range distance, ranging latency, energy/battery consumption.
- Gap analysis with existing mechanisms to enable ranging-based services.
2 References p. 8
The following documents contain provisions which, through reference in this text, constitute provisions of the present document.
- References are either specific (identified by date of publication, edition number, version number, etc.) or non-specific.
- For a specific reference, subsequent revisions do not apply.
- For a non-specific reference, the latest version applies. In the case of a reference to a 3GPP document (including a GSM document), a non-specific reference implicitly refers to the latest version of that document in the same Release as the present document.
3 Definitions, symbols and abbreviations p. 8
3.1 Definitions p. 8
For the purposes of the present document, the terms and definitions given in TR 21.905 and the following apply. A term defined in the present document takes precedence over the definition of the same term, if any, in TR 21.905.
Key performance indicators and key attributes for Ranging use cases are defined as follows:
Ranging accuracy:
describes the absolute value of the deviation of the measured distance and/or direction between two UEs to the true distance and/or direction value.
Confidence level:
describes the percentage of all the possible measured distance and/or direction that can be expected to include the true distance and/or direction considering the Ranging accuracy.
Effective Ranging distance:
the largest distance between the UE who initiates the Ranging and target UEs in the Ranging operation.
Environment of use:
the physical environment between the UE who initiate the Ranging and target UEs, such as LOS environment and NLOS environment. Also the physical environments of the UE who initiate ranging, such as in coverage and out of coverage.
Relative UE velocity:
the target UE can be either static or mobile relative to the UE who initiates the Ranging. In the latter, the attribute shall also provide some elements about its motion, e.g. maximum speed, trajectory.
Availability:
percentage value of the amount of time when a ranging system is able to provide the required Ranging-related data within the performance targets or requirements divided by the amount of time the system is expected to provide the Ranging service in a targeted service area.
Latency:
time elapsed between the event that triggers the determination of the Ranging-related data and the availability of the Ranging-related data at the Ranging system interface.
Power consumption:
electrical power used by Ranging during Ranging operation.
Ranging interval:
time difference between two consecutive Ranging operations.
3.2 Abbreviations p. 9
4 Overview p. 9
Ranging service (or Ranging in short) in this document refers to the determination of the distance between two UEs and/or the direction of one UE from the other one via direct communication connection. As shown in the following celestial coordinate, the horizontal direction (i.e. the Azimuth) of the target UE is the angle formed between a reference direction and a line from the observer UE to target UE projected on the same plane as the reference direction orthogonal to the zenith. The elevation direction of the target UE is the angle above the horizontal plane [2].
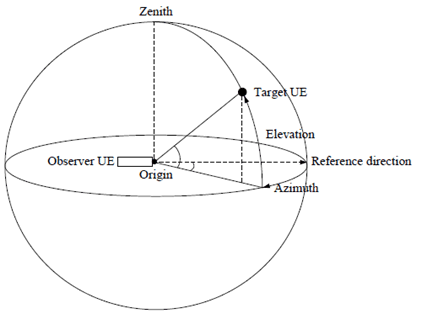
Figure 4-1: illustration of horizontal/ elevation direction in celestial coordinate
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
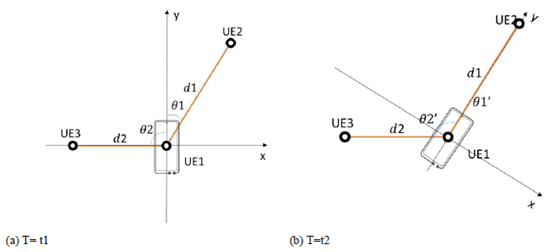
For better understanding, Ranging in 2D coordinate system is taken as an example in Fig.4-2, where UE1 initiates the ranging operation and the coordinate system is centered at UE1. Furthermore, y-axis is the UE1's pointing direction (reference direction). The ranging initiated by UE1 targets at knowing the distance of UE2 and UE3 to UE1 and also the direction (reference direction) of UE2 and UE3 relatively to UE1.
As illustrated in Figure 4-2, at T=t1 UE2 is located at the 2-o'clock direction to UE1 with the direction information as θ1 =30 ° and distance as d1. UE3 is located at the 9-o'clock direction to UE1 with the direction information as θ2 =-90° and distance as d2. When the UE1 switches its pointing direction to UE2 at T=t2, the ranging results of UE2 change to θ1' =0° and distance remains as d1, while the ranging results of UE3 change to θ2' =-120° and distance remains as d2.
Ranging service can be supported with or without 5G coverage. Fig. 4-3 is an illustration of 5G providing ranging service to UEs with or without 5G coverage. If licensed band is used for ranging, it shall be fully under operator control.
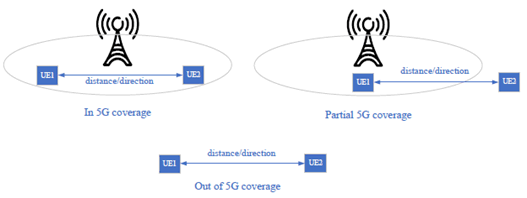
Figure 4-3: illustration of 5G providing ranging service to UEs with or without 5G coverage
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)