TR 22.838
Paging Policy enhancements
and Procedure Optimizations in LTE
V14.0.0 (Wzip)
2015/12 9 p.
- Rapporteur:
- Miss Zhang, Zhuoyun
China Unicom
Content for TR 22.838 Word version: 14.0.0
0 Introduction p. 4
3GPP has introduced paging function which is initiated by the MME/SGSN to make signaling interaction with the UE that is in IDLE state. However, both M2M devices and the OTT (over the top) applications installed on the smart phones result in great paging signaling load. Therefore, there is a need to further investigate the paging policies and procedures to solve the paging signaling load in LTE. This TR aims to study the specific scenarios where there is a need to enhance the paging policies and optimize the paging procedures.
1 Scope p. 5
The objective is to study use cases and propose potential requirements to enhance the information set (e.g., user's subscription, application characteristics) upon which paging policies may be based to allow optimization of the paging procedures in LTE.
2 References p. 5
The following documents contain provisions which, through reference in this text, constitute provisions of the present document.
- References are either specific (identified by date of publication, edition number, version number, etc.) or non specific.
- For a specific reference, subsequent revisions do not apply.
- For a non-specific reference, the latest version applies. In the case of a reference to a 3GPP document (including a GSM document), a non-specific reference implicitly refers to the latest version of that document in the same Release as the present document.
3 Definitions, symbols and abbreviations p. 5
3.1 Definitions p. 5
For the purposes of the present document, the terms and definitions given in TR 21.905 and the following apply. A term defined in the present document takes precedence over the definition of the same term, if any, in TR 21.905.
3.2 Abbreviations p. 5
4 Use Cases p. 5
4.1 Device assisted paging optimization p. 5
4.1.1 Description p. 5
The number of devices is going to increase several folds in the near future. Unless paging optimizations that reduce the paging traffic are introduced, there could be serious negative impacts on the network's paging capacity and also on the paging delays e.g. increase set up time for incoming notifications and call setup times.
There are scenarios where a device is temporary stationary or is in low mobility during a long period of time e.g. when the user is at home, or at work. If the network during these period of time, can identify the device's mobility status, it can utilize this information to optimize its paging procedure towards the device e.g. by reducing the size of the paging area to something less than the Tracking Area as illustrated in the figure below.
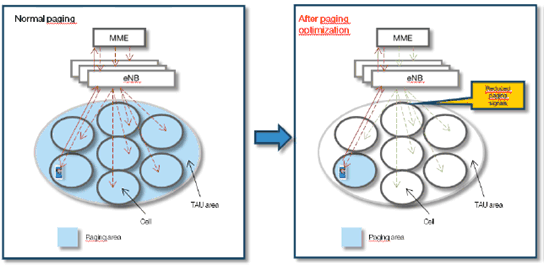
4.1.2 Pre-conditions p. 6
- Bob arrives at work.
4.1.3 Service Flows p. 6
- Bob has been working at his office for some time.
- The network determines that Bob's device is stationary or moving within a limited area.
- The network is able to optimize its paging procedure towards Bob's device.
4.1.4 Post-conditions p. 6
- Paging signalling load has been reduced.
4.1.5 Potential Requirements p. 6
- The network shall be able to take the movement of a device into account when paging the device.
4.2 Paging policy differentiation based on application characteristics p. 6
4.2.1 Description p. 6
This use case describes an enhancement that allows the paging policy to be differentiated based on the application characteristics known to and trusted by the serving network.
The serving network could identify the traffic's application characteristics. Then the serving network can differentiate the paging policies based on this information.
4.2.2 Pre-conditions p. 7
The serving network supports the ability to identify the traffic's application characteristics.
The serving network has a paging policy that allows it to optimize the paging function when the radio access network is congested.
Alice's UE is in IDLE state and IMAPP is one of IM applications running on her smart phone.
4.2.3 Service Flows p. 7
The radio access network happens to be congested.
Alice's friend sends her a message on IMAPP.
The serving network has identified that this traffic could be subjected to a paging policy optimization function.
The serving network optimizes the paging function, e.g., by delaying the paging messages towards Alice's UE.
4.2.4 Post-conditions p. 7
The serving network is able to send Alice the messages on IMAPP.
4.2.5 Potential Requirements p. 7
The 3GPP core network shall be able to identify the traffic's application characteristics, (e.g. application type, application protocol, application provider).
The 3GPP core network shall be able to apply different paging policies based on application characteristics provided by a source known to and trusted by the serving network (e.g. the home network).
4.3 Paging policy differentiation based on user's likely location p. 7
4.3.1 Description p. 7
This use case describes that the paging load could potentially be reduced if the network takes the likely location of the UE within the paging area into account (e.g., by first paging the UE in a subset of the paging area only).
4.3.2 Pre-conditions p. 7
The 3GPP core network has a paging policy that takes the likely location of the UE within the paging area into account.
4.3.3 Service Flows p. 7
Alice's UE is in IDLE state. Her friend sends her a message through an APP on her UE.
The 3GPP core network is aware about the likely location of Alice's UE within the paging area. Based on this, the network sends paging messages in a subset of the paging area only.
If the UE does not respond to the paging request, the 3GPP core network may make another attempt to page the UE. To ensure that the UE can eventually be reached, the 3GPP core network can for instance increase the paging area with every paging attempt.
4.3.4 Post-conditions p. 8
The 3GPP core network is able to page Alice's UE and send her the message. The signaling load may have been reduced (if Alice's UE was successfully paged directly) or will have increased if multiple paging attempts had to be made because the UE was not located in the assumed subset of the paging area.
4.3.5 Potential Requirements p. 8
The 3GPP core network may be able to take the likely location of the UE within the paging area into account when paging the UE.
5 Considerations p. 8
5.1 Considerations on congestion p. 8
The 3GPP core network can take various information into account to determine the paging policies. The network should be able to identify UEs requiring priority treatment. During congestion, the network should be able to provide priority treatment to those UEs that require it.
5.2 Considerations on charging p. 8
It does not have additional requirements on the 3GPP system.
6 Potential Requirements p. 8
The 3GPP network shall be able to take the movement of a device into account when paging the device.
The 3GPP core network shall be able to identify the traffic's application characteristics (e.g. application type, application protocol, application provider, and delay sensitivity).
The 3GPP core network shall be able to apply different paging policies based on application characteristics provided by a source known to and trusted by the serving network (e.g. the home network).
The 3GPP core network may be able to take the likely location of the UE within the paging area into account when paging the UE.
7 Conclusion and Recommendations p. 8
The study has identified several use cases where the 3GPP system could optimize the paging procedures in LTE. It has also resulted in a set of potential requirements as captured in the previous section.
It is recommended that the requirements in this TR are taken as a basis for the development of normative requirements.